Springboot 系列(十五)如何编写自己的 Springboot starter
-
前言
Springboot 中的自动配置确实方便,减少了我们开发上的复杂性,那么自动配置原理是什么呢?之前我也写过了一篇文章进行了分析。
Springboot 系列(三)Spring Boot 自动配置。
由于自动配置用到了配置文件的绑定,如果你还不知道常见的配置文件的用法,可以参考这篇文章。 Springboot 系列(二)Spring Boot 配置文件。
在这一次,通过学习 Springboot 自动配置模式,编写一个自己的 starter,用来加深对自动配置的理解。
熟悉模式,有助于提升编写的 starter 的规范性,编写自己的 starter 之前先来学习 Springboot 官方 starter 以及常见框架的整合 starter 的编写方式 ,可以领略到其中的奥秘。
-
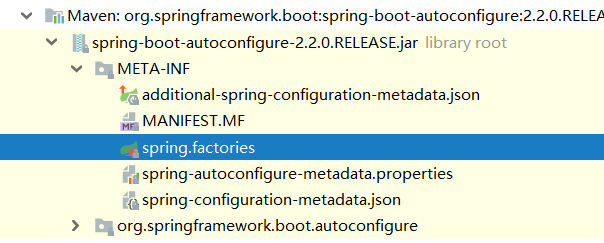
Springboot 官方模式
选择一个官方的自动配置进行分析,这里就选择常见的配置端口号配置。
2.1. 引入依赖
使用端口号之前我们需要先引入 web 依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>如果你观察 starter 多的话,也许你发已经发现了一个模式,Springboot 官方的 starter的名字都是 spring-boot-starter-xxxx命名的。
查看 spring-boot-starter-web 会发现,其实这个依赖只是一个空盒子,除了依赖其他 pom 之外,没有一行代码。
spring-boot-starter-web
这时,发现了另外一个模式:starter 只依赖其他 pom,不做代码实现。
那么 spring-boot-starter-web 到底依赖了哪些内容?
spring-boot-starter-web 的依赖
观察这个依赖信息,然后再参照其他的官方 starter ,可以找到几个固定的引入,可以被称之为模式的依赖引入。
- 依赖
spring-boot-starter。 - 依赖
spring-boot-autoconfigure。
2.2. 自动配置
引入依赖只有配置端口号,像这样。
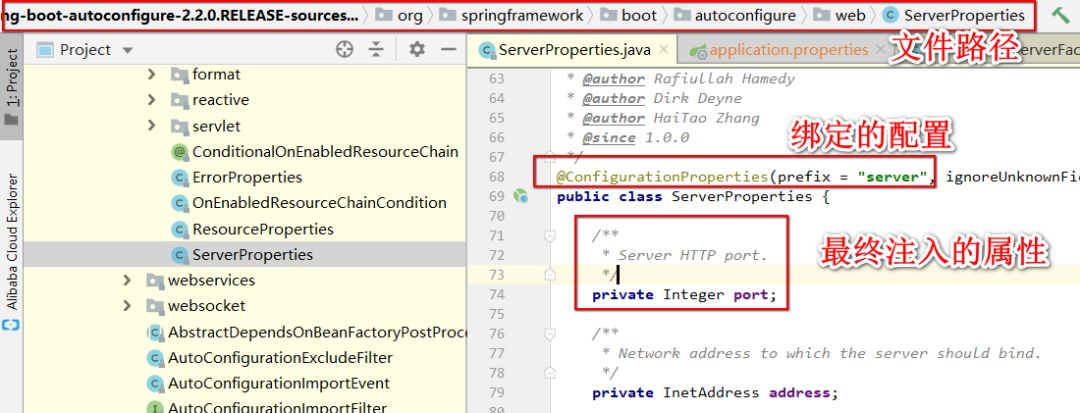
server.port=8090IDEA 中可以通过点击 server.port 找到这个配置绑定的类文件。可以看到配置最终会注入到类ServerProperties 类的 port 属性上。
Server 属性配置
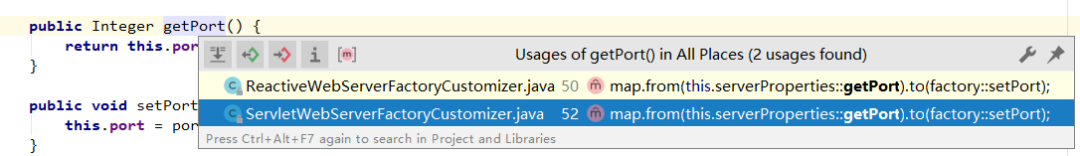
那么这个 ServerProperties 到底是哪里使用的呢?继续查找,找到一个和 Servlet 的有关的调用。
getPort 的调用
发现是被 ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer类进行了调用,这个类里面定义了
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;用来使用配置的属性。
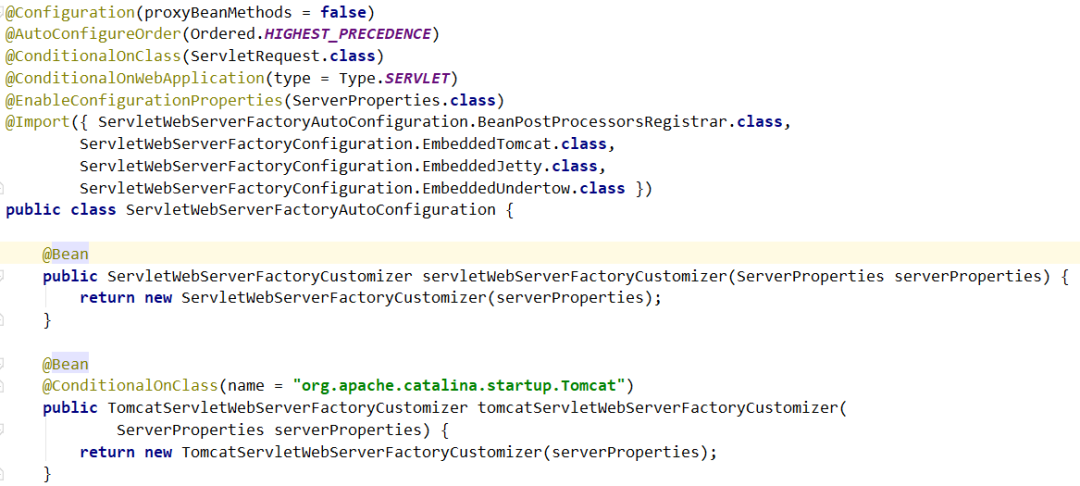
继续查看这个类的调用,发现只有一个类使用这个类,这个类是ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration。
