Linux虚拟化KVM-Qemu分析(四)之CPU虚拟化(2)
背景
Read the fucking source code!--By 鲁迅A picture is worth a thousand words.--By 高尔基
说明:
-
KVM版本:5.9.1
-
QEMU版本:5.0.0
-
工具:Source Insight 3.5, Visio
-
文章同步在博客园:
https://www.cnblogs.com/LoyenWang/ -
概述
- 本文围绕ARMv8 CPU的虚拟化展开;
- 本文会结合Qemu + KVM的代码分析,捋清楚上层到底层的脉络;
- 本文会提供一个Sample Code,用于类比Qemu和KVM的关系,总而言之,大同小异,大题小做,大道至简,大功告成,大恩不言谢;
先来两段前戏。
1.1 CPU工作原理
AI的世界,程序的执行不再冰冷,CPU对a.out说,hello啊,world已经ok啦,下来return吧!
既然要说CPU的虚拟化,那就先简要介绍一下CPU的工作原理:
- CPU的根本任务是执行指令,我们常说的
取指-译码-执行-访存-写回,就是典型的指令Pipeline操作; - 从CPU的功能出发,可以简要分成三个逻辑模块:
Control Unit:CPU的指挥中心,协调数据的移动;ALU:运算单元,执行CPU内部所有的计算;Register:寄存器和Cache,都算是CPU内部的存储单元,其中寄存器可用于存储需要被译码和执行的指令、数据、地址等;
- CPU从内存中读取指令进行译码并执行,执行的过程中需要去访问内存中的数据,CPU内部的寄存器可以暂存中间的指令和数据等信息,通常说的CPU的
context指的就是CPU寄存器值;
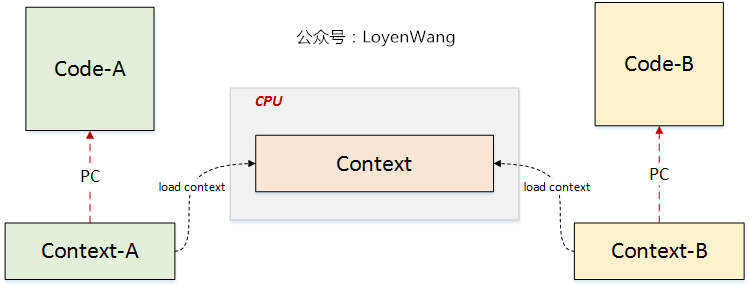
在硬件支持虚拟化之前,Qemu纯软件虚拟化方案,是通过tcg(tiny code generator)的方式来进行指令翻译,翻译成Host处理器架构的指令来执行。硬件虚拟化技术,是让虚拟机能直接执行在Host CPU上,让Host CPU直接来执行虚拟机,结合CPU的实际工作原理,应该怎么来理解呢?来张图:
- CPU通过
pc寄存器获取下一条执行指令,进行取指译码执行等操作,因此给定CPU一个Context,自然就能控制其执行某些代码; - CPU的虚拟化,最终目标让虚拟机执行在CPU上,无非也是要进行CPU的Context切换,控制CPU去执行对应的代码,下文会进一步阐述;
既然都讲CPU了,那就捎带介绍下ARMv8的寄存器吧:
1.通用寄存器:
- 图中描述的是
EL3以下,AArch32与AArch64寄存器对应关系; AArch64中,总共31个通用寄存器,64bit的为X0-X30,32bit的为W0-W30;
2.特殊用途寄存器:
- 这些特殊用途的寄存器,主要分为三种:1)存放异常返回地址的
ELR_ELx;2)各个EL的栈指针SP_ELx;3)CPU的状态相关寄存器;
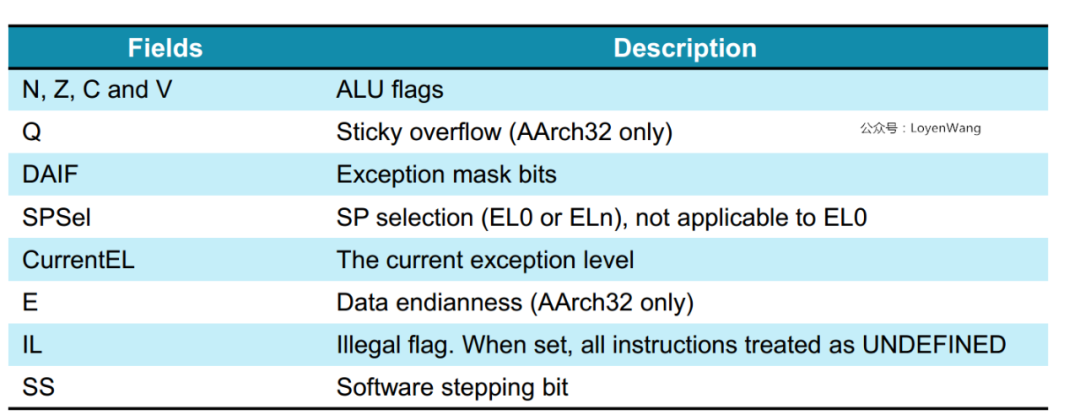
3.CPU的状态PSTATE:
- CPU的状态在
AArch32时是通过CPSR来获取,在AArch64中,使用PSTATE,PSTATE不是一个寄存器,它表示的是保存当前CPU状态信息的一组寄存器或一些标志信息的统称;
