手摸手Electron + Vue实战教程(四)
截止上一篇我们已经基本全部完成了静态页部分了,今天我们要开始玩玩数据了。。
1 数据持久化存储的必要性
electron应用说到底是个桌面级应用,我们写好的 Markdown 文档,毋庸置疑的必须要保存下来吧,否则一旦重启应用,那我们辛辛苦苦写的文档岂不是白忙活了。噢,心态炸裂……
对于一般的前端同学来说,我们请求接口拿到数据,然后把web页面展示出来就完事了。但我们现在干的其实已经不完全是纯前端的活了,如果思维还停留在纯web开发的思路上,那么大家还是赶紧把思维拐过来吧,嘿嘿
数据持久化存储对于后端同学来说应该比较熟悉,属于家常便饭那种了。通常指的是把内存里的数据以不同的存储模型存储到磁盘上,在需要的时候再从存储模型里读取读入内存中的整个流程。这里面的存储模型通常就是我们熟悉的数据库。
常用的数据库大家都知道有MySQL,Mongodb,SQLite等等,那么问题来了,我们装一个桌面应用软件,不可能要求用户再自己装一个数据库吧?当然,我们也可以链接远程数据库,但是这成本就很酸爽了……
既然让用户安装数据库不可行,但是我们有些数据又必须要在本地存储下来,这个时候NoSQL嵌入式数据库就出来了。
2 数据库的选择
前端同学玩得比较多的还是JS技术栈,所以我们还是首选纯JavaScript实现的数据库,在这里我们选择的是nedb。nedb用得很广泛,star数也很多,百度随便一搜,有很多讲到nedb和electron配合使用的文章。
NeDB是使用Nodejs实现的一个NoSQL嵌入式数据库操作模块,可以看作是精简版的MongoDB,可以充当内存数据库,也可以用来实现本地存储,甚至可以在浏览器中使用。查询方式比较灵活,支持使用正则、比较运算符、逻辑运算符、索引以及JSON深度查询等。
由于NeDB属于面向文档数据库,面向文档数据库可以看做是键值数据库的一个升级,不但允许键值嵌套,还提高了查询效率。面向文档数据库会将数据以文档形式存储。每个文档都是自包含的数据单元,是一系列数据项的集合。每个数据项都有一个名词与对应值,值既可以是简单的数据类型,如字符串、数字和日期等;也可以是复杂的类型,如有序列表和关联对象。数据存储的最小单位是文档,同一个表中存储的文档属性可以是不同的,数据可以使用XML、JSON或JSONB等多种形式存储。
当然,nedb也有点不友好的地方,原生不支持Promise,采用的是异步回调。但这其实也不是问题,我们可以使用nedb-promises:
3 nedb-promises 安装
yarn add nedb-promises安装完后在插件目录plugin里新建文件datastore.js初始化数据库,详细初始化api文档可以参考w3cschool链接https://www.w3cschool.cn/nedbintro/nedbintro-t9z327mh.html:
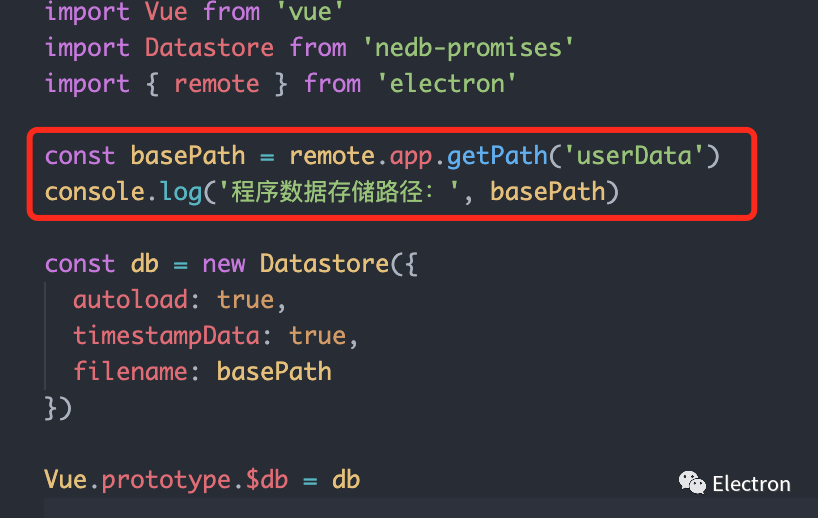
remote 模块提供了一种在渲染进程(网页)和主进程之间进行进程间通讯(IPC)的简便途径。remote.app.getPath('userData') 获取到的就是我们应用程序的用户文件夹,每个应用程序都有自己独立的文件夹。
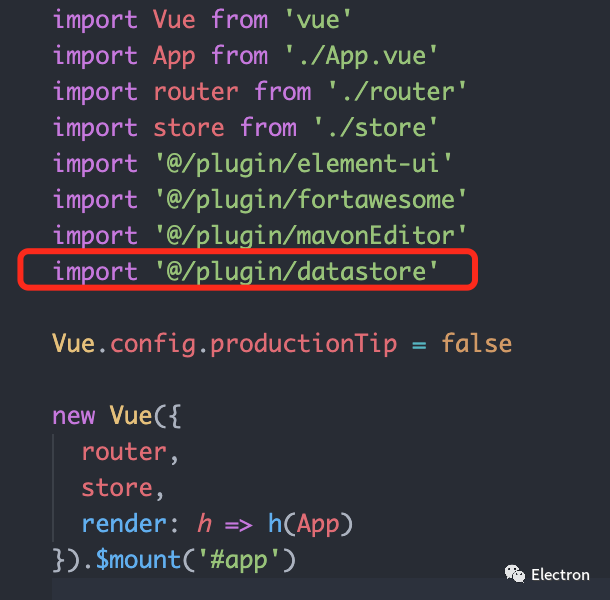
在main.js中引入我们刚编写好的datastore.js就算完成全部引入了:
nedb-promises 的使用方法跟原生的 nedb 用法基本是一致的,而且还支持promises,也可以直接使用 async/await ,具体使用也可以看看插件的 github 地址:https://github.com/bajankristof/nedb-promises
4 数据序列化 - 加密解密
到了上面那步其实我们的数据库已经可以正常使用了,但是会有个问题,我们写的内容如果直接在数据库文件里面查看会是明文的,你写的东西一清二楚的暴露出来了,强迫症的我决定给数据加个密,当然,具体是否需要加密大家可以自行选择,不需要加密的可以直接跳过这一节了。加密也只是防君子不防小人,安全永远是相对的。❄️
