【iOS开源库】SDWebImage源码阅读&原理解析
汇总记录:
本文基于SDWebImage 4.2.3版本进行分析和整理。
整体目录结构:
SDWebImage
|----SDWebImageCompat 处理不同平台(iOS、TV、OS、Watch)宏,以及根据文件名@2x、@3x进行图片处理和缩放
|----SDWebImageOperation.h 添加cancel的delegate
+----Cache
|--------SDImageCache 主要处理缓存逻辑,重点集中在:NSCache(Memory)、Disk读写、清理Old File
|--------SDImageCacheConfig 配置缓存参数:是否压缩、iCloud、InMemory、ReadingOption、时间和CacheSize
+----Downloader
|--------SDWebImageDownloaderOperation 主要提供下载的Operation操作
|--------SDWebImageDownloader 提供下载管理入口
+----Utils
|--------SDWebImageManager 提供外层管理cache和download入口
|--------SDWebImagePrefetcher 预处理获取Image,主要应用预加载的地方
+----Categories
|--------NSData+ImageContentType 提供类型判断和ImageIO类型转换
|--------UIImage+GIF Data转UIImage(GIF)扩展
|--------UIImage+MultiFormat 提供BitMap或者未知类型的Data转UIImage扩展
|--------UIImage+WebP Data转WebP扩展
|--------UIImage+ForceDecode 解压操作
|--------UIView+WebCacheOperation 提供顶层关于取消和下载记录的扩展
+----Decoder
|--------SDWebImageCodersManager 整体Coders的入口,提供是否可Coder和Coder转发
|--------SDWebImageCoder 主要说明Coder Delegate 需要实现的接口
|--------SDWebImageImageIOCoder PNG/JPEG的Encode和解压操作
|--------SDWebImageGIFCoder GIF的Coder操作
|--------SDWebImageWebPCoder WebP的Coder操作
|--------SDWebImageFrame 辅助类,主要在GIF等动态图使用
|--------SDWebImageCoderHelper 辅助类,包括方向、Gif图合成等
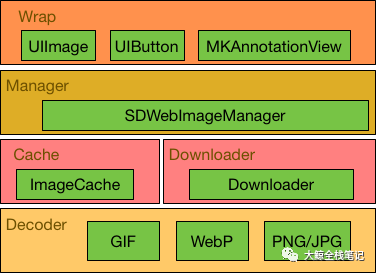
整体组件结构
整体框架结构比较清晰,因为Decoder部分相对比较独立,业务逻辑处理主要在Cache、Downloader层级以及以上。 下文会以Cache、Downloader、Manager、Wrap的顺序进行分解,最后讨论Decoder部分。
1、缓存部分解析
缓存部分逻辑主要是在SDImageCache,包括如下几个方面:
- 新增
- 删除
- 查询
- 缓存管理(过期)
SDWebImage的缓存中,主要走了一套NSCache管理内存和根据传入的Key转换MD5作为文件名存储。以及创建了一个IO操作的Queue进行管理IO操作。 这里重点注意,任何耗时:包括IO读写、转码等操作,都不应该放到主线程里面使用。
缓存部分其他地方都比较简单易懂,直接看源码即可。
重点说下如下两个值得学习的地方:
1、通过NSOperation管理queue任务
- (nullable NSOperation *)queryCacheOperationForKey:(nullable NSString *)key done:(nullable SDCacheQueryCompletedBlock)doneBlock {
if (!key) {
if (doneBlock) {
doneBlock(nil, nil, SDImageCacheTypeNone);
}
return nil;
}
// First check the in-memory cache...
UIImage *image = [self imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:key];
if (image) {
NSData *diskData = nil;
if (image.images) {
diskData = [self diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:key];
}
if (doneBlock) {
doneBlock(image, diskData, SDImageCacheTypeMemory);
}
return nil;
}
NSOperation *operation = [NSOperation new];
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
if (operation.isCancelled) {
// do not call the completion if cancelled
return;
}
@autoreleasepool {
NSData *diskData = [self diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:key];
UIImage *diskImage = [self diskImageForKey:key];
if (diskImage && self.config.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
NSUInteger cost = SDCacheCostForImage(diskImage);
[self.memCache setObject:diskImage forKey:key cost:cost];
}
if (doneBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
doneBlock(diskImage, diskData, SDImageCacheTypeDisk);
});
}
}
});
return operation;
}查询缓存的时候,这里采用了NSOperation进行是否取消的操作,因为当下载/缓存内容过多时,毕定存在先后处理顺序的问题,这时候可能由于用户操作等需要取消当前缓存处理,那么NSOperation这里起的唯一作用就是提供取消操作。可以参考具体的Manager里面缓存调起逻辑。
2、申请系统后台时间处理任务
- (void)backgroundDeleteOldFiles {
Class UIApplicationClass = NSClassFromString(@"UIApplication"); if(!UIApplicationClass || ![UIApplicationClass respondsToSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)]) { return;
} UIApplication *application = [UIApplication performSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)];
__block UIBackgroundTaskIdentifier bgTask = [application beginBackgroundTaskWithExpirationHandler:^{ // Clean up any unfinished task business by marking where you
// stopped or ending the task outright.