好了,ARMv8的介绍该打住了,否则要跑偏了。。。
1.2 guest模式
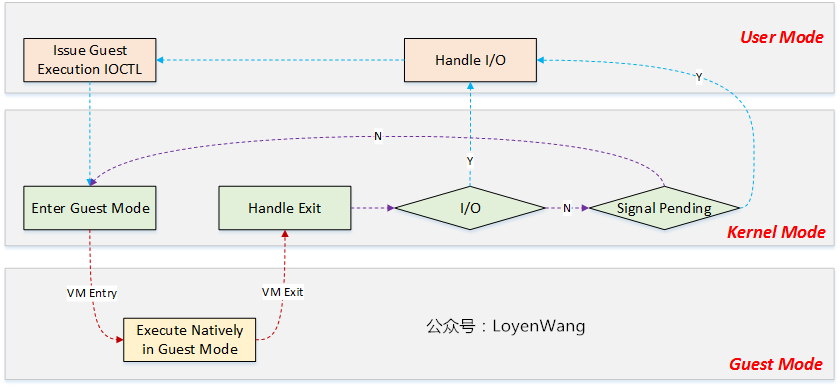
- Linux系统有两种执行模式:kernel模式与user模式,为了支持虚拟化功能的CPU,KVM向Linux内核提供了guest模式,用于执行虚拟机系统非I/O的代码;
- user模式,对应的是用户态执行,Qemu程序就执行在user模式下,并循环监听是否有I/O需要模拟处理;
- kernel模式,运行kvm模块代码,负责将CPU切换到VM的执行,其中包含了上下文的load/restore;
- guest模式,本地运行VM的非I/O代码,在某些异常情况下会退出该模式,Host OS开始接管;
好了啦,前戏结束,开始直奔主题吧。
-
流程分析
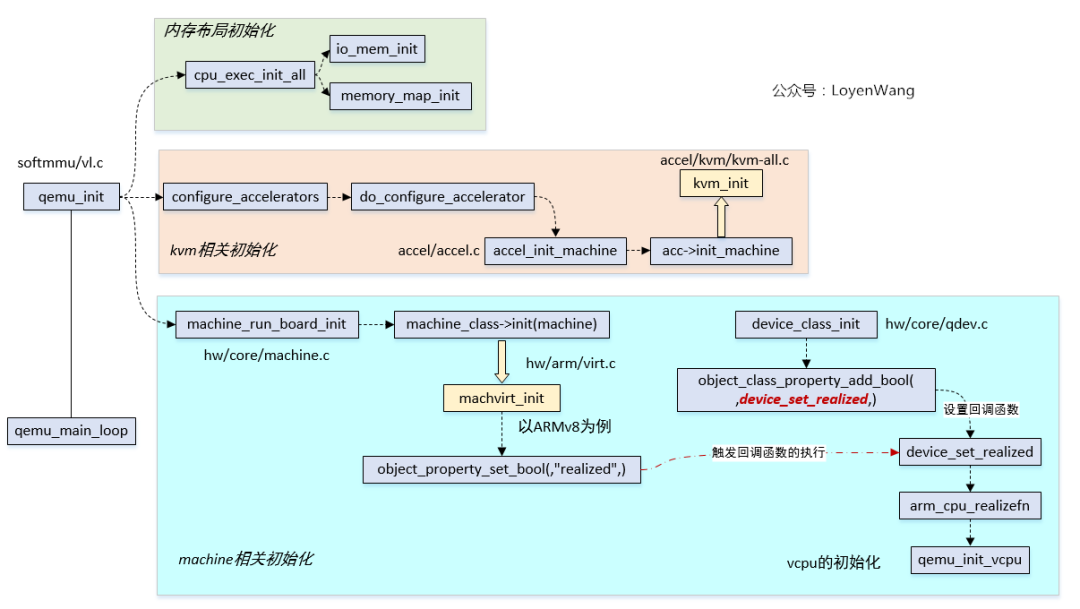
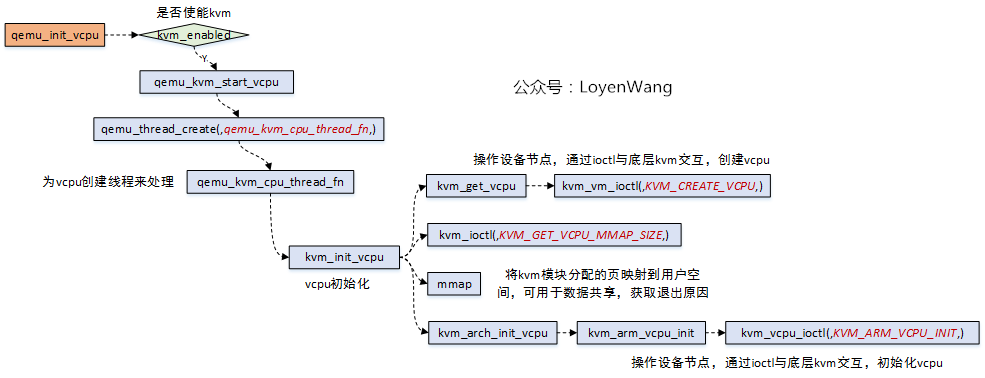
不管你说啥,我上来就是一句中国共产党万岁,对不起,跑题了。我上来就是一张Qemu初始化流程图:
- 看过Qemu源代码的人可能都有种感觉,一开始看好像摸不到门框,这图简要画了下关键模块的流程;
- Qemu的源代码,后续的文章会详细介绍,本文只focus在
vcpu相关部分;
除了找到了qemu_init_vcpu的入口,这张图好像跟本文的vcpu的虚拟化关系不是很大,不管了,就算是给后续的Qemu分析打个广告吧。
2.1 vcpu的创建
2.1.1 qemu中vcpu创建
- Qemu初始化流程图中,找到了
qemu_init_vcpu的入口,顺着这个qemu_init_vcpu就能找到与底层KVM模块交互的过程; - Qemu中为每个vcpu创建了一个线程,操作设备节点来创建和初始化vcpu;
所以,接力棒甩到了KVM内核模块。
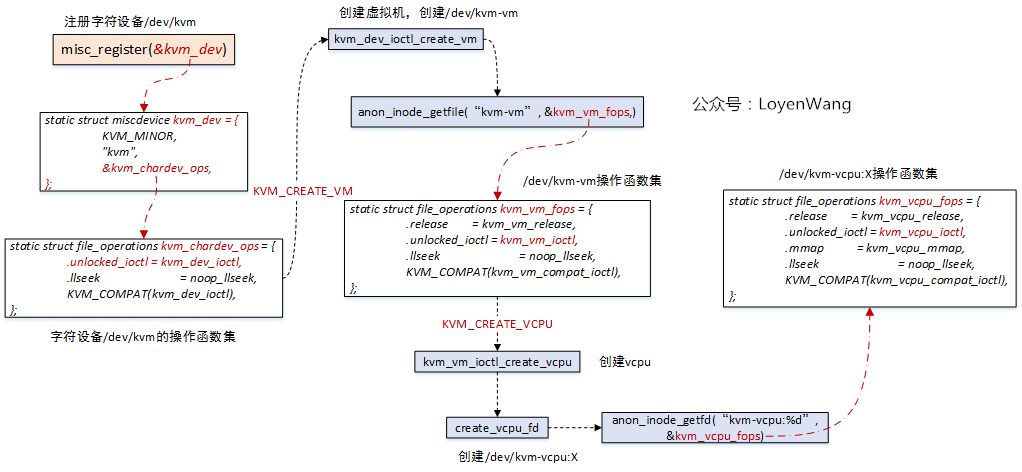
2.1.2 kvm中vcpu创建
来一张前文的图:
- 前文中分析过,系统在初始化的时候会注册字符设备驱动,设置好了各类操作函数集,等待用户层的
ioctl来进行控制; Qemu中设置KVM_CREATE_VCPU,将触发kvm_vm_ioctl_create_vcpu的执行,完成vcpu的创建工作;
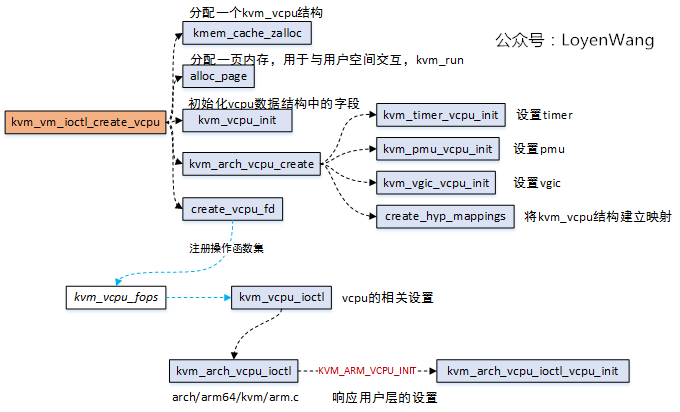
- 在底层中进行vcpu的创建工作,主要是分配一个
kvm_vcpu结构,并且对该结构中的字段进行初始化; - 其中有一个用于与应用层进行通信的数据结构
struct kvm_run,分配一页内存,应用层会调用mmap来进行映射,并且会从该结构中获取到虚拟机的退出原因; kvm_arch_vcpu_create主要完成体系架构相关的初始化,包括timer,pmu,vgic等;create_hyp_mappings将kvm_vcpu结构体建立映射,以便在Hypervisor模式下能访问该结构;create_vcpu_fd注册了kvm_vcpu_fops操作函数集,针对vcpu进行操作,Qemu中设置KVM_ARM_VCPU_INIT,将触发kvm_arch_vcpu_ioctl_vcpu_init的执行,完成的工作主要是vcpu的核心寄存器,系统寄存器等的reset操作,此外还包含了上层设置下来的值,放置在struct kvm_vcpu_init中;
