Vue 的这些技巧你真的都掌握了吗?
前言
文章目的昭然若揭,整理汇总 Vue 框架中重要的特性、框架的原理。
那 "前车之鉴" 从何而来?
是的,我又要讲小故事了,但这次是故事的续集。
故事第 1 集:CSS预处理器,你还是只会嵌套么 ?[2] 故事第 2 集:【自适应】px 转 rem,你还在手算么?[3]
为什么说是续集,因为这些都是同一大佬问的,在此感谢大佬,天降素材。
故事续集
大佬:有看过 Vue 源码么?
我:嗯嗯,看过。
大佬:那大概讲一讲 nextTick 的底层实现 ?
我:停顿了大概10s,说了句忘了。(理不直气还壮)
大佬:噢噢,没事。(内心大概已经放弃对我知识面的挖掘)
因为是视频面试,强装自信的尴尬从屏幕中溢出,这大概就是普通且自信♂️?装X失败案例引以为戒,能写出续集的面试结果不提也罢。
这次面试打击还是蛮大的,考察内容全面且细节。面试后一直在整理 Vue 相关的知识点,所以不会将nextTick实现单独成文,只是收录在下方试题中。前车之鉴可以为鉴,大家可以把本篇文章当测验,考察自己是否对这些知识点熟练于心。
万字长文,持续更新,若有遗漏知识点,后续会补充。
题目
Vue 的优缺点
优点
- 创建单页面应用的轻量级Web应用框架
- 简单易用
- 双向数据绑定
- 组件化的思想
- 虚拟DOM
- 数据驱动视图
缺点
不支持IE8(现阶段只能勉强凑出这么半点)
SPA 的理解
SPA是Single-Page-Application的缩写,翻译过来就是单页应用。在WEB页面初始化时一同加载Html、Javascript、Css。一旦页面加载完成,SPA不会因为用户操作而进行页面重新加载或跳转,取而代之的是利用路由机制实现Html内容的变换。
优点
- 良好的用户体验,内容更改无需重载页面。
- 基于上面一点,SPA相对服务端压力更小。
- 前后端职责分离,架构清晰。
缺点
- 由于单页WEB应用,需在加载渲染页面时请求JavaScript、Css文件,所以耗时更多。
- 由于前端渲染,搜索引擎不会解析JS,只能抓取首页未渲染的模板,不利于SEO。
- 由于单页应用需在一个页面显示所有的内容,默认不支持浏览器的前进后退。
缺点3,想必有人和我有同样的疑问。
通过资料查阅,其实是前端路由机制解决了单页应用无法前进后退的问题。Hash模式中Hash变化会被浏览器记录(onhashchange事件),History模式利用 H5 新增的pushState和replaceState方法可改变浏览器历史记录栈。
new Vue(options) 都做了些什么
如下 Vue 构造函数所示,主要执行了 this._init(options)方法,该方法在initMixin函数中注册。
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
import { warn } from '../util/index'
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
// Vue.prototype._init 方法
this._init(options)
}
// _init 方法在 initMixin 注册
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
复制代码查看initMixin方法的实现,其他函数具体实现可自行查看,这里就不贴出了。
let uid = 0
export function initMixin() {
Vue.prototype._init = function(options) {
const vm = this
vm._uid = uid++
vm._isVue = true
// 处理组件配置项
if (options && options._isComponent) {
/**
* 如果是子组件,走当前 if 分支
* 函数作用是性能优化:将原型链上的方法都放到vm.$options中,减少原型链上的访问
*/
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
/**
* 如果是根组件,走当前 else 分支
* 合并 Vue 的全局配置到根组件中,如 Vue.component 注册的全局组件合并到根组件的 components 的选项中
* 子组件的选项合并发生在两个地方
* 1. Vue.component 方法注册的全局组件在注册时做了选项合并
* 2. { component: {xx} } 方法注册的局部组件在执行编译器生成的 render 函数时做了选项合并
*/
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
vm._self = vm
/**
* 初始化组件实例关系属性,如:$parent $root $children $refs
*/
initLifecycle(vm)
/**
* 初始化自定义事件
* <component @click="handleClick"></component>
* 组件上注册的事件,监听者不是父组件,而是子组件本身
*/
initEvents(vm)
/**
* 解析组件插槽信息,得到vm.$slot,处理渲染函数,得到 vm.$createElement 方法,即 h 函数。
*/
initRender(vm)
/**
* 执行 beforeCreate 生命周期函数
*/
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
/**
* 解析 inject 配置项,得到 result[key] = val 的配置对象,做响应式处理且代理到 vm 实力上
*/
initInjections(vm)
/**
* 响应式处理核心,处理 props、methods、data、computed、watch
*/
initState(vm)
/**
* 解析 provide 对象,并挂载到 vm 实例上
*/
initProvide(vm)
/**
* 执行 created 生命周期函数
*/
callHook(vm, 'created')
// 如果 el 选项,自动执行$mount
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}
复制代码MVVM 的理解
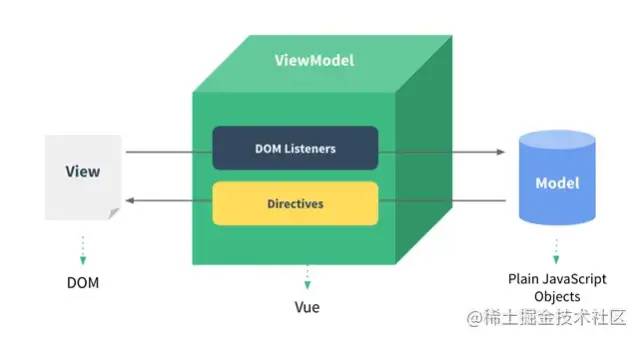
MVVM是Model-View-ViewModel的缩写。Model 代表数据层,可定义修改数据、编写业务逻辑。View 代表视图层,负责将数据渲染成页面。ViewModel 负责监听数据层数据变化,控制视图层行为交互,简单讲,就是同步数据层和视图层的对象。ViewModel 通过双向绑定把 View 和 Model 层连接起来,且同步工作无需人为干涉,使开发人员只关注业务逻辑,无需频繁操作DOM,不需关注数据状态的同步问题。
如何实现 v-model
v-model指令用于实现input、select等表单元素的双向绑定,是个语法糖。
原生 input 元素若是text/textarea类型,使用 value 属性和 input 事件。
原生 input 元素若是radio/checkbox类型,使用 checked属性和 change 事件。
原生 select 元素,使用 value 属性和 change 事件。
input 元素上使用 v-model 等价于
<input :value="message" @input="message = $event.target.value" />
复制代码实现自定义组件的 v-model
自定义组件的v-model使用prop值为value和input事件。若是radio/checkbox类型,需要使用model来解决原生 DOM 使用的是 checked 属性 和 change 事件,如下所示。
// 父组件
<template>
<base-checkbox v-model="baseCheck" />
</template>
复制代码// 子组件
<template>
<input type="checkbox" :checked="checked" @change="$emit('change', $event.target.checked)" />
</template>
<script>
export default {
model: {
prop: 'checked',
event: 'change'
},
prop: {
checked: Boolean
}
}
</script>
复制代码如何理解 Vue 单向数据流
Vue 官方文档 Prop 菜单下的有个名为单项数据流的子菜单。

我们经常说 Vue 的双向绑定,其实是在单向绑定的基础上给元素添加 input/change 事件,来动态修改视图。Vue 组件间传递数据仍然是单项的,即父组件传递到子组件。子组件内部可以定义依赖 props 中的值,但无权修改父组件传递的数据,这样做防止子组件意外变更父组件的状态,导致应用数据流向难以理解。