[application endBackgroundTask:bgTask];
bgTask = UIBackgroundTaskInvalid;
}]; // Start the long-running task and return immediately.
[self deleteOldFilesWithCompletionBlock:^{
[application endBackgroundTask:bgTask];
bgTask = UIBackgroundTaskInvalid;
}];
}这里有个疑问点要注意,为啥会存在前后两部分都去释放Task任务。 iOS的后台任务有个背景,不管任何时候,都需要手动去调用endBackgroundTask结束后台任务,其实开启一个后台job的时候,因为时长有限,所以会存在两种结局:
- 在允许的时间内执行完成
- 规定时间内未执行完成 如上两种情况,在结束后都必须手动调用endBackgroundTask:;
2、下载器(Downloader)
下载部分,主要是提供了一个Operation和一个Manager,其中SDWebImageDownloaderOperation里面提供了常用的Operation操作,也支持自定义的下载逻辑(实现SDWebImageDownloaderOperationInterface即可)。
2.1 SDWebImageDownloaderOperation 逻辑
该文件里面重点是Delegate:SDWebImageDownloaderOperationInterface 的设计和一种实现方式SDWebImageDownloaderOperation(PS:优秀的开源库基本都会设计一套接口,再做一套基础的实现)。
// 这里描述写的很清楚,如果需要自定义的Downloader op,那么需要继承NSOperation并且实现SDWebImageDownloaderOperation
/**
Describes a downloader operation. If one wants to use a custom downloader op, it needs to inherit from `NSOperation` and conform to this protocol
*/
@protocol SDWebImageDownloaderOperationInterface<NSObject>
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithRequest:(nullable NSURLRequest *)request
inSession:(nullable NSURLSession *)session
options:(SDWebImageDownloaderOptions)options;
- (nullable id)addHandlersForProgress:(nullable SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock)completedBlock;
- (BOOL)shouldDecompressImages;
- (void)setShouldDecompressImages:(BOOL)value;
- (nullable NSURLCredential *)credential;
- (void)setCredential:(nullable NSURLCredential *)value;
@endSDWebImageDownloaderOperation主要是提供内置的下载实现,重点是使用NSURLSessionTask进行下载,逻辑不复杂,详细的参考源码。里面重点有如下部分需要关注:
- 1、
_barrierQueue是共用的并发队列,而且不同的Op都是共用的同一个Queue,这里为啥要做成并发的呢?主要是优化多个线程查询callbacks的时间。
- (nullable NSArray<id> *)callbacksForKey:(NSString *)key {
__block NSMutableArray<id> *callbacks = nil;
dispatch_sync(self.barrierQueue, ^{
// We need to remove [NSNull null] because there might not always be a progress block for each callback
callbacks = [[self.callbackBlocks valueForKey:key] mutableCopy];
[callbacks removeObjectIdenticalTo:[NSNull null]];
});
return [callbacks copy]; // strip mutability here
}然后再配合dispatch_barrier_(a)sync操作来进行增删 操作。
- 2、在URLSession的Delegate实现中,存在如下函数实现:
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task didReceiveChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition, NSURLCredential *credential))completionHandler {
NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
__block NSURLCredential *credential = nil;
if ([challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod isEqualToString:NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust]) {
if (!(self.options & SDWebImageDownloaderAllowInvalidSSLCertificates)) {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
} else {
credential = [NSURLCredential credentialForTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust];
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential;
}
} else {
if (challenge.previousFailureCount == 0) {
if (self.credential) {
credential = self.credential;
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential;
} else {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeCancelAuthenticationChallenge;
}
} else {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeCancelAuthenticationChallenge;
}
}
if (completionHandler) {
completionHandler(disposition, credential);
}
}该部分重点是实现Https证书信任请求的,关于Https在iOS上的信任使用,可以搜索学习 iOS上的Https。
2.2 SDWebImageDownloader说明
SDWebImageDownloader主要是基于SDWebImageDownloaderOperation进行任务的添加和管理。使用NSOperationQueue进行任务执行操作。
-
设置了同一时间最多可执行task为6.
