Go 中的 WASM 很棒:全网最全示例教程
WASM 的概念,这几年还是挺火的,新的语言,比如 Rust、Go、Swift 等,都对 WASM 提供支持。相比之下,Go 语言的简单性,使得对 WASM 的支持,使用起来也较简单。本文是目前公开资料中为数不多较完整的教程,希望能对你有帮助。
01 WASM 是什么
标题说:“Golang 中的 Wasm 太棒了。”,但请用几句话来说“Wasm”是什么?
WebAssembly 主页说:“WebAssembly(缩写为 Wasm)是一种基于堆栈的虚拟机的二进制指令格式。Wasm 被设计为编程语言的可移植编译目标,支持在 Web 上部署客户端和服务器应用程序。”
总结就是:
- “Wasm 是一种可移植的格式(如 Java 或 .Net),你可以在任何有支持它的主机的地方执行它。最初,主要的主机是带有浏览器的 JavaScript”。
现在,你可以用 JavaScript 和 NodeJS 运行 Wasm,我们最近看到了像 Wasmer 项目这样的 Wasm 运行时的诞生,允许在任何地方运行 Wasm。
我喜欢说*“一个 wasm 文件就像一个容器镜像,但更小,没有操作系统”*。
02 Wasm 是多语言的,但是...
你可以用多种语言编译一个 Wasm 文件:C/C++、Rust、Golang、Swift ……我们甚至看到了专门用于构建 Wasm 的语言的出现,比如 AssemblyScript[1] 或有前途的 Grain[2](可以密切关注它,语法很可爱)。
今年夏天,我决定开始使用 Wasm。这种趋势似乎是使用 Rust,但我很快就明白我的小步骤会很复杂。困难不一定来自语言本身。最乏味和困难的部分是我在浏览器中运行一个简单的“Hello World”所需的所有工具。经过一番搜索,我发现 Golang 为 Wasm 提供了非常简单的支持(比 Rust 简单得多)。所以,我的假期作业是用 Golang 完成的。
Golang 对 Wasm 的支持非常棒。通常,WebAssembly 有四种数据类型(32 和 64 位整数,32 和 64 位浮点数),使用带有字符串参数(甚至 JSON 对象)的函数可能会很混乱。幸运的是,Go 提供了wasm_exec.js 与 JavaScript API 交互的文件。
03 先决条件
要运行此博客文章的示例,你需要:
- Golang 1.16
- TinyGo 0.19.0(注意:TinyGo 0.19.0 不适用于 GoLang 1.17)
- 为你的网页提供服务的 http 服务器
顺便说一句,为了提供我的页面,我使用带有以下代码的 Fastify[3] 项目:
index.js
const fastify = require('fastify')({ logger: true })
const path = require('path')
// Serve the static assets
fastify.register(require('fastify-static'), {
root: path.join(__dirname, ''),
prefix: '/'
})
const start = async () => {
try {
await fastify.listen(8080, "0.0.0.0")
fastify.log.info(`server listening on ${fastify.server.address().port}`)
} catch (error) {
fastify.log.error(error)
}
}
start()我使用这个package.json文件来安装 Fastify(使用npm install):
package.json
{
"dependencies": {
"fastify": "^3.6.0",
"fastify-static": "^3.2.1"
}
}我在这里创建了一个项目 https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo,如果你用 GitPod[4] 打开它,你会得到一个准备好的开发环境,你不需要安装任何东西。
04 必不可少的 “Hello World!”