2.2 vcpu的执行
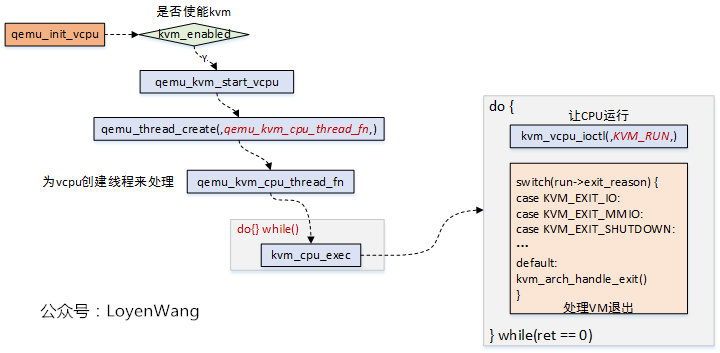
2.2.1 qemu中vcpu的执行
Qemu中为每一个vcpu创建一个用户线程,完成了vcpu的初始化后,便进入了vcpu的运行,而这是通过kvm_cpu_exec函数来完成的;kvm_cpu_exec函数中,调用kvm_vcpu_ioctl(,KVM_RUN,)来让底层的物理CPU进行运行,并且监测VM的退出,而这个退出原因就是存在放在kvm_run->exit_reason中,也就是上文中提到过的应用层与底层交互的机制;
2.2.2 kvm中vcpu的执行
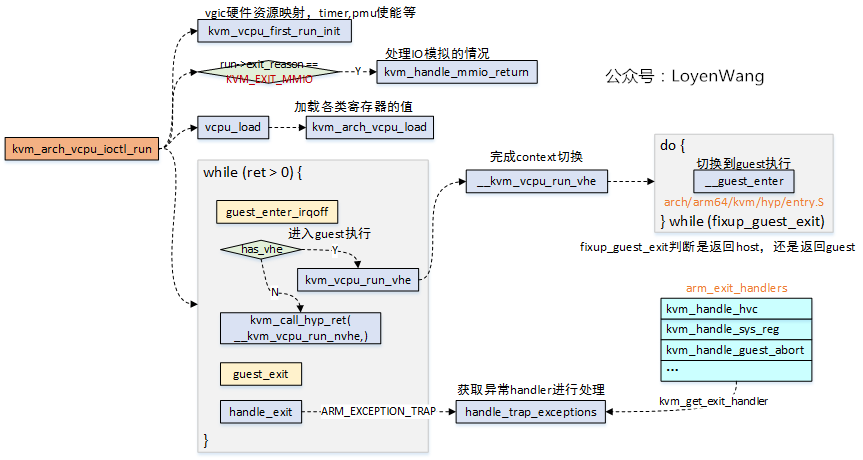
用户层通过KVM_RUN命令,将触发KVM模块中kvm_arch_vcpu_ioctl_run函数的执行:
- vcpu最终是要放置在物理CPU上执行的,很显然,我们需要进行context的切换:保存好Host的Context,并切换到Guest的Context去执行,最终在退出时再恢复回Host的Context;
__guest_enter函数完成最终的context切换,进入Guest的执行,当Guest退出时,fixup_guest_exit将会处理exit_code,判断是否继续返回Guest执行;- 当最终Guest退出到Host时,Host调用
handle_exit来处理异常退出,根据kvm_get_exit_handler去查询异常处理函数表对应的处理函数,最终进行执行处理;
-
Sample Code
- 上文已经将Qemu+KVM的CPU的虚拟化大概的轮廓已经介绍了,方方面面,问题不大;
- 来一段Sample Code类比Qemu和KVM的关系,在Ubuntu16.04系统上进行测试;
简要介绍一下:
- tiny_kernel.S,相当于Qemu中运行的Guest OS,完成的功能很简单,没错,就是
Hello, world打印; - tiny_qemu.c,相当于Qemu,用于加载Guest到vCPU上运行,最终通过kvm放到物理CPU上运行;
鲁迅在1921年的时候,说过这么一句话:Talk is cheap, show me the code。
tiny_kernel.S:
start:
/* Hello */
mov $0x48, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x65, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x6c, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x6c, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x6f, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x2c, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
