初学者也能看懂的 Vue2 源码中那些实用的基础工具函数
1 . 前言
想学源码,极力推荐之前我写的[《学习源码整体架构系列》] 包含jQuery、underscore、lodash、vuex、sentry、axios、redux、koa、vue-devtools、vuex4、koa-compose、vue-next-release、vue-this、create-vue、玩具vite等10余篇源码文章。
最近组织了[源码共读活动] ,大家一起学习源码。于是搜寻各种值得我们学习,且代码行数不多的源码。
之前写了 Vue3 相关的两篇文章。
- [初学者也能看懂的 Vue3 源码中那些实用的基础工具函数]
这篇写了如何学习 JavaScript 基础知识,推荐了很多书籍和学习资料,还有我的一些经验分享。
- [Vue 3.2 发布了,那尤雨溪是怎么发布 Vue.js 的?]
参加[源码共读] 的读者反馈,TA 其实还是用着 Vue2。能不能写篇 Vue2 基础工具函数。作为一名知识博主卑微号主,本着学我所学,为我所用,帮助他人的宗旨,于是写上了这篇文章。算是 Vue3 工具函数的姐妹篇,本文和这篇文章会有类似的地方。
阅读本文,你将学到:
1. Vue2 源码 shared 模块中的几十个实用工具函数
2. 如何学习源码中优秀代码和思想,投入到自己的项目中
3. 如何学习 JavaScript 基础知识,会推荐很多学习资料
4. 我的一些经验分享
5. 等等2 . 环境准备
2.1 读开源项目 贡献指南
打开 vue 仓库[2], 开源项目一般都能在 README.md 或者 .github/contributing.md[3] 找到贡献指南。
而贡献指南写了很多关于参与项目开发的信息。比如怎么跑起来,项目目录结构是怎样的。怎么投入开发,需要哪些知识储备等。
我们可以在 项目目录结构[4] 描述中,找到shared模块。
shared: contains utilities shared across the entire codebase.
README.md 和 contributing.md 一般都是英文的。可能会难倒一部分人。其实看不懂,完全可以可以借助划词翻译,整页翻译和谷歌翻译等翻译工具。再把英文加入后续学习计划。
本文就是讲 shared 模块,对应的文件路径是:vue/vue/src/shared[5]。
也可以用github1s访问,速度更快。github1s vue/vue/src/shared[6]
2.2 为了降低文章难度,直接学习打包后的源码
源代码的代码vue/vue/src/shared[7],使用了Flow[8] 类型,可能不太好理解。
为了降低文章难度,我们直接学习源码仓库中的打包后的 dist/vue.js 14行到379行[9]。
当然,前面可能比较啰嗦。我可以直接讲
3. 工具函数。但通过我上文的介绍,即使是初学者,都能看懂一些开源项目源码,也许就会有一定的成就感。另外,面试问到被类似的问题或者笔试题时,你说看Vue2源码学到的,面试官绝对对你刮目相看。
3 . 工具函数
打包后的 vue.js 14行到379行[10],接下来就是解释其中的这些方法。
3.1 emptyObject
/*!
* Vue.js v2.6.14
* (c) 2014-2021 Evan You
* Released under the MIT License.
*/
/* */
var emptyObject = Object.freeze({});冻结对象。第一层无法修改。对象中也有判断是否冻结的方法。
Object.isFrozen(emptyObject); // true
关于对象 API 推荐看之前我的文章 JavaScript 对象所有API解析[11]
还可以看阮一峰老师的ES6 入门书籍 reflect[12]
3.2 isUndef 是否是未定义
// These helpers produce better VM code in JS engines due to their
// explicitness and function inlining.
function isUndef (v) {
return v === undefined || v === null
}3.3 isDef 是否是已经定义
JavaScript中假值有六个。
false
null
undefined
0
'' (空字符串)
NaN为了判断准确,Vue2 源码中封装了isDef、 isTrue、isFalse函数来准确判断。
见名知意。
function isDef (v) {
return v !== undefined && v !== null
}3.4 isTrue 是否是 true
见名知意。
function isTrue (v) {
return v === true
}3.5 isFalse 是否是 false
见名知意。
function isFalse (v) {
return v === false
}3.6 isPrimitive 判断值是否是原始值
判断是否是字符串、或者数字、或者 symbol、或者布尔值。
/**
* Check if value is primitive.