如果在子组件内部直接更改prop,会遇到警告处理。
2 种定义依赖 props 中的值
1 . 通过 data 定义属性并将 prop 作为初始值。
<script>
export default {
props: ['initialNumber'],
data() {
return {
number: this.initailNumber
}
}
}
</script>
复制代码2 . 用 computed 计算属性去定义依赖 prop 的值。若页面会更改当前值,得分 get 和 set 方法。
<script>
export default {
props: ['size'],
computed: {
normalizedSize() {
return this.size.trim().toLowerCase()
}
}
}
</sciprt>
复制代码Vue 响应式原理
核心源码位置:vue/src/core/observer/index.js
响应式原理3个步骤:数据劫持、依赖收集、派发更新。
数据分为两类:对象、数组。
对象
遍历对象,通过Object.defineProperty为每个属性添加 getter 和 setter,进行数据劫持。getter 函数用于在数据读取时进行依赖收集,在对应的 dep 中存储所有的 watcher;setter 则是数据更新后通知所有的 watcher 进行更新。
核心源码
function defineReactive(obj, key, val, shallow) {
// 实例化一个 dep, 一个 key 对应一个 dep
const dep = new Dep()
// 获取属性描述符
const getter = property && property.get
const setter = property && property.set
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
// 通过递归的方式处理 val 为对象的情况,即处理嵌套对象
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
// 拦截obj.key,进行依赖收集
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
// Dep.target 是当前组件渲染的 watcher
if (Dep.target) {
// 将 dep 添加到 watcher 中
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
// 嵌套对象依赖收集
childOb.dep.depend()
// 响应式处理 value 值为数组的情况
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
// 获取旧值
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
// 判断新旧值是否一致
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
if (getter && !setter) return
// 如果是新值,用新值替换旧值
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
// 新值做响应式处理
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
// 当响应式数据更新,依赖通知更新
dep.notify()
}
})
}
复制代码数组
用数组增强的方式,覆盖原属性上默认的数组方法,保证在新增或删除数据时,通过 dep 通知所有的 watcher 进行更新。
核心源码
const arrayProto = Array.prototype
// 基于数组原型对象创建一个新的对象
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto)
const methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
]
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
const original = arrayProto[method]
// 分别在 arrayMethods 对象上定义7个方法
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator (...args) {
// 先执行原生的方法
const result = original.apply(this, args)
const ob = this.__ob__
let inserted
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2)
break
}
// 针对新增元素进行响应式处理
if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted)
// 数据无论是新增还是删除都进行派发更新
ob.dep.notify()
return result
})
})
复制代码
手写观察者模式
当对象间存在一对多的关系,使用观察者模式。比如:当一个对象被修改,会自动通知依赖它的对象。
let uid = 0
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.id = uid++
// 存储所有的 watcher
this.subs = []
}
addSub(sub) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
removeSub(sub) {
if(this.subs.length) {
const index = this.subs.indexOf(sub)
if(index > -1) return this.subs.splice(index, 1)
}
}
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update()
})
}
}
class Watcher {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
update() {
console.log('更新')
}
}
复制代码手写发布订阅模式
与观察者模式相似,区别在于发布者和订阅者是解耦的,由中间的调度中心去与发布者和订阅者通信。
Vue响应式原理个人更倾向于发布订阅模式。其中 Observer 是发布者,Watcher 是订阅者,Dep 是调度中心。
vue中数据绑定原理的设计模式到底观察者还是发布订阅?[4],知乎有相关争论,感兴趣的可以看下。
class EventEmitter {
constructor() {
this.events = {}
}
on(type, cb) {
if(!this.events[type]) this.events[type] = []
this.events[type].push(cb)
}
emit(type, ...args) {
if(this.events[type]) {
this.events[type].forEach(cb => {
cb(...args)
})
}
}
off(type, cb) {
if(this.events[type]) {
const index = this.events[type].indexOf(cb)
if(index > -1) this.events[type].splice(index, 1)
}
}
}
复制代码关于 Vue.observable 的了解
Vue.observable 可使对象可响应。返回的对象可直接用于渲染函数和计算属性内,并且在发生变更时触发相应的更新。也可以作为最小化的跨组件状态存储器。
Vue 2.x 中传入的对象和返回的对象是同一个对象。 Vue 3.x 则不是一个对象,源对象不具备响应式功能。
适用的场景:在项目中没有大量的非父子组件通信时,可以使用 Vue.observable 去替代 eventBus和vuex方案。
用法如下
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
export const state = Vue.observable({
count: 1
})
export const mutations = {
setCount(count) {
state.count = count
}
}
// vue 文件
<template>
<div>{{ count }}</div>
</template>
<script>
import { state, mutation } from './store.js'
export default {
computed: {
count() {