创建一个项目
首先,创建一个hello-world目录,然后在该目录中创建 2 个文件:
main.goindex.html
使用以下源代码:
main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(" Hello World ")
// Prevent the function from returning, which is required in a wasm module
<-make(chan bool)
}index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<script src="wasm_exec.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>WASM Experiments</h1>
<script>
// This is a polyfill for FireFox and Safari
if (!WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming) {
WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming = async (resp, importObject) => {
const source = await (await resp).arrayBuffer()
return await WebAssembly.instantiate(source, importObject)
}
}
// Promise to load the wasm file
function loadWasm(path) {
const go = new Go()
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(fetch(path), go.importObject)
.then(result => {
go.run(result.instance)
resolve(result.instance)
})
.catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
}
// Load the wasm file
loadWasm("main.wasm").then(wasm => {
console.log("main.wasm is loaded ")
}).catch(error => {
console.log("ouch", error)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>备注:最重要的部分是:
- 这行代码
<script src="wasm_exec.js"></script>- 和这一行
WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming,它是允许加载 wasm 文件的 JavaScript API。
你还需要go.mod文件,使用以下命令生成一个:go mod init hello-world,它的内容如下:
module hello-world
go 1.16构建你的第一个 Wasm 模块
在构建 Wasm 模块之前,你需要获取wasm_exec.js文件,然后才能启动编译:
$ cp "$(go env GOROOT)/misc/wasm/wasm_exec.js" .
$ GOOS=js GOARCH=wasm go build -o main.wasm现在,使用命令 node index.js 为你的 html 页面提供服务,以运行 Fastify http 服务器,并使用你喜欢的浏览器打开 http://localhost:8080,然后打开开发人员控制台工具:
wasm experiments
所以,上手很简单,但是如果你查看 main.wasm 的大小,你会发现生成的文件大小在 2.1M 左右!!!老实说,我觉得这是不可接受的。幸运的是,使用 TinyGo 是一个较友好的解决方案。让我们看看。
source code: https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo/-/tree/main/01-hello-world
05 TinyGo 版的 “Hello World”
首先,什么是 TinyGo?TinyGo 允许为微控制器编译 Golang 源代码,它也可以将 Go 代码编译为 Wasm。TinyGo 是一个用于“小地方”的编译器,因此生成的文件要小得多。
将你的 hello-world 项目复制到一个新目录 hello-world-tinygo 并更改go.mod文件的内容:
module hello-world-tinygo
go 1.16在构建 Wasm 文件之前,这一次,你需要获取 wasm_exec.js 与 TinyGo 的相关信息,然后才能编译:
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tinygo-org/tinygo/v0.19.0/targets/wasm_exec.js
$ tinygo build -o main.wasm -target wasm ./main.go如果你提供 html 页面,你将获得与前一个示例相同的结果。但是看看 main.wasm 的大小。现在大小是 223K,小好多。
请记住,TinyGo 支持 Go 语言的一个子集,因此并非所有语言都可用(https://tinygo.org/docs/reference/lang-support/)。对于我的实验来说,这就足够了。
源代码:https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo/-/tree/main/02-hello-world-tinygo
06 我的私藏货
我看过太多冗长的教程,最终停留在这个简单的“hello world”上而没有进一步。他们甚至没有解释如何将参数传递给函数。通常,这只是项目“入门”的掩饰,没有后续深入的讲解。
今天,我给你分享所有让你对 WASM 理解更多的私藏货。
以下是我今天将介绍的 Wasm 和浏览器之间的不同交互:
- 与 DOM 交互
- 以字符串为参数调用 Golang 函数来获取字符串
- 如何通过 JavaScript 返回“可读”的对象?
- 如何使用 JSON 对象作为参数?
- 如何使用数组作为参数?
- 如何返回一个数组?