nedb 已经有自带的序列化方法,在数据库初始化中直接调用即可。
既然我们程序本身集成了node,我们当然直接选择 node 自身的 crypto 加密模块即可,加密类型这里选择的是 aes-128-cbc ,详细可以参考文档:http://nodejs.cn/api/crypto.html,https://www.jianshu.com/p/09350dc1ab97
首先我们定义好加密算法类型,生成秘钥和初始化向量:
❝afterSerialization(可选): 在数据被序列化成字符串之后和被写入磁盘前,可以使用该方法对数据进行转换。比如可以做一些数据加密工作。
❞
在 new Datastore 中定义加密方法,plaintext 参数是需要加密的内容,即写入磁盘的数据:
❝beforeDeserialization(可选): 与afterSerialization相反。两个必须成对出现,否则会引起数据丢失,可以理解为一个加密解密的过程。
❞
接着还需要定义解密的数据,依然是在 new Datastore 中添加,ciphertext 参数是需要解密的内容,即从磁盘中读取的数据:
4 增删改查
我们先写几个增删改查的小 demo 看看如何使用我们的数据库。
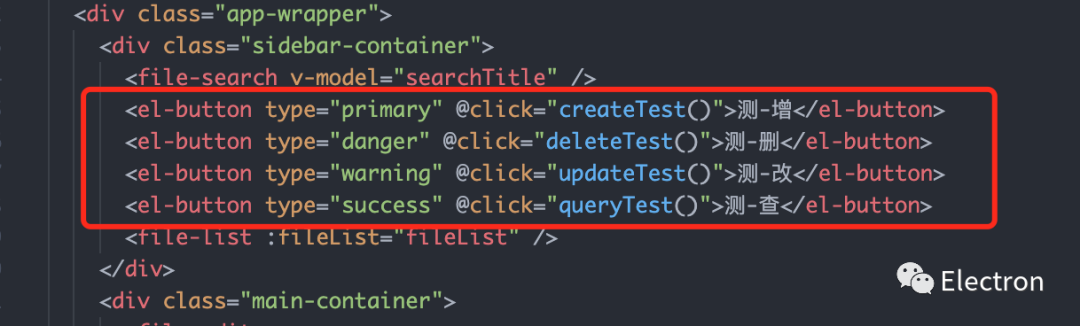
先在我们的左侧列表栏新增四个按钮,demo 我们姑且先这么写(后面我们再删掉 demo 代码哈):
操作按钮
具体代码实现
看起来很简单是吧(事实上也很简单嘛),跟官网的操作例子几乎是一模一样的了。示例代码中promise、async/await都使用了。sort可以将数据排序,updatedAt: -1是将修改时间最近的排在最前面。
我们新增文件的时候只需要title和content两个字段就足够了,一个是标题,一个是内容。所以后续我们真正实现新增文件的时候也是这么写的:
const fileNew = { title: '无标题笔记', content: '' }
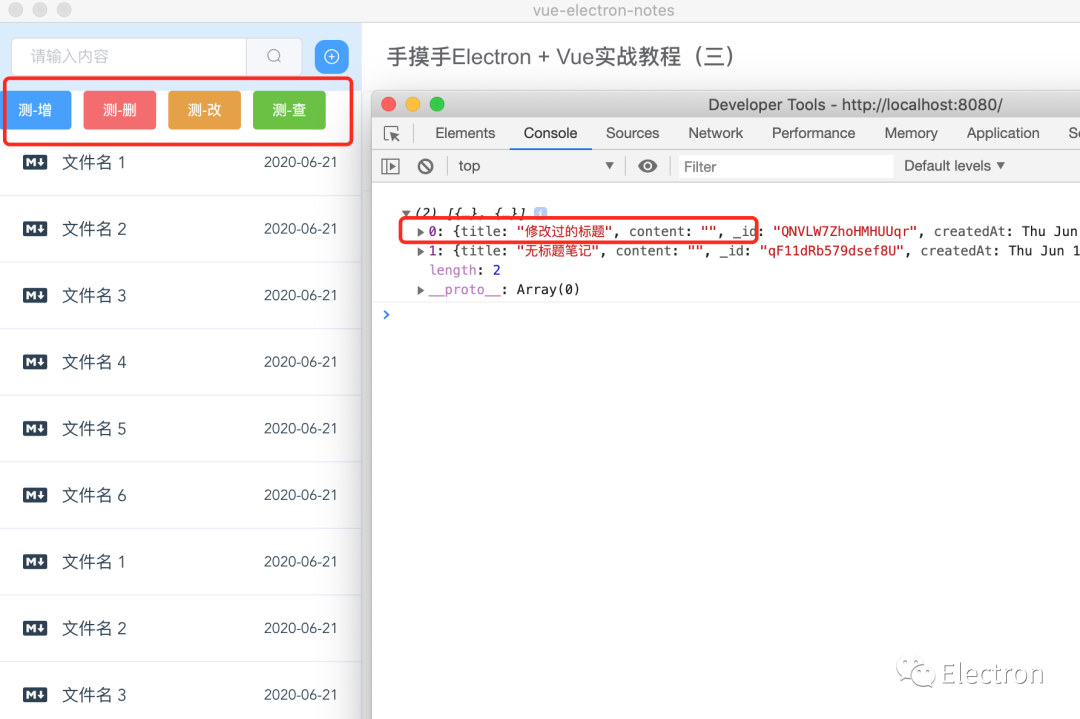
this.$db.insert(fileNew)到这一步就搞定了,从控制台中已经看得到我们的数据增删改查都木有问题了。
增删改查示意图
贴一下完整代码,Home.vue:
<template>
<div class="app-wrapper">
<div class="sidebar-container">
<file-search v-model="searchTitle" />
<el-button type="primary" @click="createTest()">测-增</el-button>
<el-button type="danger" @click="deleteTest()">测-删</el-button>
<el-button type="warning" @click="updateTest()">测-改</el-button>
<el-button type="success" @click="queryTest()">测-查</el-button>
<file-list :fileList="fileList" />
</div>
<div class="main-container">
<file-edit
v-model="fileItem.content"
:title.sync="fileItem.title"
:boxShadow="false"
:subfield="false"
:shortCut="false"
@change="onSubmit"
/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import FileSearch from '@/components/FileSearch'
