深入浅出虚拟内存(二)绘制虚拟内存排布图
通过实践画出虚拟内存空间排布图
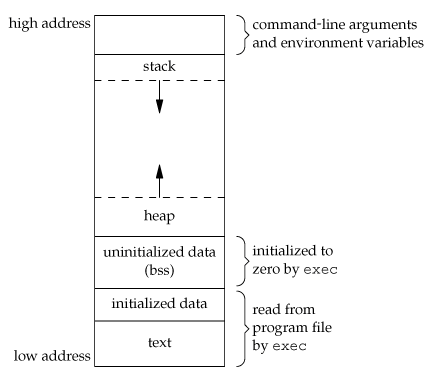
基本上每个人或多或少都了解虚拟内存的空间分布(如下图所示),那如何验证它呢? 别急,我们接下来会讲到。
virtual memory 图片来自Holberton
堆栈空间
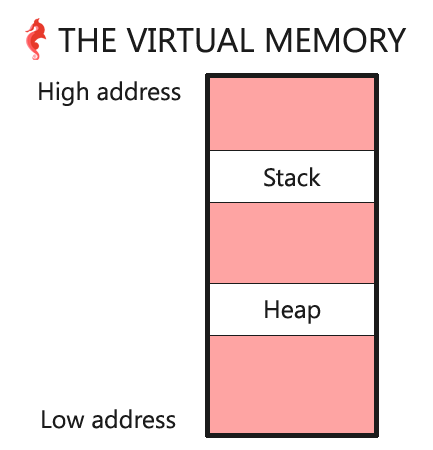
首先验证栈空间的位置,我们都知道C中局部变量是存储在栈空间的,malloc分配的内存是存储在堆空间,所以可以通过打印出局部变量地址和malloc的返回内存地址的方式来验证堆栈空间在整个虚拟空间中的位置。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/**
* main - print locations of various elements
*
* Return: EXIT_FAILURE if something failed. Otherwise EXIT_SUCCESS
*/
int main(void)
{
int a;
void *p;
printf("Address of a: %p\n", (void *)&a);
p = malloc(98);
if (p == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't malloc\n");
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Allocated space in the heap: %p\n", p);
return (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
编译运行:gcc -Wall -Wextra -pedantic -Werror main.c -o test; ./test
输出:
Address of a: 0x7ffedde9c7fc
Allocated space in the heap: 0x55ca5b360670通过结果可以看出堆地址空间在栈地址空间下面,整理如图:
virtual memory stack heap 图片来自Holberton
可执行程序
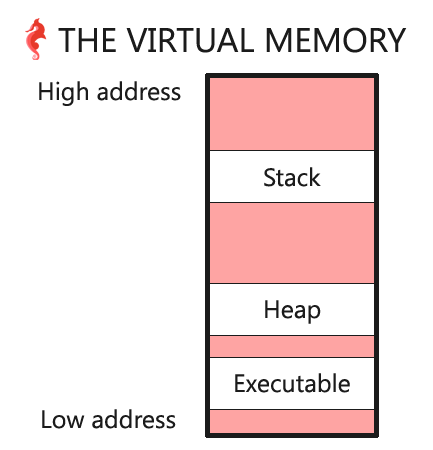
可执行程序也在虚拟内存中,可以通过打印main函数的地址,并与堆栈地址相比较,即可知道可执行程序地址相对于堆栈地址的分布。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/**
* main - print locations of various elements
*
* Return: EXIT_FAILURE if something failed. Otherwise EXIT_SUCCESS
*/
int main(void)
{
int a;
void *p;
printf("Address of a: %p\n", (void *)&a);
p = malloc(98);
if (p == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't malloc\n");
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Allocated space in the heap: %p\n", p);
printf("Address of function main: %p\n", (void *)main);
return (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
编译运行:gcc main.c -o test; ./test
输出:
Address of a: 0x7ffed846de2c
Allocated space in the heap: 0x561b9ee8c670
Address of function main: 0x561b9deb378a由于main(0x561b9deb378a)< heap(0x561b9ee8c670) < (0x7ffed846de2c),可以画出分布图如下:
virtual memory stack heap executable 图片来自Holberton
命令行参数和环境变量
程序入口main函数可以携带参数:
- 第一个参数(argc): 命令行参数的个数
- 第二个参数(argv): 指向命令行参数数组的指针
- 第三个参数(env): 指向环境变量数组的指针
通过程序可以看见这些元素在虚拟内存中的位置:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/**
* main - print locations of various elements
*
* Return: EXIT_FAILURE if something failed. Otherwise EXIT_SUCCESS
*/
int main(int ac, char **av, char **env)
{
int a;
void *p;
int i;
printf("Address of a: %p\n", (void *)&a);
p = malloc(98);
if (p == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't malloc\n");
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Allocated space in the heap: %p\n", p);
printf("Address of function main: %p\n", (void *)main);
printf("First bytes of the main function:\n\t");
for (i = 0; i < 15; i++)
{
printf("%02x ", ((unsigned char *)main)[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Address of the array of arguments: %p\n", (void *)av);
printf("Addresses of the arguments:\n\t");
for (i = 0; i < ac; i++)
{
printf("[%s]:%p ", av[i], av[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Address of the array of environment variables: %p\n", (void *)env);
printf("Address of the first environment variable: %p\n", (void *)(env[0]));
return (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
