一文详解「队列」,手撸队列的3种方法!
前面我们介绍了栈(Stack),队列和栈是比较像的一种数据结构。我们可以想象有很多辆汽车正在通过单行道的隧道,所有车辆不能插队、不能掉头,先进来的车也先出去,我们可以把这种特征的数据结构称之为队列。
队列特性
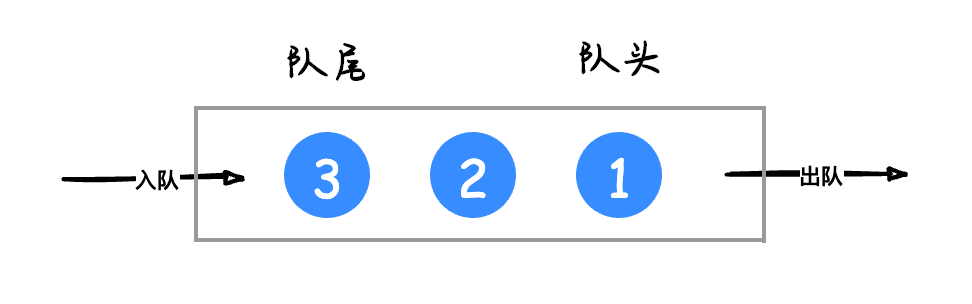
队列中的元素必须是先进先出(First In First Out,FIFO)的,它有两个重要的方法:入队(enqueue)和出队(dequeue)。队列的入口端叫队尾(rear),出口端叫队头(front),如下图所示:
手撸队列
学习了队列的基本知识之后,接下来我们将使用代码来实现一个队列。
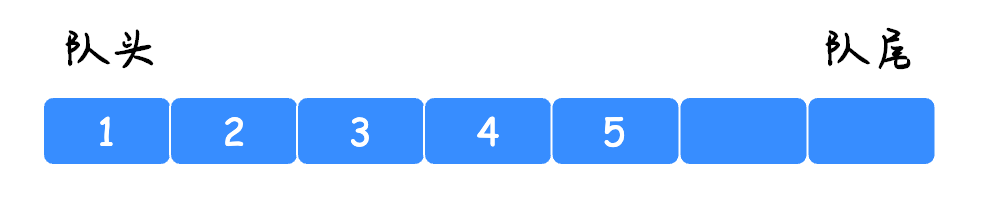
首先我们先使用数组来实现一个队列,它的结构如下图所示:
1.自定义队列—数组
public class MyQueue<E> {
private Object[] queue; // 存储容器
private int head; // 头部指针
private int tail; // 尾部指针
private int size; // 队列实际存储长度
private int maxSize; // 最大容量
public MyQueue() {
// 无参构造函数,设置默认参数
this.maxSize = 10;
this.head = 0;
this.tail = -1;
this.size = 0;
this.queue = new Object[this.maxSize];
}
public MyQueue(int initSize) {
// 有参构造函数,设置参数
this.maxSize = initSize;
this.head = 0;
this.tail = -1;
this.size = 0;
this.queue = new Object[this.maxSize];
}
/**
* 查询队头元素
*/
public E peek() throws Exception {
if (size == 0) {
throw new Exception("队列中暂无数据");
}
return (E) this.queue[this.head];
}
/**
* 入列
*/
public boolean offer(E e) throws Exception {
if (tail >= (maxSize - 1)) {
throw new Exception("添加失败,队列已满");
}
this.queue[++tail] = e;
size++;
return true;
}
/**
* 出列
*/
public E poll() throws Exception {
if (size == 0) {
throw new Exception("删除失败,队列为空");
}
size--;
return (E) this.queue[head++];
}
/**
* 代码测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.offer("Hello");
queue.offer("Java");
System.out.println(queue.peek());
queue.poll();
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}以上代码的执行结果如下:
Hello
Java
2.自定义队列—链表
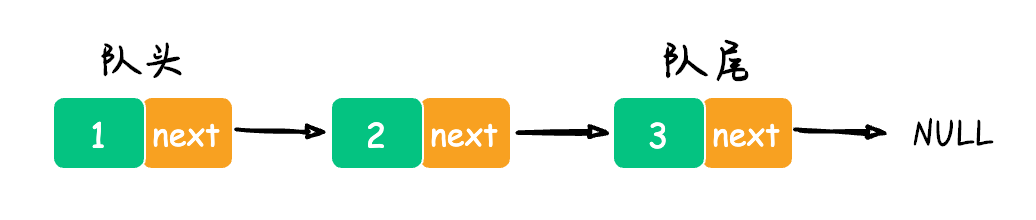
用链表实现队列的数据结构如下图所示:
实现代码如下:
public class QueueByLinked {
/**
* 声明链表节点
*/
static class Node<E> {
E item; // 当前的值
Node<E> next; // 下一个节点
Node(E e) {
this.item = e;
}
}
private Node firstNode; // 队头元素
private Node lastNode; // 队尾元素
private int size; // 队列实际存储数量
private int maxSize; // 队列最大容量
public QueueByLinked(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) throw new RuntimeException("队列最大容量不能为空");
// 默认初始化函数
firstNode = lastNode = new Node(null);
this.size = 0;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
/**
* 判断队列是否为空
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* 入列
*/
public void offer(Object e) {
// 最大值效验
if (maxSize <= size) throw new RuntimeException("队列已满");
Node node = new Node(e);
lastNode = lastNode.next = node; // 设置最后一个节点和倒数第二个节点的 next
size++; // 队列数量 +1
}
/**
* 出列
*/
public Node poll() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
size--; // 队列数量 -1
return firstNode = firstNode.next; // 设置并返回队头元素(第一个节点是 null,当前元素则为 Node.next)
}
/**
* 查询队头元素
*/
public Node peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
return firstNode.next; // 返回队头元素(第一个节点是 null,当前元素则为 Node.next)
}
/**
* 代码测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueByLinked queue = new QueueByLinked(10);
queue.offer("Hello");
queue.offer("JDK");
queue.offer("Java");
System.out.println(queue.poll().item);
System.out.println(queue.poll().item);
System.out.println(queue.poll().item);
}
}以上代码的执行结果如下:
Hello
JDK
Java
3.扩展:使用 List 实现自定义队列
除了以上两种方式之外,我们还可以使用 Java 自身的数据结构来实现队列,比如 List,我们这里提供一个实现的思路(但并不建议在实际工作中使用),实现代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 自定义队列(List方式)
*/
public class QueueByList<E> {
private List value; // 队列存储容器
public QueueByList() {
// 初始化
value = new ArrayList();
}
/**
* 判断队列是否为空
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return value.size() == 0;
}
/**
* 入列
*/
public void offer(Object e) {
value.add(e);
}
/**
* 出列
*/
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
E item = (E) value.get(0);
value.remove(0);
return item;
}
/**
* 查询队头元素
*/
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
return (E) value.get(0);
}
/**
* 代码测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueByList queue = new QueueByList();
queue.offer("Hello");
queue.offer("JDK");
queue.offer("Java");
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}以上代码的执行结果如下:
Hello
JDK
Java
队列使用场景
队列的常见使用场景有:
- 存储多线程中等待排队执行的任务;
- 存储多线程公平锁中等待执行任务的线程;
- 常见消息中间件的任务队列等。
总结
通过以上三种队列的实现方式我们可以看出,任意容器都是可以用来实现队列(Queue)的,只要保证队列的元素先进先出(FIFO),并且在实现类中需要包含队列的四个核心方法:入列、出列、查询队列是否为空、返回队头元素等,就可以称为实现了一个自定义的队列。