/* world */
mov $0x77, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x6f, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x72, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x6c, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x64, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
mov $0x0a, %al
outb %al, $0xf1
hlttiny_qemu.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/kvm.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#define KVM_DEV "/dev/kvm"
#define TINY_KERNEL_FILE "./tiny_kernel.bin"
#define PAGE_SIZE 0x1000
int main(void)
{
int kvm_fd;
int vm_fd;
int vcpu_fd;
int tiny_kernel_fd;
int ret;
int mmap_size;
struct kvm_sregs sregs;
struct kvm_regs regs;
struct kvm_userspace_memory_region mem;
struct kvm_run *kvm_run;
void *userspace_addr;
/* open kvm device */
kvm_fd = open(KVM_DEV, O_RDWR);
assert(kvm_fd > 0);
/* create VM */
vm_fd = ioctl(kvm_fd, KVM_CREATE_VM, 0);
assert(vm_fd >= 0);
/* create VCPU */
vcpu_fd = ioctl(vm_fd, KVM_CREATE_VCPU, 0);
assert(vcpu_fd >= 0);
/* open tiny_kernel binary file */
tiny_kernel_fd = open(TINY_KERNEL_FILE, O_RDONLY);
assert(tiny_kernel_fd > 0);
/* map 4K into memory */
userspace_addr = mmap(NULL, PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
assert(userspace_addr > 0);
/* read tiny_kernel binary into the memory */
ret = read(tiny_kernel_fd, userspace_addr, PAGE_SIZE);
assert(ret >= 0);