-
提供设置Http头信息入口
-
允许使用自定义的
SDWebImageDownloaderOperationInterfaceOperation进行操作,如果没有指定,那么就用默认的SDWebImageDownloaderOperation -
详细的逻辑参考代码即可,比较简单
-
3、针对通用组件封装(Wrap)
该部分的代码主要是在WebCache Categories文件夹下面,除了UIView+WebCache 以外,其他的涉及UIImage、UIButton等都是下载完成后赋值给到Image的区别,下载过程处理都是在UIView+WebCache中实现。
这里主要说下UIView+WebCache中的细节,其他的阅读源码即可,里面主要的逻辑函数为:
- (void)sd_internalSetImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url
placeholderImage:(nullable UIImage *)placeholder
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
operationKey:(nullable NSString *)operationKey
setImageBlock:(nullable SDSetImageBlock)setImageBlock
progress:(nullable SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDExternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock
context:(nullable NSDictionary *)context详细的步骤逻辑如下:
// 第一步:取消老的下载,这就是UITableViewCell重用后,快速滑动时,中间部分的图片不会被下载的原因。
NSString *validOperationKey = operationKey ?: NSStringFromClass([self class]);
[self sd_cancelImageLoadOperationWithKey:validOperationKey];
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &imageURLKey, url, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
//////////////////////////////////////////////
// 第二步:看是否设置默认图片,这里一个点。如果[context valueForKey:SDWebImageInternalSetImageGroupKey],那么就enter group,这个是干啥的呢,其实主要是给到FLAnimatedImageView+WebCache使用,
// 这里是等待setImageBlock会调用的,会结合dispatch_group_leave 和 dispatch_group_notify 使用
if (!(options & SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder)) {
if ([context valueForKey:SDWebImageInternalSetImageGroupKey]) {
dispatch_group_t group = [context valueForKey:SDWebImageInternalSetImageGroupKey];
dispatch_group_enter(group);
}
dispatch_main_async_safe(^{
[self sd_setImage:placeholder imageData:nil basedOnClassOrViaCustomSetImageBlock:setImageBlock];
});
}
if (url) {
// 这里是状态栏的扩展,主要是显示流量那个菊花,可以忽略
// check if activityView is enabled or not
if ([self sd_showActivityIndicatorView]) {
[self sd_addActivityIndicator];
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 第三步:获取Manager进行下载
SDWebImageManager *manager;
if ([context valueForKey:SDWebImageExternalCustomManagerKey]) {
manager = (SDWebImageManager *)[context valueForKey:SDWebImageExternalCustomManagerKey];
} else {
manager = [SDWebImageManager sharedManager];
}
__weak __typeof(self)wself = self;
id <SDWebImageOperation> operation = [manager loadImageWithURL:url options:options progress:progressBlock completed:^(UIImage *image, NSData *data, NSError *error, SDImageCacheType cacheType, BOOL finished, NSURL *imageURL) {
__strong __typeof (wself) sself = wself;
[sself sd_removeActivityIndicator];
if (!sself) { return; }
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 第四步:下载完成后,进行状态设置和相关状态回调
BOOL shouldCallCompletedBlock = finished || (options & SDWebImageAvoidAutoSetImage);
BOOL shouldNotSetImage = ((image && (options & SDWebImageAvoidAutoSetImage)) ||
(!image && !(options & SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder)));
SDWebImageNoParamsBlock callCompletedBlockClojure = ^{
if (!sself) { return; }
if (!shouldNotSetImage) {
[sself sd_setNeedsLayout];
}
if (completedBlock && shouldCallCompletedBlock) {
completedBlock(image, error, cacheType, url);
}
};
// case 1a: we got an image, but the SDWebImageAvoidAutoSetImage flag is set
// OR
// case 1b: we got no image and the SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder is not set
if (shouldNotSetImage) {
dispatch_main_async_safe(callCompletedBlockClojure);
return;
}
UIImage *targetImage = nil;
NSData *targetData = nil;
if (image) {
// case 2a: we got an image and the SDWebImageAvoidAutoSetImage is not set
targetImage = image;
targetData = data;
} else if (options & SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder) {
// case 2b: we got no image and the SDWebImageDelayPlaceholder flag is set
targetImage = placeholder;
targetData = nil;
}
if ([context valueForKey:SDWebImageInternalSetImageGroupKey]) {
dispatch_group_t group = [context valueForKey:SDWebImageInternalSetImageGroupKey];
dispatch_group_enter(group);
dispatch_main_async_safe(^{
[sself sd_setImage:targetImage imageData:targetData basedOnClassOrViaCustomSetImageBlock:setImageBlock];
});
// ensure completion block is called after custom setImage process finish
dispatch_group_notify(group, dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
callCompletedBlockClojure();
});
} else {
dispatch_main_async_safe(^{
[sself sd_setImage:targetImage imageData:targetData basedOnClassOrViaCustomSetImageBlock:setImageBlock];
callCompletedBlockClojure();
});
}
}];
[self sd_setImageLoadOperation:operation forKey:validOperationKey];
} else {
dispatch_main_async_safe(^{
[self sd_removeActivityIndicator];
if (completedBlock) {
NSError *error = [NSError errorWithDomain:SDWebImageErrorDomain code:-1 userInfo:@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey : @"Trying to load a nil url"}];
completedBlock(nil, error, SDImageCacheTypeNone, url);
}
});
}4、Decoder模块
Decoder模块部分的源码重点是在目录Decoder和Categories两个地方,其中Categories提供NSData、UIImage等的直接调用extend。核心实现还是基于Decoder。
相关模块的详细说明可以参考目录说明部分。
这里主要说下几个部分,主要包括个人觉得可能产生障碍的点,便于理解:
- 为啥要压缩和Decompressed?