*/
function isPrimitive (value) {
return (
typeof value === 'string' ||
typeof value === 'number' ||
// $flow-disable-line
typeof value === 'symbol' ||
typeof value === 'boolean'
)
}3.7 isObject 判断是对象
因为 typeof null 是 'object'。数组等用这个函数判断也是 true
/**
* Quick object check - this is primarily used to tell
* Objects from primitive values when we know the value
* is a JSON-compliant type.
*/
function isObject (obj) {
return obj !== null && typeof obj === 'object'
}
// 例子:
isObject([]) // true
// 有时不需要严格区分数组和对象3.8 toRawType 转换成原始类型
Object.prototype.toString() 方法返回一个表示该对象的字符串。
mdn[13]
ecma 规范[14],说明了这些类型。
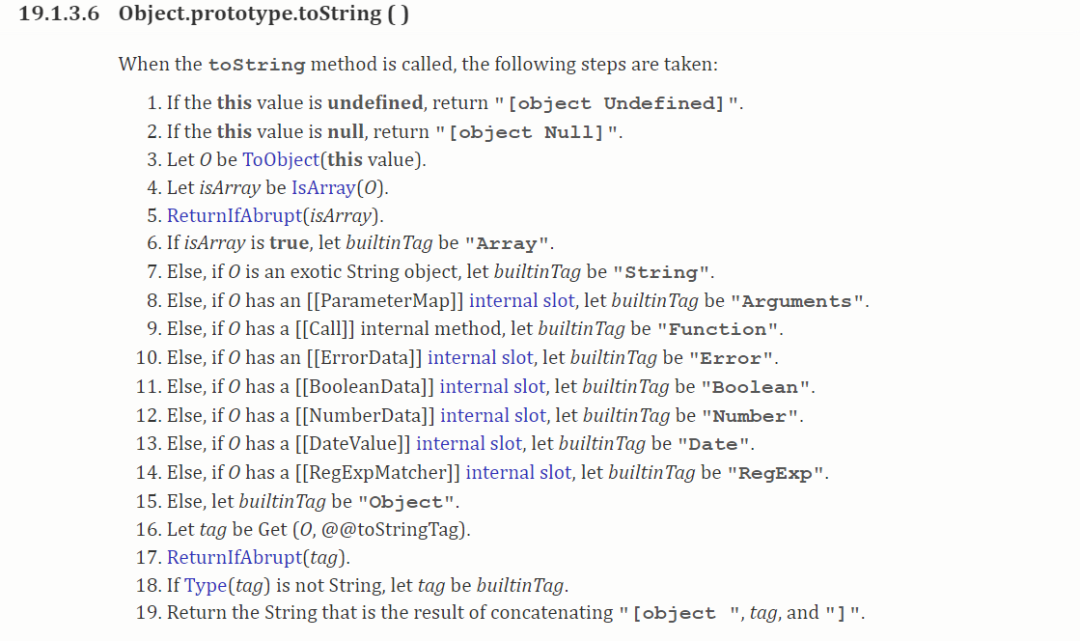
ECMAScript5.1 中文版[15]
/**
* Get the raw type string of a value, e.g., [object Object].
*/
var _toString = Object.prototype.toString;
function toRawType (value) {
return _toString.call(value).slice(8, -1)
}
// 例子:
toRawType('') // 'String'
toRawType() // 'Undefined'3.9 isPlainObject 是否是纯对象
/**
* Strict object type check. Only returns true
* for plain JavaScript objects.