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 类
根据我们对注解的理解,这个类就是自动配置主要类了。同时自动配置类都是以 AutoConfiguration 结尾。
看这个类的几个注解的意思。
1.优先级别较高。
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)2.只有在 ServletRequest 类存在和是 Web 应用时生效。
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)3.开启了 ServerProperties 的配置绑定。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)4.导入了几个类。 5.
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })同时注入配置到 Bean 工厂以供其他地方调用。
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer servletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}自动配置仅仅是这些东西吗?根据之前文章里的分析,我们知道不止代码,至少还有一个指定自动配置类的配置文件需要读取。也就是 spring.factories 文件。
spring.factories
如果你不知道,可以先看这篇文章。Springboot 系列(三)Spring Boot 自动配置 。
事实确实如此,可以在 spring.factories 中找到上面跟踪到的类。
也就是 ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.
根据上面的分析,可以发现 Springboot 官方 starter 的几个模式。
-
使用
XXXProperties自动绑定XXX开头的配置信息,如:ServerProperties。 -
把
XXXProperties定义到要使用的类中,如:ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer。 -
编写一个
XXXAutoConfiguration,开启XXXProperties的自动配置,限定生效场景,创建需要的类到Bean工厂。如:ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration。 -
第三方集成模式
Springboot 官方如果把所有的框架都编写成 starter,是不现实的。因此很多第三方框架需要主动集成到 springboot,所以我们选择一个常用的框架分析它的 starter 实现。因为已经看过了 springboot 官方 starter 是如何配置的, 第三方框架也是类似,所以在下面观察的过程中会直接指出相同点,而不再做对比详细对比。
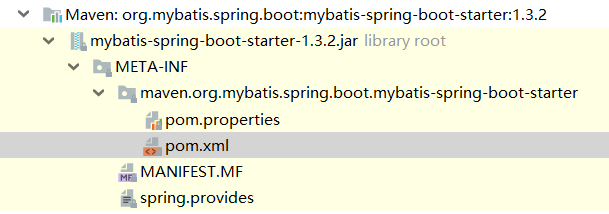
这里选择 mybatis-spring-boot-starter 进行学习分析。
3.1 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>这里 mybatis 框架的 starter 依赖符合一定的规则,即 xxx-spring-boot-starter.