SDWebImageFrame和SDWebImageCoderHelper中animatedImageWithFrames的逻辑- 大图片缩放逻辑辅助说明
4.1 为啥要压缩和Decompressed
我们都知道,在iOS中,我加载PNG和JPEG,直接调用[UIImage imageNamed:@"pic"];就好,而且本来从网络上下载的图片也都是PNG或者JPEG的,又没用Zip等去进行压缩,为啥还有这么一个Decoder模块呢。
其实这里重点就是针对性能做优化,我们平时直接加载图片的时候,因为图片都很小,所以基本不会消耗时间,但是我们从url中拉取的图片,一般都是运营配置,基本都不小。
如果加载过本地未处理的PNG(文件比较大)的兄弟应该有过这种感觉,跑完加载的时候,刷出界面开始会白那么一下,图片才出来。那就是因为图片太大了。
那么针对PNG和JPEG,SDWebImage的Decompressed又是做什么操作呢,我们知道图片显示到设备上,是按照RGBA等显示,但是PNG和JPEG自身的格式并非RGBA的。这里的解压其实就是创建一个BitmapImage,先在非UI线程渲染图片,然后拿到UIImage去显示。
代码参考如下:
const size_t partialHeight = CGImageGetHeight(partialImageRef);
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = SDCGColorSpaceGetDeviceRGB();
CGContextRef bmContext = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL, _width, _height, 8, 0, colorSpace, kCGBitmapByteOrderDefault | kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst);
if (bmContext) {
CGContextDrawImage(bmContext, (CGRect){.origin.x = 0.0f, .origin.y = 0.0f, .size.width = _width, .size.height = partialHeight}, partialImageRef);
CGImageRelease(partialImageRef);
partialImageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(bmContext);
CGContextRelease(bmContext);
}4.2SDWebImageFrame 和SDWebImageCoderHelper中animatedImageWithFrames的逻辑
这两个类里面,有部分函数主要是提供GIF图片的辅助,当我们从NSData拿到图片数据的时候,其实是拿到了多张图片的Data,当我们分成多张图(参考SDWebImageGIFCoder)后,我们要合成到UIImage的images中。
每个SDWebImageFrame就代表了一张图片,每个图片有个播放时长,但是总的一个animationImage并未对每个Image进行时长设置。他的逻辑是怎样的呢?
假如我们有两张图AB,动画要显示A3s,显示B1s,那么我们可以指定显示四张图片:AAAB,总时长是4s。
所以当拿到GIF对应的UIImage和显示时长后,怎么去合成AAAB 和 4s 的时长呢,流程如下: -获取每个图片总时长,totalTimes -计算没个图片时长的最大公约数,再用每张图片的时长除以最大公约数,就是每张图片要显示的次数 -根据显示次数构建UIImage的Array,根据UIImage的Array和总时长,就能通过GIF转成UIImage动画了
4.3 大图片缩放逻辑辅助说明
图片缩放逻辑主要函数:
- (nullable UIImage *)sd_decompressedAndScaledDownImageWithImage:(nullable UIImage *)image {
if (![[self class] shouldDecodeImage:image]) {
return image;
}
if (![[self class] shouldScaleDownImage:image]) {
return [self sd_decompressedImageWithImage:image];
}
CGContextRef destContext;
// autorelease the bitmap context and all vars to help system to free memory when there are memory warning.