*/
function isPlainObject (obj) {
return _toString.call(obj) === '[object Object]'
}
// 上文 isObject([]) 也是 true
// 这个就是判断对象是纯对象的方法。
// 例子:
isPlainObject([]) // false
isPlainObject({}) // true3.10 isRegExp 是否是正则表达式
function isRegExp (v) {
return _toString.call(v) === '[object RegExp]'
}
// 例子:
// 判断是不是正则表达式
isRegExp(/ruochuan/) // true3.11 isValidArrayIndex 是否是可用的数组索引值
数组可用的索引值是 0 ('0')、1 ('1') 、2 ('2') ...
/**
* Check if val is a valid array index.
*/
function isValidArrayIndex (val) {
var n = parseFloat(String(val));
return n >= 0 && Math.floor(n) === n && isFinite(val)
}该全局 isFinite() 函数用来判断被传入的参数值是否为一个有限数值(finite number)。在必要情况下,参数会首先转为一个数值。
isFinite mdn[16]
isFinite(Infinity); // false
isFinite(NaN); // false
isFinite(-Infinity); // false
isFinite(0); // true
isFinite(2e64); // true, 在更强壮的Number.isFinite(null)中将会得到false
isFinite('0'); // true, 在更强壮的Number.isFinite('0')中将会得到false3.12 isPromise 判断是否是 promise
function isPromise (val) {
return (
isDef(val) &&
typeof val.then === 'function' &&
typeof val.catch === 'function'
)
}
// 例子:
isPromise(new Promise()) // true这里用 isDef 判断其实相对 isObject 来判断 来说有点不严谨。但是够用。
3.13 toString 转字符串
转换成字符串。是数组或者对象并且对象的 toString 方法是 Object.prototype.toString,用 JSON.stringify 转换。
/**
* Convert a value to a string that is actually rendered.
*/
function toString (val) {
return val == null
? ''
: Array.isArray(val) || (isPlainObject(val) && val.toString === _toString)
? JSON.stringify(val, null, 2)
: String(val)
}3.14 toNumber 转数字
转换成数字。如果转换失败依旧返回原始字符串。
/**
* Convert an input value to a number for persistence.
* If the conversion fails, return original string.
*/
function toNumber (val) {
var n = parseFloat(val);
return isNaN(n) ? val : n
}
toNumber('a') // 'a'
toNumber('1') // 1
toNumber('1a') // 1
toNumber('a1') // 'a1'3.15 makeMap 生成一个 map (对象)
传入一个以逗号分隔的字符串,生成一个 map(键值对),并且返回一个函数检测 key 值在不在这个 map 中。第二个参数是小写选项。
/**
* Make a map and return a function for checking if a key
* is in that map.
*/
function makeMap (
str,
expectsLowerCase
) {
var map = Object.create(null);
var list = str.split(',');
for (var i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
map[list[i]] = true;
}
return expectsLowerCase
? function (val) { return map[val.toLowerCase()]; }
: function (val) { return map[val]; }
}
// Object.create(null) 没有原型链的空对象3.16 isBuiltInTag 是否是内置的 tag
/**
* Check if a tag is a built-in tag.
*/
var isBuiltInTag = makeMap('slot,component', true);
// 返回的函数,第二个参数不区分大小写
isBuiltInTag('slot') // true
isBuiltInTag('component') // true
isBuiltInTag('Slot') // true
isBuiltInTag('Component') // true3.17 isReservedAttribute 是否是保留的属性
/**
* Check if an attribute is a reserved attribute.
*/
var isReservedAttribute = makeMap('key,ref,slot,slot-scope,is');
isReservedAttribute('key') // true
isReservedAttribute('ref') // true
isReservedAttribute('slot') // true
isReservedAttribute('slot-scope') // true
isReservedAttribute('is') // true
isReservedAttribute('IS') // undefined3.18 remove 移除数组中的中一项
/**
* Remove an item from an array.