return state.count
}
}
}
</script>
复制代码原理部分和响应式原理处理组件 data 是同一个函数,实例化一个 Observe,对数据劫持。
组件中的 data 为什么是个函数
对象在栈中存储的都是地址,函数的作用就是属性私有化,保证组件修改自身属性时不会影响其他复用组件。
Vue 生命周期
| 生命周期 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| beforeCreate | vue实例初始化后,数据观测(data observer)和事件配置之前。data、computed、watch、methods都无法访问。 |
| created | vue实例创建完成后立即调用 ,可访问 data、computed、watch、methods。未挂载 DOM,不能访问 、ref。 |
| beforeMount | 在 DOM 挂载开始之前调用。 |
| mounted | vue实例被挂载到 DOM。 |
| beforeUpdate | 数据更新之前调用,发生在虚拟 DOM 打补丁之前。 |
| updated | 数据更新之后调用。 |
| beforeDestroy | 实例销毁前调用。 |
| destroyed | 实例销毁后调用 。 |
调用异步请求可在created、beforeMount、mounted生命周期中调用,因为相关数据都已创建。最好的选择是在created中调用。
获取DOM在mounted中获取,获取可用$ref方法,这点毋庸置疑。
Vue 父组件和子组件生命周期执行顺序
加载渲染过程
父先创建,才能有子;子创建完成,父才完整。
顺序:父 beforeCreate -> 父 created -> 父 beforeMount -> 子 beforeCreate -> 子 created -> 子 beforeMount -> 子 mounted -> 父 mounted
子组件更新过程
1 . 子组件更新 影响到 父组件的情况。
顺序:父 beforeUpdate -> 子 beforeUpdate -> 子 updated -> 父 updated
2 . 子组件更新 不影响到 父组件的情况。
顺序:子 beforeUpdate -> 子 updated
父组件更新过程
1 . 父组件更新 影响到 子组件的情况。
顺序:父 beforeUpdate -> 子 beforeUpdate -> 子 updated -> 父 updated
2 . 父组件更新 不影响到 子组件的情况。
顺序:父 beforeUpdate -> 父 updated
销毁过程
顺序:父 beforeDestroy -> 子 beforeDestroy -> 子 destroyed -> 父 destroyed
父组件如何监听子组件生命周期的钩子函数
两种方式都以 mounted 为例子。
$emit实现
// 父组件
<template>
<div class="parent">
<Child @mounted="doSomething"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
doSomething() {
console.log('父组件监听到子组件 mounted 钩子函数')
}
}
}
</script>
//子组件
<template>
<div class="child">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
console.log('触发mounted事件...')
this.$emit("mounted")
}
}
</script>
复制代码@hook实现
// 父组件
<template>
<div class="parent">
<Child @hook:mounted="doSomething"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
doSomething() {
console.log('父组件监听到子组件 mounted 钩子函数')
}
}
}
</script>
//子组件
<template>
<div class="child">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
console.log('触发mounted事件...')
}
}
</script>
复制代码Vue 组件间通讯方式
父子组件通讯
- props 与 $emit
- 与children
隔代组件通讯
- 与listeners
- provide 和 inject
父子、兄弟、隔代组件通讯
- EventBus
- Vuex
v-on 监听多个方法
<button v-on="{mouseenter: onEnter, mouseleave: onLeave}">鼠标进来1</button>`
复制代码常用的修饰符
表单修饰符
- lazy: 失去焦点后同步信息
- trim: 自动过滤首尾空格
- number: 输入值转为数值类型
事件修饰符
- stop:阻止冒泡
- prevent:阻止默认行为
- self:仅绑定元素自身触发
- once:只触发一次
鼠标按钮修饰符
- left:鼠标左键
- right:鼠标右键
- middle:鼠标中间键
class 与 style 如何动态绑定
class 和 style 可以通过对象语法和数组语法进行动态绑定
对象写法
<template>
<div :class="{ active: isActive }"></div>
<div :style="{ fontSize: fontSize }">
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
isActive: true,
fontSize: 30
}
}
}
</script>
复制代码数组写法
<template>
<div :class="[activeClass]"></div>
<div :style="[styleFontSize]">
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
activeClass: 'active',
styleFontSize: {
fontSize: '12px'
}
}
}
}
</script>
复制代码v-show 和 v-if 区别
共同点:控制元素显示和隐藏。 不同点:
- v-show 控制的是元素的CSS(display);v-if 是控制元素本身的添加或删除。
- v-show 由 false 变为 true 的时候不会触发组件的生命周期。v-if 由 false 变为 true 则会触发组件的
beforeCreate、create、beforeMount、mounted钩子,由 true 变为 false 会触发组件的beforeDestory、destoryed方法。 - v-if 比 v-show有更高的性能消耗。
为什么 v-if 不能和 v-for 一起使用
性能浪费,每次渲染都要先循环再进行条件判断,考虑用计算属性替代。
Vue2.x中v-for比v-if更高的优先级。
Vue3.x中v-if 比 v-for 更高的优先级。
computed 和 watch 的区别和运用的场景
computed 和 watch 本质都是通过实例化 Watcher 实现,最大区别就是适用场景不同。
computed
计算属性,依赖其他属性值,且值具备缓存的特性。只有它依赖的属性值发生改变,下一次获取的值才会重新计算。
适用于数值计算,并且依赖于其他属性时。因为可以利用缓存特性,避免每次获取值,都需要重新计算。
watch
观察属性,监听属性值变动。每当属性值发生变化,都会执行相应的回调。
适用于数据变化时执行异步或开销比较大的操作。
slot 插槽
slot 插槽,可以理解为slot在组件模板中提前占据了位置。当复用组件时,使用相关的slot标签时,标签里的内容就会自动替换组件模板中对应slot标签的位置,作为承载分发内容的出口。
主要作用是复用和扩展组件,做一些定制化组件的处理。
插槽主要有3种
1 . 默认插槽
// 子组件
<template>
<slot>
<div>默认插槽备选内容</div>
</slot>
</template>
// 父组件
<template>
<Child>
<div>替换默认插槽内容</div>
</Child>
</template>
复制代码2 . 具名插槽
slot 标签没有name属性,则为默认插槽。具备name属性,则为具名插槽
// 子组件
<template>
<slot>默认插槽的位置</slot>
<slot name="content">插槽content内容</slot>
</template>
// 父组件
<template>
<Child>
<template v-slot:default>
默认...
</template>
<template v-slot:content>
内容...