观察这个 starter,发现它也没有做任何的代码实现,这一点和 springboot 官方一致。
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
查看 mybatis-spring-boot-starter 的依赖项,有很多,其中和自动配置有关的主要是。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>3.2 自动配置
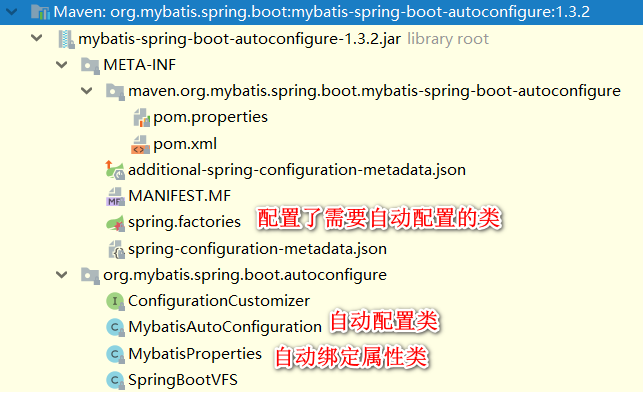
查看 mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure 的内容发现和 springboot 官方的 autoconfigure结构上是差不多的。
mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure
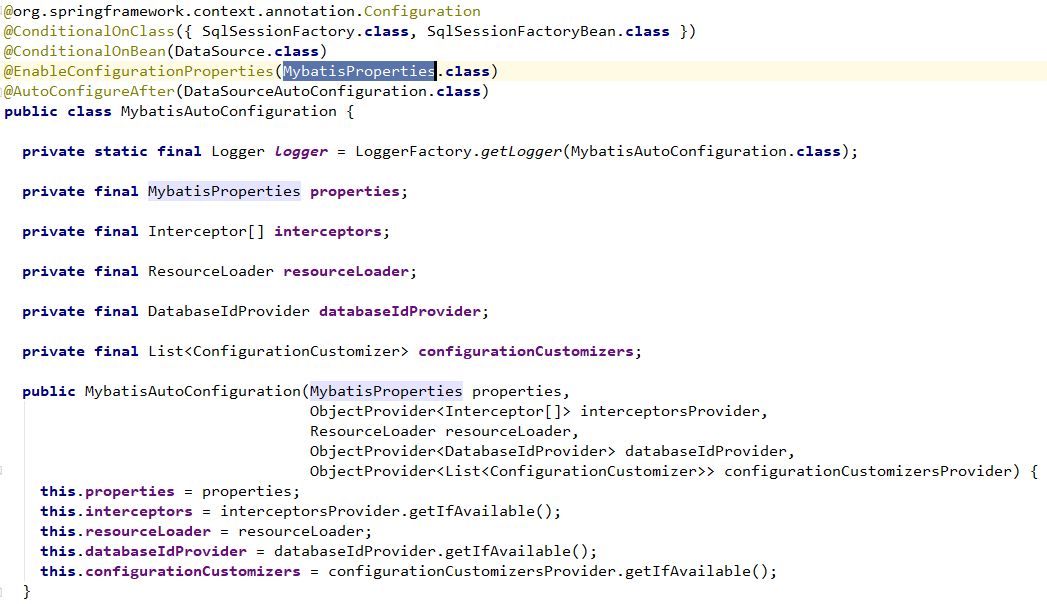
mybatis 的自动配置也是通过 spring.factories 来指明自动配置,然后通过 XxxAutoConfiguration 绑定 XxxProperties 来进行自动配置.