*/
function remove (arr, item) {
if (arr.length) {
var index = arr.indexOf(item);
if (index > -1) {
return arr.splice(index, 1)
}
}
}splice 其实是一个很耗性能的方法。删除数组中的一项,其他元素都要移动位置。
引申:axios InterceptorManager 拦截器源码[17] 中,拦截器用数组存储的。但实际移除拦截器时,只是把拦截器置为 null 。而不是用splice移除。最后执行时为 null 的不执行,同样效果。axios 拦截器这个场景下,不得不说为性能做到了很好的考虑。因为拦截器是用户自定义的,理论上可以有无数个,所以做性能考虑是必要的。
看如下 axios 拦截器代码示例:
// 代码有删减
// 声明
this.handlers = [];
// 移除
if (this.handlers[id]) {
this.handlers[id] = null;
}
// 执行
if (h !== null) {
fn(h);
}3.19 hasOwn 检测是否是自己的属性
/**
* Check whether an object has the property.
*/
var hasOwnProperty = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty;
function hasOwn (obj, key) {
return hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)
}
// 例子:
// 特别提醒:__proto__ 是浏览器实现的原型写法,后面还会用到
// 现在已经有提供好几个原型相关的API
// Object.getPrototypeOf
// Object.setPrototypeOf
// Object.isPrototypeOf
// .call 则是函数里 this 显示指定以为第一个参数,并执行函数。
hasOwn({__proto__: { a: 1 }}, 'a') // false
hasOwn({ a: undefined }, 'a') // true
hasOwn({}, 'a') // false
hasOwn({}, 'hasOwnProperty') // false
hasOwn({}, 'toString') // false
// 是自己的本身拥有的属性,不是通过原型链向上查找的。3.20 cached 缓存
利用闭包特性,缓存数据
/**
* Create a cached version of a pure function.
*/
function cached (fn) {
var cache = Object.create(null);
return (function cachedFn (str) {
var hit = cache[str];
return hit || (cache[str] = fn(str))
})
}
系统学习正则推荐老姚:《JavaScript 正则表达式迷你书》问世了![18],看过的都说好。所以本文不会很详细的描述正则相关知识点。
3.21 camelize 连字符转小驼峰
连字符 - 转驼峰 on-click => onClick
/**
* Camelize a hyphen-delimited string.
*/
var camelizeRE = /-(\w)/g;
var camelize = cached(function (str) {
return str.replace(camelizeRE, function (_, c) { return c ? c.toUpperCase() : ''; })
});3.22 capitalize 首字母转大写
首字母转大写
/**
* Capitalize a string.
*/
var capitalize = cached(function (str) {
return str.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + str.slice(1)
});3.23 hyphenate 小驼峰转连字符
onClick => on-click
/**
* Hyphenate a camelCase string.
*/
var hyphenateRE = /\B([A-Z])/g;
var hyphenate = cached(function (str) {
return str.replace(hyphenateRE, '-$1').toLowerCase()
});3.24 polyfillBind bind 的垫片
/**
* Simple bind polyfill for environments that do not support it,
* e.g., PhantomJS 1.x. Technically, we don't need this anymore
* since native bind is now performant enough in most browsers.
* But removing it would mean breaking code that was able to run in
* PhantomJS 1.x, so this must be kept for backward compatibility.
*/
/* istanbul ignore next */
function polyfillBind (fn, ctx) {
function boundFn (a) {
var l = arguments.length;
return l
? l > 1
? fn.apply(ctx, arguments)
: fn.call(ctx, a)
: fn.call(ctx)
}
boundFn._length = fn.length;
return boundFn
}
function nativeBind (fn, ctx) {
return fn.bind(ctx)
}
var bind = Function.prototype.bind
? nativeBind
: polyfillBind;简单来说就是兼容了老版本浏览器不支持原生的 bind 函数。同时兼容写法,对参数的多少做出了判断,使用call和apply实现,据说参数多适合用 apply,少用 call 性能更好。
如果对于call、apply、bind的用法和实现不熟悉,可以查看我在[面试官问系列] 中写的[面试官问:能否模拟实现JS的call和apply方法] [面试官问:能否模拟实现JS的bind方法]
3.25 toArray 把类数组转成真正的数组
把类数组转换成数组,支持从哪个位置开始,默认从 0 开始。
/**
* Convert an Array-like object to a real Array.