</template>
</Child>
</template>
复制代码3 . 作用域插槽
子组件在作用域上绑定的属性来将组件的信息传给父组件使用,这些属性会被挂在父组件接受的对象上。
// 子组件
<template>
<slot name="footer" childProps="子组件">
作用域插槽内容
</slot>
</template>
// 父组件
<template>
<Child v-slot="slotProps">
{{ slotProps.childProps }}
</Child>
</template>
复制代码Vue.$delete 和 delete 的区别
Vue.$delete 是直接删除了元素,改变了数组的长度;delete 是将被删除的元素变成内 undefined ,其他元素键值不变。
Vue.$set 如何解决对象新增属性不能响应的问题
Vue.$set的出现是由于Object.defineProperty的局限性:无法检测对象属性的新增或删除。
源码位置:vue/src/core/observer/index.js
export function set(target, key, val) {
// 数组
if(Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
// 修改数组长度,避免索引大于数组长度导致splice错误
target.length = Math.max(target.length, key)
// 利用数组splice触发响应
target.splice(key, 1, val)
return val
}
// key 已经存在,直接修改属性值
if(key in target && !(key in Object.prototype)) {
target[key] = val
return val
}
const ob = target.__ob__
// target 不是响应式数据,直接赋值
if(!ob) {
target[key] = val
return val
}
// 响应式处理属性
defineReactive(ob.value, key, val)
// 派发更新
ob.dep.notify()
return val
}
复制代码实现原理:
- 若是数组,直接使用数组的 splice 方法触发响应式。
- 若是对象,判断属性是否存在,对象是否是响应式。
- 以上都不满足,最后通过 defineReactive 对属性进行响应式处理。
Vue 异步更新机制
Vue 异步更新机制核心是利用浏览器的异步任务队列实现的。
当响应式数据更新后,会触发 dep.notify 通知所有的 watcher 执行 update 方法。
dep 类的 notify 方法
notify() {
// 获取所有的 watcher
const subs = this.subs.slice()
// 遍历 dep 中存储的 watcher,执行 watcher.update
for(let i = 0; i < subs.length; i++) {
subs[i].update()
}
}
复制代码watcher.update 将自身放入全局的 watcher 队列,等待执行。
watcher 类的 update 方法
update() {
if(this.lazy) {
// 懒执行走当前 if 分支,如 computed
// 这里的 标识 主要用于 computed 缓存复用逻辑
this.dirty = true
} else if(this.sync) {
// 同步执行,在 watch 选项参数传 sync 时,走当前分支
// 若为 true ,直接执行 watcher.run(),不塞入异步更新队列
this.run()
} else {
// 正常更新走当前 else 分支
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
复制代码queueWatcher 方法,发现熟悉的 nextTick 方法。看到这可以先跳到nextTick的原理,看明白了再折返。
function queueWatcher(watcher) {
const id = watcher.id
// 根据 watcher id 判断是否在队列中,若在队列中,不重复入队
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true
// 全局 queue 队列未处于刷新状态,watcher 可入队
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher)
// 全局 queue 队列处于刷新状态
// 在单调递增序列寻找当前 id 的位置并进行插入操作
} else {
let i = queue.length - 1
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher)
}
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true
// 同步执行逻辑
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
flushSchedulerQueue()
return
}
// 将回调函数 flushSchedulerQueue 放入 callbacks 数组
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)
}
}
}
复制代码nextTick 函数最终其实是执行 flushCallbacks 函数,flushCallbacks 函数则是运行 flushSchedulerQueue 回调和项目中调用 nextTick 函数传入的回调。
搬运 flushSchedulerQueue 源码看做了些什么
/**
* 更新 flushing 为 true,表示正在刷新队列,在此期间加入的 watcher 必须有序插入队列,保证单调递增
* 按照队列的 watcher.id 从小到大排序,保证先创建的先执行
* 遍历 watcher 队列,按序执行 watcher.before 和 watcher.run,最后清除缓存的 watcher
*/
function flushSchedulerQueue () {
currentFlushTimestamp = getNow()
// 标识正在刷新队列
flushing = true
let watcher, id
queue.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id)
// 未缓存长度是因为可能在执行 watcher 时加入 watcher
for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) {
watcher = queue[index]
if (watcher.before) {
watcher.before()
}
id = watcher.id
// 清除缓存的 watcher
has[id] = null
// 触发更新函数,如 updateComponent 或 执行用户的 watch 回调
watcher.run()
}
const activatedQueue = activatedChildren.slice()
const updatedQueue = queue.slice()
// 执行 waiting = flushing = false,标识刷新队列结束,可以向浏览器的任务队列加入下一个 flushCallbacks
resetSchedulerState()
callActivatedHooks(activatedQueue)
callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue)
if (devtools && config.devtools) {
devtools.emit('flush')
}
}
复制代码查看下 watcher.run 做了些什么,首先调用了 get 函数,我们一起看下。
/**
* 执行实例化 watcher 传递的第二个参数,如 updateComponent
* 更新旧值为新值
* 执行实例化 watcher 时传递的第三个参数,用户传递的 watcher 回调
*/
run () {
if (this.active) {
// 调用 get
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// 更新旧值为新值
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
// 若是项目传入的 watcher,则执行实例化传递的回调函数。
if (this.user) {
const info = `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`
invokeWithErrorHandling(this.cb, this.vm, [value, oldValue], this.vm, info)
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}
/**
* 执行 this.getter,并重新收集依赖。
* 重新收集依赖是因为触发更新 setter 中只做了响应式观测,但没有收集依赖的操作。
* 所以,在更新页面时,会重新执行一次 render 函数,执行期间会触发读取操作,这时进行依赖收集。
*/
get () {
// Dep.target = this
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
// 执行回调函数,如 updateComponent,进入 patch 阶段
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// watch 参数为 deep 的情况
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
// 关闭 Dep.target 置空
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}
复制代码Vue.$nextTick 的原理
nextTick:在下次 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调。常用于修改数据后获取更新后的DOM。
源码位置:vue/src/core/util/next-tick.js
import { noop } from 'shared/util'
import { handleError } from './error'
import { isIE, isIOS, isNative } from './env'
// 是否使用微任务标识
export let isUsingMicroTask = false
// 回调函数队列
const callbacks = []
// 异步锁
let pending = false
function flushCallbacks () {
// 表示下一个 flushCallbacks 可以进入浏览器的任务队列了