与 DOM 交互
我们将使用"syscall/js" 这个 Go 包从 Go 代码向 Html 文档对象模型添加子标签。根据文档:“使用 js/wasm 架构时,Package js 可以访问 WebAssembly 主机环境。它的 API 基于 JavaScript 语义。” . 这个包公开了一小组功能:类型 Value(Go JavaScript 数据表示)和从 JavaScript 主机请求 Go 的方式。
- 通过复制前一个目录创建一个新目录并命名为
dom - 更新
go.mod文件:
module dom
go 1.16只需更改以下代码 main.go:
package main
import (
"syscall/js"
)
func main() {
message := " Hello World "
document := js.Global().Get("document")
h2 := document.Call("createElement", "h2")
h2.Set("innerHTML", message)
document.Get("body").Call("appendChild", h2)
<-make(chan bool)
}编译代码:tinygo build -o main.wasm -target wasm ./main.go 并提供 html 页面 node index.js,然后打开 http://localhost:8080/。
- 我们得到了对 DOM 的引用
js.Global().Get("document") - 我们创建了 `
元素document.Call("createElement", "h2")` - 我们通过
h2.Set("innerHTML", message)来设置innerHTML的值 - 最后将元素添加到 body 中
document.Get("body").Call("appendChild", h2)
完整源码:https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo/-/tree/main/03-dom
现在,让我们看看如何创建一个可调用的 Go 函数,我们将在我们的 html 页面中使用它。
调用 Go 函数
这一次,我们需要将函数“导出”到全局上下文中(即浏览器中的 window,或 NodeJS 中的 global)。"syscall/js" 这个 Go 包再次提供了必要的帮助程序来做到这一点。
像往常一样,创建一个新目录 first-function(使用前面的示例)并通过 go.mod 更改模块的值来更新文件:module first-function。
这是的源代码main.go:
package main
import (
"syscall/js"
)
func Hello(this js.Value, args []js.Value) interface{} {
message := args[0].String() // get the parameters
return "Hello " + message
}
func main() {
js.Global().Set("Hello", js.FuncOf(Hello))
<-make(chan bool)
}- 为了导出函数到全局上下文,我们使用的
FuncOf函数:js.Global().Set("Hello", js.FuncOf(Hello))。该FuncOf函数用于创建Func类型。 - 该
Hello函数接受两个参数并返回一个interface{}类型。该函数将从 Javascript 同步调用。第一个参数 (this) 指的是 JavaScript 的global对象。第二个参数是[]js.Value表示传递给 Javascript 函数调用的参数的切片。
我们需要修改 index.html 文件来调用 Go 函数 Hello:
index.html:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<script src="wasm_exec.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>WASM Experiments</h1>
<script>
// polyfill
if (!WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming) {
WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming = async (resp, importObject) => {