import FileList from '@/components/FileList'
import FileEdit from '@/components/FileEdit'
export default {
name: 'Home',
components: { FileSearch, FileList, FileEdit },
data() {
return {
searchTitle: '',
fileList: [
{ id: 1, title: '文件名 1', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 2, title: '文件名 2', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 3, title: '文件名 3', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 4, title: '文件名 4', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 5, title: '文件名 5', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 6, title: '文件名 6', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 1, title: '文件名 1', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 2, title: '文件名 2', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 3, title: '文件名 3', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 4, title: '文件名 4', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 5, title: '文件名 5', time: '2020-06-21' },
{ id: 6, title: '文件名 6', time: '2020-06-21' }
],
fileItem: {
title: '手摸手Electron + Vue实战教程(三)',
content: ''
}
}
},
methods: {
// 增
createTest() {
const fileNew = { title: '无标题笔记', content: '' }
this.$db.insert(fileNew)
},
// 删
async deleteTest() {
const list = await this.$db.find().sort({ updatedAt: -1 })
if (list.length === 0) return
this.$db.remove({ _id: list[0]._id }).then(() => {
this.$message.warning('删除成功')
})
},
// 改
async updateTest() {
const list = await this.$db.find().sort({ updatedAt: -1 })
if (list.length === 0) return
this.$db.update({ _id: list[0]._id }, { $set: { title: '修改过的标题' } }).then(() => {
this.$message.success('修改成功')
})
},
// 查
async queryTest() {