pending = false
// 防止 nextTick 中包含 nextTick时出现问题,在执行回调函数队列前,提前复制备份,清空回调函数队列
const copies = callbacks.slice(0)
// 清空 callbacks 数组
callbacks.length = 0
for (let i = 0; i < copies.length; i++) {
copies[i]()
}
}
let timerFunc
// 浏览器能力检测
// 使用宏任务或微任务的目的是宏任务和微任务必在同步代码结束之后执行,这时能保证是最终渲染好的DOM。
// 宏任务耗费时间是大于微任务,在浏览器支持的情况下,优先使用微任务。
// 宏任务中效率也有差距,最低的就是 setTimeout
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
const p = Promise.resolve()
timerFunc = () => {
p.then(flushCallbacks)
if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop)
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MutationObserver) ||
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {
let counter = 1
const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks)
const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter))
observer.observe(textNode, {
characterData: true
})
timerFunc = () => {
counter = (counter + 1) % 2
textNode.data = String(counter)
}
isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
timerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks)
}
} else {
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
}
}
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
// 将 nextTick 的回调函数用 try catch 包裹一层,用于异常捕获
// 将包裹后的函数放到 callback 中
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
// pengding 为 false, 执行 timerFunc
if (!pending) {
// 关上锁
pending = true
timerFunc()
}
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(resolve => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
}
复制代码总结:
- 运用异步锁的概念,保证同一时刻任务队列中只有一个 flushCallbacks。当 pengding 为 false 的时候,表示浏览器任务队列中没有 flushCallbacks 函数;当 pengding 为 true 的时候,表示浏览器任务队列中已经放入 flushCallbacks;待执行 flushCallback 函数时,pengding 会被再次置为 false,表示下一个 flushCallbacks 可进入任务队列。
- 环境能力检测,选择可选中效率最高的(宏任务/微任务)进行包装执行,保证是在同步代码都执行完成后再去执行修改 DOM 等操作。
- flushCallbacks 先拷贝再清空,为了防止nextTick嵌套nextTick导致循环不结束。
实现虚拟 DOM
虚拟 DOM 的出现解决了浏览器的性能问题。虚拟 DOM 是一个用 JS 模拟的 DOM 结构对象(Vnode),用于频繁更改 DOM 操作后不立即更新 DOM,而是对比新老 Vnode,更新获取最新的Vnode,最后再一次性映射成真实的 DOM。这样做的原因是操作内存中操作 JS 对象速度比操作 DOM 快很多。
举个真实 DOM 的
<div id="container">
<p>real dom </p>
<ul>
<li class="item">item 1</li>
<li class="item">item 2</li>
<li class="item">item 3</li>
</ul>
</div
复制代码用 JS 来模拟 DOM 节点实现虚拟 DOM
function Element(tagName, props, children) {
this.tageName = tagName
this.props = props || {}
this.children = children || []
this.key = props.key
let count = 0
this.children.forEach(child => {
if(child instanceof Element) count += child.count
count++
})
this.count = count
}
const tree = Element('div', { id: container }, [
Element('p', {}, ['real dom'])
Element('ul', {}, [
Element('li', { class: 'item' }, ['item1']),
Element('li', { class: 'item' }, ['item2']),
Element('li', { class: 'item' }, ['item3'])
])
])
复制代码虚拟 DOM 转为真实的节点
Element.prototype.render = function() {
let el = document.createElement(this.tagName)
let props = this.props
for(let key in props) {
el.setAttribute(key, props[key])
}
let children = this.children || []
children.forEach(child => {
let child = (child instanceof Element) ? child.render() : document.createTextNode(child)
el.appendChild(child)
})
return el
}
复制代码Vue 中 Diff 的原理
核心源码:vue/src/core/vdom/patch.js
搬运对比新老节点 patch 函数入口
/**
* 新节点不存在,老节点存在,调用 destroy,销毁老节点
* 如果 oldVnode 是真实元素,则表示首次渲染,创建新节点,并插入 body,然后移除来节点
* 如果 oldVnode 不是真实元素,则表示更新阶段,执行patchVnode
*/
function patch(oldVnode, vnode) {
// 新的 Vnode 不存在,老的 Vnode 存在,销毁老节点
if(isUndef(vnode)) {
if(isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
return
}
// 新的 Vnode 存在,老的 Vnode 不存在
// <div id="app"><comp></comp></div>
// 这里的 com 组件初次渲染就走当前的 if 逻辑
if(isUndef(oldVnode)) {
isInitialPatch = true
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType)
// 新老节点相同,更精细化对比
if(!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode)
} else {
// 是真实元素,渲染根组件
if(isRealElement) {
// 挂载到真实元素以及处理服务端渲染情况
if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) {
oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR)
hydrating = true
}
if (isTrue(hydrating)) {
if (hydrate(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) {
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true)
return oldVnode
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(
'The client-side rendered virtual DOM tree is not matching ' +
'server-rendered content. This is likely caused by incorrect ' +
'HTML markup, for example nesting block-level elements inside ' +
'<p>, or missing <tbody>. Bailing hydration and performing ' +
'full client-side render.'
)
}
}
// 基于真实节点创建一个 vnode
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode)
}
// 获取老节点的真实元素
const oldElm = oldVnode.elm
// 获取老节点的父元素,即 body
const parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm)
// 基于新的 vnode 创建整颗 DOM 树并插入到 body 元素下
creatElm(
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm,
nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm)
)
// 递归更新父占位符节点元素
if(isDef(vnode.parent)) {
...
}
// 移除老节点
if(isDef(parentEle)) {
...
} else if(isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
...