const source = await (await resp).arrayBuffer()
return await WebAssembly.instantiate(source, importObject)
}
}
function loadWasm(path) {
const go = new Go()
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(fetch(path), go.importObject)
.then(result => {
go.run(result.instance)
resolve(result.instance)
})
.catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
}
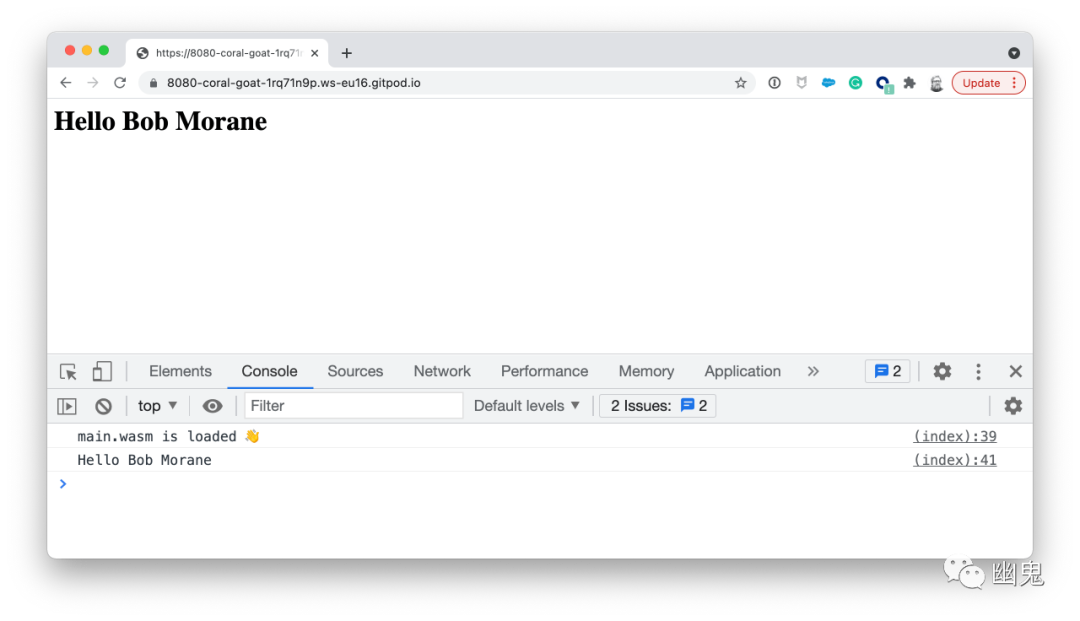
loadWasm("main.wasm").then(wasm => {
console.log("main.wasm is loaded ")
console.log(Hello("Bob Morane"))
document.querySelector("h1").innerHTML = Hello("Bob Morane")
}).catch(error => {
console.log("ouch", error)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>发生了什么变化?,只有这两行:
console.log(Hello("Bob Morane")):使用"Bob Morane"作为参数调用 Go 函数Hello并在浏览器控制台中显示结果。document.querySelector("h1").innerHTML = Hello("Bob Morane"):使用"Bob Morane"作为参数调用 Go 函数Hello并使用结果更改h1的值。
所以,
- 构建 Wasm 文件:
tinygo build -o main.wasm -target wasm ./main.go - 提供 html 页面:
node index.js
你可以看到页面内容已更新,但我们在控制台中有一些错误消息。不用担心,它很容易修复;这是一个已知错误 https://github.com/tinygo-org/tinygo/issues/1140,解决方法很简单:
function loadWasm(path) {
const go = new Go()
//remove the message: syscall/js.finalizeRef not implemented
go.importObject.env["syscall/js.finalizeRef"] = () => {}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(fetch(path), go.importObject)
.then(result => {
go.run(result.instance)
resolve(result.instance)
})
.catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
}- 我只添加了这一行
go.importObject.env["syscall/js.finalizeRef"] = () => {}以避免错误消息。
刷新页面,没有问题了。
现在,你几乎拥有深入 WASM 所需的一切。不过,我想把我的更多私藏货分享给你。
完整代码:https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo/-/tree/main/04-first-function
07 我的其他私藏货
如何通过 JavaScript 返回“可读”的对象?
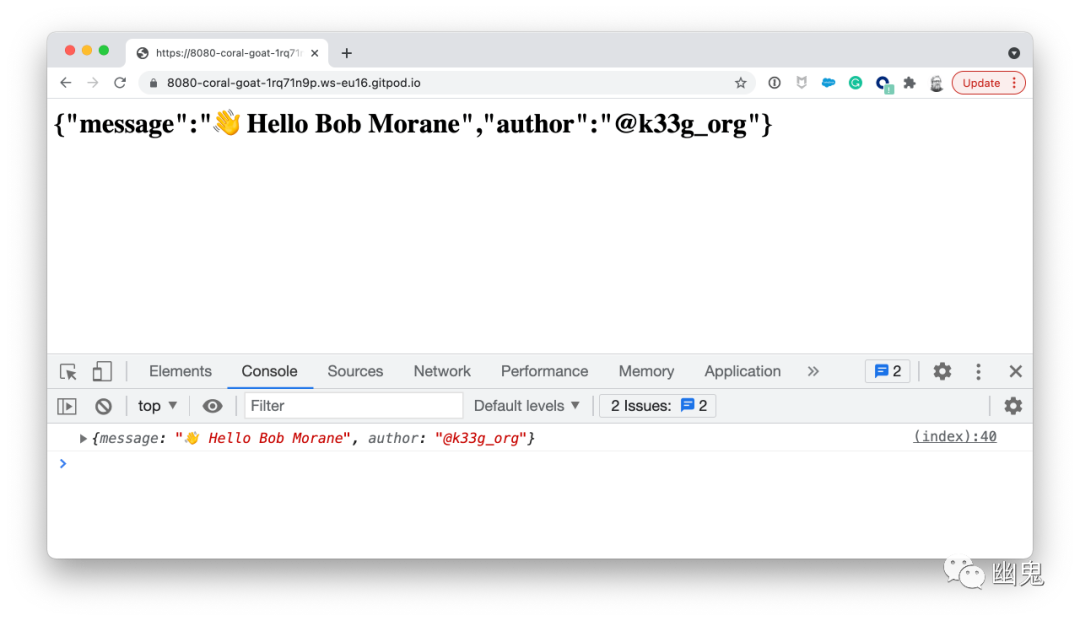
这一次,我们将 2 个字符串参数传递给 Hello 函数 ( firstName 和 lastName),并使用类型 map[string]interface{} 返回一个 json 对象 :
Golang 函数:
func Hello(this js.Value, args []js.Value) interface{} {
firstName := args[0].String()
lastName := args[1].String()
return map[string]interface{}{
"message": " Hello " + firstName + " " + lastName,
"author": "@k33g_org",