const list = await this.$db.find().sort({ updatedAt: -1 })
console.log(list)
},
onSubmit(value) {
console.log(value)
console.log(this.fileItem)
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.app-wrapper {
display: flex;
.sidebar-container {
width: 300px;
height: 100vh;
border-right: 1px solid #eaeefb;
}
.main-container {
flex: 1;
overflow: hidden;
}
}
</style>datastore.js:
/*
* @Description: 引入 nedb 数据库
* @Author: sufen
* @Date: 2020-06-10 22:30:35
* @LastEditTime: 2020-06-11 12:20:39
* @LastEditors: sufen
*/
import Vue from 'vue'
import crypto from 'crypto'
import Datastore from 'nedb-promises'
import { remote } from 'electron'
const basePath = remote.app.getPath('userData')
console.log('程序数据存储路径:', basePath)
const algorithm = 'aes-128-cbc' // 加密算法类型
const password = 'vue-electron-notes' // 用于生成秘钥的密码
const key = crypto.scryptSync(password, 'salt', 16) // 秘钥
const iv = Buffer.alloc(16, 0) // 初始化向量
const db = new Datastore({
autoload: true,
timestampData: true,
filename: basePath,
afterSerialization(plaintext) {
// 实例化一个cipher加密对象,使用加密算法进行加密,key作为密钥
// 使用cipher对 plaintext 进行加密,源数据类型为utf-8,输出数据类型为hex
const cipher = crypto.createCipheriv(algorithm, key, iv)
let crypted = cipher.update(plaintext, 'utf-8', 'hex')
crypted += cipher.final('hex')
return crypted
},
beforeDeserialization(ciphertext) {
// 实例化一个decipher解密对象,使用解密算法进行解密,key作为密钥
// 使用decipher对 ciphertext 进行解密,源数据类型为hex,输出数据类型为utf-8
const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv(algorithm, key, iv)
let decrypted = decipher.update(ciphertext, 'hex', 'utf-8')
decrypted += decipher.final('utf-8')
return decrypted
}
})
Vue.prototype.$db = db这一篇章就先到这里了,我们下一篇再真正实现 Markdown 文件的创建、编辑以及实时保存。有兴趣的童鞋可以先自己实现看看,对比一下和我的写法有何不同,说不定我的写法还不如你的呢(请不吝惕教……)