}
}
}
}
复制代码搬运 patchVnode 部分源码。
/**
* 更新节点
* 如果新老节点都有孩子,则递归执行 updateChildren
* 如果新节点有孩子,老节点没孩子,则新增新节点的这些孩子节点
* 如果老节点有孩子,新节点没孩子,则删除老节点这些孩子
* 更新文本节点
*/
function patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode) {
// 如果新老节点相同,直接返回
if(oldVnode === vnode) return
// 获取新老节点的孩子节点
const oldCh = oldVnode.children
const ch = vnode.children
// 新节点不是文本节点
if(isUndef(vnode.text)) {
// 新老节点都有孩子,则递归执行 updateChildren
if(isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch) && oldCh !== ch) { // oldVnode 与 vnode 的 children 不一致,更新children
updateChildren(oldCh,ch)
// 如果新节点有孩子,老节点没孩子,则新增新节点的这些孩子节点
} else if(isDef(ch)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 如果老节点有孩子,新节点没孩子,则删除老节点这些孩子
} else if(isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
// 老节点文本存在,新的节点不存在文本,清空文本
} else if(isDef(oldVnode.text)){
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
// 新老文本节点都是文本节点,且文本发生改变,则更新文本节点
} else if(oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text)
}
}
复制代码搬运 updateChildren 源码。
function updateChildren(oldCh, ch) {
// const oldCh = [n1, n2, n3, n4]
// const ch = [n1, n2, n3, n4, n5]
// 旧节点起始索引
let oldStartIdx = 0
// 新节点起始索引
let newStartIdx = 0
// 旧节点结束索引
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
// 新节点结束索引
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
while(oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
const newStartVnode = ch[newStartIdx]
const oldStartVnode = oldCh[oldStartIdx]
const newEndVnode = ch[newEndIdx]
const oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
// 如果节点被移动,在当前索引上可能不存在,检测这种情况,如果节点不存在则调整索引
if(isUndef(oldStartVnode)) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
} else if(isUndef(oldEndVnode)) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
// 新开始和老开始节点是同一个节点
} else if(sameVnode(oldStartNode, newStartNode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartNode , newStartNode)
oldStartIdx++
newStartIdx++
// 新开始节点和老结束节点是同一节点
} else if(sameVnode(oldEndNode, newEndNode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndNode, newEndNode)
oldEndIdx--
newEndIdx--
// 老开始和新结束是同一节点
} else if(sameVnode(oldStartNode, newEndNode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartNode, newEndNode)
oldStartIdx++
newEndIdx--
// 老结束和新开始是同一节点
} else if(sameVnode(oldEndNode, newStartNode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndNode, newStartNode)
oldEndIdx--
newStartIdx++
} else {
// 上面假设都不成立,则通过遍历找到新开始节点和老节点中的索引位置
// 创建老节点每个节点 key 和 索引的关系 { key: idx }
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
// 寻找新开始节点在老节点的索引位置
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key)
? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
: findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
// 没有找到,则说明是新创建的元素,执行创建
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) {
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
} else {
// 在关系映射表中找到新开始节点
vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld]
// 如果是同一个节点,则执行patch
if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx)
// patch 结束后将老节点置为 undefined
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
} else {
// 最后这种情况是,找到节点,但发现两个节点不是同一个节点,则视为新元素,执行创建
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
}
}
// 新节点向后移动一位
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
if(newStartIdx < newEndIdx) {} // 旧节点先遍历结束,将剩余的新节点添加到DOM中
if(oldStartIdx < oldEndIdx) {} // 新节点先遍历结束,将剩余的旧节点删掉
}
}
复制代码Vue 中的 key 的作用
key 是 Vue 中 vnode 的唯一标记,我们的 diff 的算法中 sameVnode 和 updateChildren 中就使用到了 key。
sameVnode 用来判断是否为同一节点。常见的业务场景是一个列表,若 key 值是列表索引,在新增或删除的情况下会存在就地复用的问题。(简单说,复用了上一个在当前位置元素的状态)所以 key 值的唯一,确保 diff 更准确。
updateChildren 中当其中四种假设都未匹配,就需要依赖老节点的 key 和 索引创建关系映射表,再用新节点的 key 去关系映射表去寻找索引进行更新,这保证 diff 算法更加快速。
Vue 动态组件是什么
动态组件通过is特性实现。适用于根据数据、动态渲染的场景,即组件类型不确定。
举个新闻详情页案例,如下图所示。
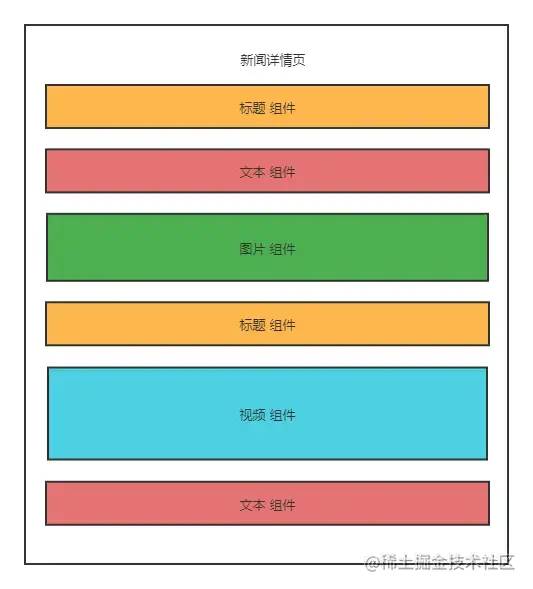
但是每篇新闻的详情页组件顺序可能是不一样的,所以我们得通过数据来动态渲染组件,而非写死每个组件的顺序。
<template>
<div v-for="val in componentsData" :key="val.id">
<component :is="val.type">
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CustomTitle from './CustomTitle'
import CustomText from './CustomText'
import CustomImage from './CustomImage'
export default {
data() {
return {
componentsData: [{
id: 1,
type: 'CustomTitle'
},{
id: 2,
type: 'CustomText'
},{
id: 3
type: 'CustomImage'
}]
}
}
}
</script>
复制代码Vue.directive 有写过么,应用场景有哪些?