MybatisAutoConfiguration
在原理上,和上面 springboot 官方的 starter是相同的,所以不做过多的介绍了。
-
编写自己的 starter
说了那么多,终于到了实操环节,通过上面的介绍,我们可以大致得出编写自己的 starter步骤。
1. 创建名字为 xxx-spring-boot-starter 的启动器项目。
2. 创建名字为 xxx-spring-boot-autoconfigure的项目。
- 编写属性绑定类
xxxProperties. - 编写服务类,引入
xxxProperties. - 编写自动配置类
XXXAutoConfiguration注入配置。 - 创建
spring.factories文件,用于指定要自动配置的类。
3. 启动器项目为空项目,用来引入 xxx-spring-boot-autoconfigure等其他依赖。
4. 项目引入 starter,配置需要配置的信息。
4.1 创建启动器项目
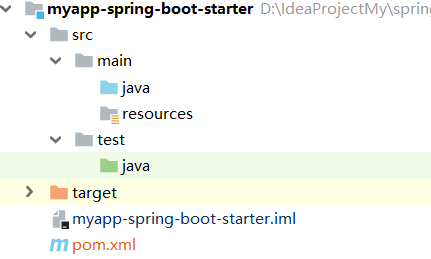
由于启动器不需要代码实现,只需要依赖其他项目,所以直接创建一个空的 maven 项目。但是名字要规范。
这里创建的 starter 是 myapp-spring-boot-starter。
myapp-spring-boot-starter
pom 文件非常简单,只需要引入接下来要创建的 myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>net.codingme.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- 启动器 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- 引入自动配置项目 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.codingme.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>4.2 创建自动配置项目
结合上面对 starter 的分析,直接创建一个名字为 myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure 的项目。项目中只引入 springboot 父项目以及 spring-boot-starter。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.codingme.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
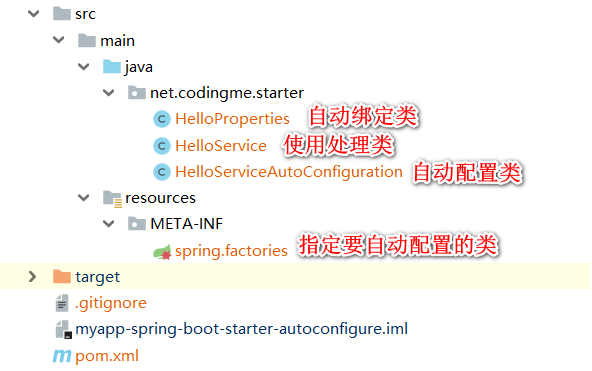
</project>项目的总体结构看图。
myapp-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure
在 HelloProperties中通过注解 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "myapp.hello")让类中的属性与 myapp.hello开头的配置进行绑定。
/**
* <p>
*
* @Author niujinpeng
* @Date 2019/10/29 23:51
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "myapp.hello")
public class HelloProperties {
private String suffix;
public String getSuffix() {
return suffix;
}
public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
this.suffix = suffix;
}
}然后在 HelloService中的 sayHello方法使用 HelloProperties 中自动绑定的值。
public class HelloService {
HelloProperties helloProperties;
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "Hello " + name + "," + helloProperties.getSuffix();
}
public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() {
return helloProperties;
}
public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) {
this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
}
}为了让 HelloService 可以自动注入且能正常使用 HelloProperties,所以我们在
HelloServiceAutoConfiguration 类中把 HelloProperties.class 引入,然后把 HelloService 注入到 Bean。
/**
* web应用才生效
*/
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
/**
* 让属性文件生效
*/
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
/***
* 声明是一个配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean
public HelloService helloService() {
HelloService helloService = new HelloService();
helloService.setHelloProperties(helloProperties);
return helloService;
}
}最后在 spring.factories中只需要指定要自动配置的类即可。
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
net.codingme.starter.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration到这里,自动配置项目就完成了。可以在 myapp-spring-boot-autoconfigure项目执行 mvn install 把自动配置项目打包到本地仓库,然后使用相同的命令把 myapp-spring-boot-starter 安装到仓库。因为后者依赖于前者项目,所以这里前者需要先进 mvn install。
4.3 使用自定义的启动器
创建一个 springboot项目myapp-spring-boot-starter-test。
myapp-spring-boot-starter-test
引入 web 依赖,引入自己编写的 myapp-spring-boot-starter.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入自己的 starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.codingme.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>编写一个 HelloController 注入自动配置里的 HelloService用于测试。
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(String name) {
return helloService.sayHello(name);
}
}由于 autoConfigure 项目中定义了 sayHello 方法会输出“Hello”+传入的 name + 配置的 hello.suffix,所以我们在 springboot 配置文件中配置这个属性。
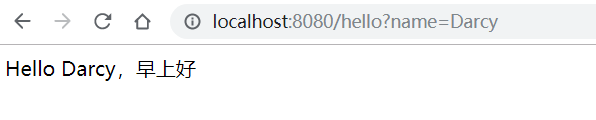
myapp.hello.suffix=早上好运行测试项目,访问 /hello 路径传入一个 name 看看自动配置有没有生效。
访问测试
从测试结果可以看到自动配置的早上好已经生效了。到这里自己编写的 starter也已经完工。
项目已经传到 Github. https://github.com/niumoo/springboot/tree/master/springboot-starter