// on iOS7, do not forget to call [[SDImageCache sharedImageCache] clearMemory];
@autoreleasepool {
CGImageRef sourceImageRef = image.CGImage;
CGSize sourceResolution = CGSizeZero;
sourceResolution.width = CGImageGetWidth(sourceImageRef);
sourceResolution.height = CGImageGetHeight(sourceImageRef);
float sourceTotalPixels = sourceResolution.width * sourceResolution.height;
// Determine the scale ratio to apply to the input image
// that results in an output image of the defined size.
// see kDestImageSizeMB, and how it relates to destTotalPixels.
float imageScale = kDestTotalPixels / sourceTotalPixels;
CGSize destResolution = CGSizeZero;
destResolution.width = (int)(sourceResolution.width*imageScale);
destResolution.height = (int)(sourceResolution.height*imageScale);
// current color space
CGColorSpaceRef colorspaceRef = [[self class] colorSpaceForImageRef:sourceImageRef];
// kCGImageAlphaNone is not supported in CGBitmapContextCreate.
// Since the original image here has no alpha info, use kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast
// to create bitmap graphics contexts without alpha info.
destContext = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL,
destResolution.width,
destResolution.height,
kBitsPerComponent,
0,
colorspaceRef,
kCGBitmapByteOrderDefault|kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast);
if (destContext == NULL) {
return image;
}
CGContextSetInterpolationQuality(destContext, kCGInterpolationHigh);
// Now define the size of the rectangle to be used for the
// incremental blits from the input image to the output image.
// we use a source tile width equal to the width of the source
// image due to the way that iOS retrieves image data from disk.
// iOS must decode an image from disk in full width 'bands', even
// if current graphics context is clipped to a subrect within that
// band. Therefore we fully utilize all of the pixel data that results
// from a decoding opertion by achnoring our tile size to the full
// width of the input image.
CGRect sourceTile = CGRectZero;
sourceTile.size.width = sourceResolution.width;
// The source tile height is dynamic. Since we specified the size
// of the source tile in MB, see how many rows of pixels high it
// can be given the input image width.
sourceTile.size.height = (int)(kTileTotalPixels / sourceTile.size.width );
sourceTile.origin.x = 0.0f;
// The output tile is the same proportions as the input tile, but
// scaled to image scale.
CGRect destTile;
destTile.size.width = destResolution.width;
destTile.size.height = sourceTile.size.height * imageScale;
destTile.origin.x = 0.0f;
// The source seem overlap is proportionate to the destination seem overlap.
// this is the amount of pixels to overlap each tile as we assemble the ouput image.
float sourceSeemOverlap = (int)((kDestSeemOverlap/destResolution.height)*sourceResolution.height);
CGImageRef sourceTileImageRef;
// calculate the number of read/write operations required to assemble the
// output image.
int iterations = (int)( sourceResolution.height / sourceTile.size.height );
// If tile height doesn't divide the image height evenly, add another iteration
// to account for the remaining pixels.
int remainder = (int)sourceResolution.height % (int)sourceTile.size.height;
if(remainder) {
iterations++;
}
// Add seem overlaps to the tiles, but save the original tile height for y coordinate calculations.
float sourceTileHeightMinusOverlap = sourceTile.size.height;
sourceTile.size.height += sourceSeemOverlap;
destTile.size.height += kDestSeemOverlap;
for( int y = 0; y < iterations; ++y ) {
@autoreleasepool {
sourceTile.origin.y = y * sourceTileHeightMinusOverlap + sourceSeemOverlap;
destTile.origin.y = destResolution.height - (( y + 1 ) * sourceTileHeightMinusOverlap * imageScale + kDestSeemOverlap);
sourceTileImageRef = CGImageCreateWithImageInRect( sourceImageRef, sourceTile );
if( y == iterations - 1 && remainder ) {
float dify = destTile.size.height;
destTile.size.height = CGImageGetHeight( sourceTileImageRef ) * imageScale;
dify -= destTile.size.height;
destTile.origin.y += dify;
}
CGContextDrawImage( destContext, destTile, sourceTileImageRef );
CGImageRelease( sourceTileImageRef );
}
}
CGImageRef destImageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(destContext);
CGContextRelease(destContext);
if (destImageRef == NULL) {
return image;
}
UIImage *destImage = [UIImage imageWithCGImage:destImageRef scale:image.scale orientation:image.imageOrientation];
CGImageRelease(destImageRef);
if (destImage == nil) {
return image;
}
return destImage;
}
}
这里光看代码,肯定会一头雾水,其实逻辑很简单,避免要缩放的图片太大,采用的方式是将图片分割成一系列大小的小方块,然后每个方块去获取Image并draw到目标BitmapContext上。重点还是在于内存优化方面。