Vue.directive 可以注册全局指令和局部指令。
指令定义函数提供如下钩子函数
- bind:指令第一次绑定到元素时调用(只调用一次)
- inserted: 被绑定元素插入父节点时使用(父节点存在即可调用)
- update:被绑定元素所在模板更新时调用,不论绑定值是否变化。通过比较更新前后的绑定值。
- componentUpdated: 被绑定元素所在模板完成一次更新周期时调用。
- unbind: 只调用一次,指令与元素解绑时调用。
我项目中有涉及 一键copy、权限控制 都可以用指令的方式控制,目的就是简化我们的工作量。
推荐一篇 分享8个非常实用的Vue自定义指令[5] 。
Vue 过滤器了解么
Vue 过滤器可用在两个地方:双花括号插值和 v-bind 表达式。
Vue3 中已经废弃这个特点。
过滤器分为 全局过滤器 和 局部过滤器。
局部过滤器
<template>
<div>{{ message | formatMessage }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
filters: {
formatMessage: function(value) {
// 可基于源值做一些处理
return value
}
}
}
</script>
复制代码全局过滤器
Vue.filter('formatMessage', function(value) {
// 可基于源值做一些处理
return value
})
复制代码过滤器可串联,执行顺序从左到右,第二个过滤器输入值是第一个过滤器的输出值。
<div>{{ message | formatMessage1 | formatMessage2 }}</div>
复制代码关于 mixin 的理解,有什么应用场景
定义:mixin(混入),提供了一种非常灵活的方式,来分发 Vue 组件中可复用的功能。
mixin 混入分全局混入和局部混入,本质是 JS 对象,如 data、components、computed、methods 等。
全局混入不推荐使用,会影响后续每个Vue实例的创建。局部混入可提取组件间相同的代码,进行逻辑复用。
适用场景:如多个页面具备相同的悬浮定位浮窗,可尝试用 mixin 封装。
// customFloatDialog.js
export const customFloatDialog = {
data() {
return {
visible: false
}
},
methods: {
toggleShow() {
this.visible = !this.visible
}
}
}
</script>
//需要引入的组件
<template>
<div></div>
</template>
<script>
import { customFloatDialog } from './customFloatDialog.js'
export default {
mixins: [customFloatDialog],
}
</script>
复制代码介绍一下 keep-alive
keep-alive 是 Vue 内置的一个组件,可以缓存组件的状态,避免重复渲染,提高性能。
keep-alive 内置组件有3个属性
- include:字符串或正则表达式,名称匹配的组件会被缓存。
- exclude:字符串或正则表达式,名称匹配的组件不会被缓存。
- max:缓存组件数量阈值
设置 keep-alive 的组件,会增加两个生命钩子(activated / deactivated)。
首次进入组件:beforeCreate -> created -> beforeMount -> mounted -> activated
离开组件触发deactivated,因为组件缓存不销毁,所以不会触发 beforeDestroy 和 destroyed 生命钩子。再次进入组件后直接从 activated 生命钩子开始。
常见业务场景:在列表页的第 2 页进入详情页,详情页返回,依然停留在第 2 页,不重新渲染。但从其他页面进入列表页,还是需要重新渲染。
思路:vuex 使用数组存储列表页名字,列表页离开结合 beforeRouteLeave 钩子判断是否需要缓存,对全局数组进行更改。
在 router-view 标签位置如下使用
<template>
<keep-alive :include="cacheRouting">
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed: {
cacheRouting() {
return this.$store.state.cacheRouting
}
}
}
</script>
复制代码列表页如下使用
<template>
<div></div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) {
if(to.name === '详情页') {
// ... 向全局缓存路由数组添加列表页
next()
} else {
// ... 向全局缓存路由数组删除列表页
next()
}
}
}
</script>
复制代码keep-alive 的实现
核心源码:vue/src/core/components/keep-alive.js
LRU(Least Recently Used) 替换策略核心思想是替换最近最少使用。
/**
* 遍历 cache 将不需要的缓存的从 cache 中清除
*/
function pruneCache (keepAliveInstance, filter) {
const { cache, keys, _vnode } = keepAliveInstance
for (const key in cache) {
const cachedNode = cache[key]
if (cachedNode) {
const name = getComponentName(cachedNode.componentOptions)
if (name && !filter(name)) {
pruneCacheEntry(cache, key, keys, _vnode)
}
}
}
}
/**
* 删除 cache 中键值为 key 的虚拟DOM
*/
function pruneCacheEntry (cache, key, keys, current) {
const entry = cache[key]
if (entry && (!current || entry.tag !== current.tag)) {
// 执行组件的 destroy 钩子
entry.componentInstance.$destroy()
}
// cache 中组件对应的虚拟DOM置null
cache[key] = null
// 删除缓存虚拟DOM的 key
remove(keys, key)
}
export default {
name: 'keep-alive',
abstract: true,
props: {
include: patternTypes,
exclude: patternTypes,
max: [String, Number]
},
created () {
// 缓存虚拟 DOM
this.cache = Object.create(null)
// 缓存虚拟DOM的键集合
this.keys = []
},
destroyed () {
// 删除所有的缓存内容
for (const key in this.cache) {
pruneCacheEntry(this.cache, key, this.keys)
}
},
mounted () {
// 监听 include、exclude 参数变化,调用 pruneCache修改缓存中的缓存数据
this.$watch('include', val => {
pruneCache(this, name => matches(val, name))
})
this.$watch('exclude', val => {
pruneCache(this, name => !matches(val, name))
})
},
// 由 render 函数决定渲染结果
render () {
const slot = this.$slots.default
// 获取第一个子组件虚拟DOM
const vnode: VNode = getFirstComponentChild(slot)
// 获取虚拟 DOM 的配置参数
const componentOptions: ? VNodeComponentOptions = vnode && vnode.componentOptions
if (componentOptions) {
// 获取组件名称
const name: ?string = getComponentName(componentOptions)
const { include, exclude } = this
// 若不在include或者在exclude中,直接退出,不走缓存机制
if (
(include && (!name || !matches(include, name))) ||
(exclude && name && matches(exclude, name))
) {
return vnode
}
const { cache, keys } = this
// 获取组件key
const key: ?string = vnode.key == null
? componentOptions.Ctor.cid + (componentOptions.tag ? `::${componentOptions.tag}` : '')
: vnode.key
// 命中缓存
if (cache[key]) {
// 从 cache 中获取缓存的实例设置到当前的组件上
vnode.componentInstance = cache[key].componentInstance
// 删除原有存在的key,并置于最后
remove(keys, key)
keys.push(key)
// 未命中缓存
} else {
// 缓存当前虚拟节点
cache[key] = vnode
// 添加当前组件key
keys.push(key)
// 若缓存组件超过max值,LRU 替换
if(this.max && keys.length > parseInt(this.max)) {
pruneCacheEntry(cache, keys[0], keys, this._vnode)
}
}
// 设置当前组件 keep-alive 为 true
vnode.data.keepAlive = true
}
return vnode || (slot && slot[0])
}
}
复制代码Vue-Router 配置 404 页面
* 代表通配符,若放在任意路由前,会被先匹配,导致跳转到 404 页面,所以需将如下配置置于最后。
{
path: '*',
name: '404'
component: () => import('./404.vue')
}
复制代码Vue-Router 有哪几种导航守卫
全局前置守卫
在路由跳转前触发,可在执行 next 方法前做一些身份登录验证的逻辑。
const router = new VueRouter({})
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
...
// 必须执行 next 方法来触发路由跳转
next()
})
复制代码全局解析守卫
与 beforeEach 类似,也是路由跳转前触发,区别是还需在所有组件内守卫和异步路由组件被解析之后,也就是在组件内 beforeRouteEnter 之后被调用。
const router = new VueRouter({})
router.beforeResolve((to, from, next) => {
...
// 必须执行 next 方法来触发路由跳转
next()
})
复制代码全局后置钩子
和守卫不同的是,这些钩子不会接受 next 函数也不会改变导航本身。
router.afterEach((to, from) => {
// ...