*/
function toArray (list, start) {
start = start || 0;
var i = list.length - start;
var ret = new Array(i);
while (i--) {
ret[i] = list[i + start];
}
return ret
}
// 例子:
function fn(){
var arr1 = toArray(arguments);
console.log(arr1); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
var arr2 = toArray(arguments, 2);
console.log(arr2); // [3, 4, 5]
}
fn(1,2,3,4,5);3.26 extend 合并
/**
* Mix properties into target object.
*/
function extend (to, _from) {
for (var key in _from) {
to[key] = _from[key];
}
return to
}
// 例子:
const data = { name: '若川' };
const data2 = extend(data, { mp: '若川视野', name: '是若川啊' });
console.log(data); // { name: "是若川啊", mp: "若川视野" }
console.log(data2); // { name: "是若川啊", mp: "若川视野" }
console.log(data === data2); // true3.27 toObject 转对象
/**
* Merge an Array of Objects into a single Object.
*/
function toObject (arr) {
var res = {};
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i]) {
extend(res, arr[i]);
}
}
return res
}
// 数组转对象
toObject(['若川', '若川视野'])
// {0: '若', 1: '川', 2: '视', 3: '野'}3.28 noop 空函数
/* eslint-disable no-unused-vars */
/**
* Perform no operation.
* Stubbing args to make Flow happy without leaving useless transpiled code
* with ...rest (https://flow.org/blog/2017/05/07/Strict-Function-Call-Arity/).
*/
function noop (a, b, c) {}
// 初始化赋值3.29 no 一直返回 false
/**
* Always return false.
*/
var no = function (a, b, c) { return false; };
/* eslint-enable no-unused-vars */3.30 identity 返回参数本身
/**
* Return the same value.
*/
var identity = function (_) { return _; };3.31 genStaticKeys 生成静态属性
/**
* Generate a string containing static keys from compiler modules.
*/
function genStaticKeys (modules) {
return modules.reduce(function (keys, m) {
return keys.concat(m.staticKeys || [])
}, []).join(',')
}3.32 looseEqual 宽松相等
由于数组、对象等是引用类型,所以两个内容看起来相等,严格相等都是不相等。
var a = {};
var b = {};
a === b; // false
a == b; // false所以该函数是对数组、日期、对象进行递归比对。如果内容完全相等则宽松相等。
/**
* Check if two values are loosely equal - that is,
* if they are plain objects, do they have the same shape?
*/
function looseEqual (a, b) {
if (a === b) { return true }
var isObjectA = isObject(a);
var isObjectB = isObject(b);
if (isObjectA && isObjectB) {
try {
var isArrayA = Array.isArray(a);
var isArrayB = Array.isArray(b);
if (isArrayA && isArrayB) {
return a.length === b.length && a.every(function (e, i) {
return looseEqual(e, b[i])
})
} else if (a instanceof Date && b instanceof Date) {
return a.getTime() === b.getTime()
} else if (!isArrayA && !isArrayB) {
var keysA = Object.keys(a);
var keysB = Object.keys(b);
return keysA.length === keysB.length && keysA.every(function (key) {
return looseEqual(a[key], b[key])
})
} else {
/* istanbul ignore next */
return false
}
} catch (e) {
/* istanbul ignore next */
return false
}
} else if (!isObjectA && !isObjectB) {
return String(a) === String(b)
} else {
return false
}
}3.33 looseIndexOf 宽松的 indexOf
该函数实现的是宽松相等。原生的 indexOf 是严格相等。
/**
* Return the first index at which a loosely equal value can be
* found in the array (if value is a plain object, the array must
* contain an object of the same shape), or -1 if it is not present.