}
}从 JavaScript 调用 Hello 函数很简单:
loadWasm("main.wasm").then(wasm => {
let jsonData = Hello("Bob", "Morane")
console.log(jsonData)
document.querySelector("h1").innerHTML = JSON.stringify(jsonData)
}).catch(error => {
console.log("ouch", error)
})为你的页面提供服务 node index.js:
完整源码:https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo/-/tree/main/05-return-object
调用 Hello 时如何使用 Json 对象作为参数?
如果我想在 JavaScript 中使用 Json 对象作为参数,就像这样:
let jsonData = Hello({firstName: "Bob", lastName: "Morane"})
我会像这样写我的 Golang 函数:
func Hello(this js.Value, args []js.Value) interface{} {
// get an object
human := args[0]
// get members of an object
firstName := human.Get("firstName")
lastName := human.Get("lastName")
return map[string]interface{}{
"message": " Hello " + firstName.String() + " " + lastName.String(),
"author": "@k33g_org",
}
}args[0]包含 Json 对象- 使用
Get(field_name)方法检索字段的值
完整代码:https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo/-/tree/main/06-json-as-parameter
调用 Hello 时如何使用数组作为参数?
JavaScript 调用:
let jsonData = Hello(["Bob", "Morane", 42, 1.80])
Golang 函数:
func Hello(this js.Value, args []js.Value) interface{} {
// get members of an array
firstName := args[0].Index(0)
lastName := args[0].Index(1)
age := args[0].Index(2)
size := args[0].Index(3)
return map[string]interface{}{
"message": " Hello",
"firstName": firstName.String(),
"lastName": lastName.String(),
"age": age.Int(),
"size": size.Float(),
"author": "@k33g_org",
}
}完整代码:https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo/-/tree/main/07-array-as-parameter
如何返回一个数组?
Golang 函数:
func GiveMeNumbers(_ js.Value, args []js.Value) interface{} {
return []interface{} {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
}完整代码:https://gitlab.com/k33g_org/suborbital-demo/-/tree/main/08-return-an-array
就这些了吧。目前,我仍在学习 Wasm 和 Golang 的 Js 包,但我已经从中获得了一些乐趣。希望你也一样。
原文链接:https://blog.suborbital.dev/foundations-wasm-in-golang-is-fantastic
参考资料
[1]AssemblyScript: https://www.assemblyscript.org/
[2]Grain: https://grain-lang.org/
[3]Fastify: https://www.fastify.io/
[4]GitPod: https://www.gitpod.io/