编译运行:gcc main.c -o test; ./test nihao hello
输出:
Address of a: 0x7ffcc154a748
Allocated space in the heap: 0x559bd1bee670
Address of function main: 0x559bd09807ca
First bytes of the main function:
55 48 89 e5 48 83 ec 40 89 7d dc 48 89 75 d0
Address of the array of arguments: 0x7ffcc154a848
Addresses of the arguments:
[./test]:0x7ffcc154b94f [nihao]:0x7ffcc154b956 [hello]:0x7ffcc154b95c
Address of the array of environment variables: 0x7ffcc154a868
Address of the first environment variable: 0x7ffcc154b962结果如下:
main(0x559bd09807ca) < heap(0x559bd1bee670)
< stack(0x7ffcc154a748) < argv(0x7ffcc154a848)
< env(0x7ffcc154a868) < arguments(0x7ffcc154b94f->0x7ffcc154b95c + 6)
(6为hello+1('\0')) < env first(0x7ffcc154b962)可以看出所有的命令行参数都是相邻的,并且紧接着就是环境变量。
argv和env数组地址是相邻的吗?
上例中argv有4个元素,命令行中有三个参数,还有一个NULL指向标记数组的末尾,每个指针是8字节,
8*4=32,argv(0x7ffcc154a848)+32(0x20)=env(0x7ffcc154a868)
所以,argv和env数组指针是相邻的。
命令行参数地址紧随环境变量地址之后吗?
首先,需要获取环境变量数组的大小。环境变量数组是以NULL结束的,所以可以遍历env数组,检查是否为NULL,获取数组大小,代码如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/**
* main - print locations of various elements
*
* Return: EXIT_FAILURE if something failed. Otherwise EXIT_SUCCESS
*/
int main(int ac, char **av, char **env)
{
int a;
void *p;
int i;
int size;
printf("Address of a: %p\n", (void *)&a);
p = malloc(98);
if (p == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't malloc\n");
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Allocated space in the heap: %p\n", p);
printf("Address of function main: %p\n", (void *)main);
printf("First bytes of the main function:\n\t");
for (i = 0; i < 15; i++)
{
printf("%02x ", ((unsigned char *)main)[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Address of the array of arguments: %p\n", (void *)av);
printf("Addresses of the arguments:\n\t");
for (i = 0; i < ac; i++)
{
printf("[%s]:%p ", av[i], av[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Address of the array of environment variables: %p\n", (void *)env);
printf("Address of the first environment variables:\n");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("\t[%p]:\"%s\"\n", env[i], env[i]);
}
/* size of the env array */
i = 0;
while (env[i] != NULL)
{
i++;
}
i++; /* the NULL pointer */
size = i * sizeof(char *);
printf("Size of the array env: %d elements -> %d bytes (0x%x)\n", i, size, size);
return (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
编译运行:gcc main.c -o test; ./test nihao hello
输出:
Address of a: 0x7ffd5ebadff4
Allocated space in the heap: 0x562ba4e13670
Address of function main: 0x562ba2f1881a
First bytes of the main function:
55 48 89 e5 48 83 ec 40 89 7d dc 48 89 75 d0
Address of the array of arguments: 0x7ffd5ebae0f8
Addresses of the arguments:
[./test]:0x7ffd5ebae94f [nihao]:0x7ffd5ebae956 [hello]:0x7ffd5ebae95c
Address of the array of environment variables: 0x7ffd5ebae118
Address of the first environment variables:
[0x7ffd5ebae962]:"LS_COLORS=rs=0:di=01;34:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:mi=00:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arc=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lha=01;31:*.lz4=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.lzma=01;31:*.tlz=01;31:*.txz=01;31:*.tzo=01;31:*.t7z=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.Z=01;31:*.dz=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.lrz=01;31:*.lz=01;31:*.lzo=01;31:*.xz=01;31:*.zst=01;31:*.tzst=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.bz=01;31:*.tbz=01;31:*.tbz2=01;31:*.tz=01;31:*.deb=01;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.war=01;31:*.ear=01;31:*.sar=01;31:*.rar=01;31:*.alz=01;31:*.ace=01;31:*.zoo=01;31:*.cpio=01;31:*.7z=01;31:*.rz=01;31:*.cab=01;31:*.wim=01;31:*.swm=01;31:*.dwm=01;31:*.esd=01;31:*.jpg=01;35:*.jpeg=01;35:*.mjpg=01;35:*.mjpeg=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.tiff=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.svg=01;35:*.svgz=01;35:*.mng=01;35:*.pcx=01;35:*.mov=01;35:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.m2v=01;35:*.mkv=01;35:*.webm=01;35:*.ogm=01;35:*.mp4=01;35:*.m4v=01;35:*.mp4v=01;35:*.vob=01;35:*.qt=01;35:*.nuv=01;35:*.wmv=01;35:*.asf=01;35:*.rm=01;35:*.rmvb=01;35:*.flc=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.flv=01;35:*.gl=01;35:*.dl=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:*.yuv=01;35:*.cgm=01;35:*.emf=01;35:*.ogv=01;35:*.ogx=01;35:*.aac=00;36:*.au=00;36:*.flac=00;36:*.m4a=00;36:*.mid=00;36:*.midi=00;36:*.mka=00;36:*.mp3=00;36:*.mpc=00;36:*.ogg=00;36:*.ra=00;36:*.wav=00;36:*.oga=00;36:*.opus=00;36:*.spx=00;36:*.xspf=00;36:"
[0x7ffd5ebaef4e]:"HOSTNAME=3e8650948c0c"
[0x7ffd5ebaef64]:"OLDPWD=/"
Size of the array env: 11 elements -> 88 bytes (0x58)
运算结果如下:
root@3e8650948c0c:/ubuntu# bc
bc 1.07.1
Copyright 1991-1994, 1997, 1998, 2000, 2004, 2006, 2008, 2012-2017 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.
For details type `warranty'.
obase=16
ibase=16
58+7ffd5ebae118
(standard_in) 3: syntax error
58+7FFD5EBAE118
7FFD5EBAE170
quit通过结果可知7FFD5EBAE170 != 0x7ffd5ebae94f,所以命令行参数地址不是紧随环境变量地址之后。
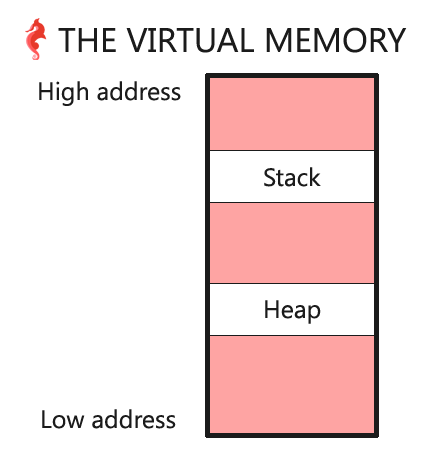
截至目前画出图表如下:
virtual memory stack heap 图片来自Holberton
栈内存真的向下增长吗?
可以通过调用函数来确认,如果真的是向下增长,那么调用函数的地址应该高于被调用函数地址, 代码如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void f(void)
{
int a;
int b;
int c;
a = 98;
b = 1024;
c = a * b;
printf("[f] a = %d, b = %d, c = a * b = %d\n", a, b, c);
printf("[f] Adresses of a: %p, b = %p, c = %p\n", (void *)&a, (void *)&b, (void *)&c);
}
int main(int ac, char **av, char **env)
{
int a;
void *p;
int i;
int size;
printf("Address of a: %p\n", (void *)&a);
p = malloc(98);
if (p == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't malloc\n");
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Allocated space in the heap: %p\n", p);
printf("Address of function main: %p\n", (void *)main);
f();
return (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
编译运行:gcc main.c -o test; ./test
输出:
Address of a: 0x7ffefc75083c
Allocated space in the heap: 0x564d46318670
Address of function main: 0x564d45b9880e
[f] a = 98, b = 1024, c = a * b = 100352
[f] Adresses of a: 0x7ffefc7507ec, b = 0x7ffefc7507f0, c = 0x7ffefc7507f4结果可知: f{a} 0x7ffefc7507ec < main{a} 0x7ffefc75083c 可画图如下:
virtual memory 图片来自Holberton
其实也可以写一个简单的代码,通过查看/proc文件系统中map内容来查看内存分布,这里就不举例啦。