*/
function looseIndexOf (arr, val) {
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (looseEqual(arr[i], val)) { return i }
}
return -1
}3.34 once 确保函数只执行一次
利用闭包特性,存储状态
/**
* Ensure a function is called only once.
*/
function once (fn) {
var called = false;
return function () {
if (!called) {
called = true;
fn.apply(this, arguments);
}
}
}
const fn1 = once(function(){
console.log('哎嘿,无论你怎么调用,我只执行一次');
});
fn1(); // '哎嘿,无论你怎么调用,我只执行一次'
fn1(); // 不输出
fn1(); // 不输出
fn1(); // 不输出3.35 生命周期等
var SSR_ATTR = 'data-server-rendered';
var ASSET_TYPES = [
'component',
'directive',
'filter'
];
[Vue 生命周期](https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#%E9%80%89%E9%A1%B9-%E7%94%9F%E5%91%BD%E5%91%A8%E6%9C%9F%E9%92%A9%E5%AD%90 "Vue 生命周期")
var LIFECYCLE_HOOKS = [
'beforeCreate',
'created',
'beforeMount',
'mounted',
'beforeUpdate',
'updated',
'beforeDestroy',
'destroyed',
'activated',
'deactivated',
'errorCaptured',
'serverPrefetch'
];4 . 最后推荐一些文章和书籍
这部分和Vue3工具函数文章一样,值得推荐,所以复制到这里。
先推荐我认为不错的JavaScript API的几篇文章和几本值得读的书。
JavaScript字符串所有API全解密[19]
【深度长文】JavaScript数组所有API全解密[20]
正则表达式前端使用手册[21]
老姚:《JavaScript 正则表达式迷你书》问世了![22]
[老姚浅谈:怎么学JavaScript?]
[JavaScript 对象所有API解析] https://lxchuan12.gitee.io/js-object-api/
MDN JavaScript[23]
《JavaScript高级程序设计》第4版[24]
《JavaScript 权威指南》第7版[25]
《JavaScript面向对象编程2》[26] 面向对象讲的很详细。
阮一峰老师:《ES6 入门教程》[27]
《现代 JavaScript 教程》[28]
《你不知道的JavaScript》上中卷[29]
《JavaScript 设计模式与开发实践》[30]
我也是从小白看不懂书经历过来的。到现在写文章分享。
我看书的方法:多本书同时看,看相同类似的章节,比如函数。看完这本可能没懂,看下一本,几本书看下来基本就懂了,一遍没看懂,再看几遍,可以避免遗忘,巩固相关章节。当然,刚开始看书很难受,看不进。这些书大部分在微信读书都有,如果习惯看纸质书,那可以买来看。
这时可以看些视频和动手练习一些简单的项目。
比如:可以自己注册一个github账号,分章节小节,抄写书中的代码,提交到github,练习了才会更有感觉。
再比如 freeCodeCamp 中文在线学习网站[31] 网站。看书是系统学习非常好的方法。后来我就是看源码较多,写文章分享出来给大家。
5 . 总结
本文通过查看 Vue2 源码中 shared 模块打包后的 dist/vue.js 14行到379行[32]。源码也不是那么难,至少很多能看懂,比如工具函数。难可能是难在:不知道应用场景。
Vue2 工具函数命名很规范,比如:is 判断,to 转换,has 是否有,让开发者一眼就能看出函数语意。
这些函数也非常单一,基本一个函数只做一件事。
建议读者朋友把不熟悉的函数,动手写写,有助于巩固基础知识,查漏补缺。
参考资料
[1]本文仓库 vue-analysis,求个star^_^: https://github.com/lxchuan12/vue-analysis.git
[2]vue 仓库: https://github.com/vuejs/vue
[3]更多参考资料可以点击阅读原文查看