/* set user memory region */
mem.slot = 0;
mem.flags = 0;
mem.guest_phys_addr = 0;
mem.memory_size = PAGE_SIZE;
mem.userspace_addr = (unsigned long)userspace_addr;
ret = ioctl(vm_fd, KVM_SET_USER_MEMORY_REGION, &mem);
assert(ret >= 0);
/* get kvm_run */
mmap_size = ioctl(kvm_fd, KVM_GET_VCPU_MMAP_SIZE, NULL);
assert(mmap_size >= 0);
kvm_run = (struct kvm_run *)mmap(NULL, mmap_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, vcpu_fd, 0);
assert(kvm_run >= 0);
/* set cpu registers */
ret = ioctl(vcpu_fd, KVM_GET_SREGS, &sregs);
assert(ret >= 0);
sregs.cs.base = 0;
sregs.cs.selector = 0;
ret = ioctl(vcpu_fd, KVM_SET_SREGS, &sregs);
memset(®s, 0, sizeof(struct kvm_regs));
regs.rip = 0;
ret = ioctl(vcpu_fd, KVM_SET_REGS, ®s);
assert(ret >= 0);
/* vcpu run */
while (1) {
ret = ioctl(vcpu_fd, KVM_RUN, NULL);
assert(ret >= 0);
switch(kvm_run->exit_reason) {
case KVM_EXIT_HLT:
printf("----KVM EXIT HLT----\n");
close(kvm_fd);
close(tiny_kernel_fd);
return 0;
case KVM_EXIT_IO:
putchar(*(((char *)kvm_run) + kvm_run->io.data_offset));
break;
default:
printf("Unknow exit reason: %d\n", kvm_run->exit_reason);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}为了表明我没有骗人,上一张在Ubuntu16.04的虚拟机上运行的结果图吧:
草草收工吧。
-
参考
ARMv8-A Architecture Overview``ARMv8 Techinology Preview``Arm Architecture Reference Manual, Armv8, for Armv8-A architecture profile``Virtual lockstep for fault tolerance and architectural vulnerability analysis