})
复制代码4 . 路由独享守卫
可在路由配置上直接定义 beforeEnter
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/home',
component: Home,
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
}
}
]
})
复制代码组件内的守卫
组件内可直接定义如下路由导航守卫
const Foo = {
template: `...`,
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {
// 不能获取组件实例 this
// 当守卫执行前,组件实例还没被创建
},
beforeRouteUpdate(to, from, next) {
// 当前路由改变,但是组件被复用时调用
// 可访问实例 this
},
beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) {
// 导航离开组件时被调用
}
}
复制代码Vue-Router 完整的导航解析流程
- 导航被触发
- 在失活的组件里调用 beforeRouteLeave 守卫
- 调用全局 beforeEach 前置守卫
- 重用的组件调用 beforeRouteUpdate 守卫(2.2+)
- 路由配置调用 beforeEnter
- 解析异步路由组件
- 在被激活的组件里调用 beforeRouteEnter 守卫
- 调用全局的 beforeResolve 守卫(2.5+)
- 导航被确认
- 调用全局的 afterEach
- 触发 DOM 更新
- 调用 beforeRouteEnter 守卫中传给 next 的回调函数,创建好的组件实例会作为回调函数的参数传入
Vue-Router 路由有几种模式?说说他们的区别?
Vue-Router 有 3 种路由模式:hash、history、abstract。
hash 模式
Vue-Router 默认为 hash 模式,基于浏览器的onhashchange事件,地址变化时,通过window.location.hash获取地址上的hash值;根据hash值匹配 routes 对象对应的组件内容。
特点
- hash值存在 URL 中,携带
#,hash值改变不会重载页面。 - hash改变会触发
onhashchange事件,可被浏览器记录,从而实现浏览器的前进后退。 - hash传参基于url,传递复杂参数会有体积限制。
- 兼容性好,支持低版本浏览器和 IE 浏览器。
案例代码,需在本地启用服务(http-server)访问, 已测试过,可直接 cv 体验。
实现原理
<div class="main">
<a href="#/home">home</a>
<a href="#/detail">detail</a>
<div id="content"><span>暂无内容</span></div>
</div>
<script>
const routers = [{
path: '/',
component: `<span>暂无内容</span>`
},
{
path: '/home',
component: `<span>我是Home页面</span>`
}, {
path: '/detail',
component: `<span>我是Detail页面</span>`
}]
function Router(routers) {
console.log('执行')
this.routers = {}
// 初始化生成 routers
routers.forEach((router) => {
this.routers[router.path] = () => {
document.getElementById("content").innerHTML = router.component;
}
})
this.updateView = function(e) {
let hash = window.location.hash.slice(1) || '/'
console.log('hash更新', hash, this.routers[hash])
this.routers[hash] && this.routers[hash]()
}
// 路由加载触发视图更新
window.addEventListener('load', this.updateView.bind(this))
// 路由改变触发视图更新
window.addEventListener('hashchange', this.updateView.bind(this))
}
// 实例化 hash 模式的 Router
let router = new Router(routers)
</scrip
复制代码history 模式
基于HTML5新增的 pushState 和 replaceState 实现在不刷新的情况下,操作浏览器的历史纪录。前者是新增历史记录,后者是直接替换历史记录。
特点
1 . URL 不携带#,利用 pushState 和 replaceState 完成 URL 跳转而无须重新加载页面。
2 . URL 更改会触发 http 请求。所以在服务端需增加一个覆盖所有情况的候选资源:若URL匹配不到任何静态资源,则应该返回同一个index.html。这个页面就是app依赖的页面。
// nginx 服务端配置
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
复制代码3 . 兼容性 IE10+
实现原理
<div class="main">
<a href="javascript:;" path="/home">home</a>
<a href="javascript:;" path="/detail">detail</a>
<div id="content"><span>暂无内容</span></div>
</div>
<script>
const routers = [{
path: '/home',
component: `<span>我是Home页面</span>`
}, {
path: '/detail',
component: `<span>我是Detail页面</span>`
}, {
path: '/',
component: '<span>暂无内容</span>'
}]
function Router(routers) {
this.routers = {}
// 初始化生成 routers
routers.forEach((router) => {
this.routers[router.path] = () => {
document.getElementById("content").innerHTML = router.component;
}
})
const links = [...document.getElementsByTagName('a')]
links.forEach(link => {
link.addEventListener('click', () => {
window.history.pushState({}, null, link.getAttribute('path'))
this.updateView()
})
})
this.updateView = function() {
let url = window.location.pathname || '/'
this.routers[url] && this.routers[url]()
}
// 路由加载触发视图更新
window.addEventListener('load', this.updateView.bind(this))
// 路由改变触发视图更新
window.addEventListener('popstate', this.updateView.bind(this))
}
// 实例化 history 模式的 Router
const router = new Router(routers)
</script>
复制代码abstract 模式
支持所有 JS 运行模式,Vue-Router 自身会对环境做校验,如果发现没有浏览器 API,路由会自动强制进入 abstract 模式。在移动端原生环境也是使用 abstract 模式。
Vue 路由传参方式
Vue 路由有 三种 方式进行传参
1 . 方案一
// 路由配置
{
path: '/detail/:id',
name: 'Detail',
component: () => import('./Detail.vue')
}
// 路由跳转
let id = 1
this.$router.push({ path: '/detail/${id}'})
// 获取参数
this.$route.params.id
复制代码2 . 方案二
方案二,URL 虽然不显示我们的传参,但是是可以在子组件获取参数的。当然也有问题:会存在刷新丢失参数。
若想不丢失,需和方案一路由配置一样。原因是第二种方式传参是上一个页面 push 函数中携带的,刷新没有 push 的动作。
// 路由配置
{
path: '/detail',
name: 'Detail',
component: () => import('./Detail.vue')
}
// 路由跳转
let id = 1
this.$router.push({ name: 'Detail', params: { id: id } })
// 获取参数
this.$route.params.id
复制代码3 . 方案三
// 路由配置
{
path: '/detail',
name: 'Detail',
component: () => import('./Detail.vue')
}
// 路由跳转
let id = 1
this.$router.push({ name: 'Detail', query: { id: id } })
// 获取参数
this.$route.query.id
复制代码Vuex 的理解及使用
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式,采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态。
主要解决如下 两个 问题
- 多个视图依赖同一状态。
- 来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一个状态。
其包含如下模块,搬官网图
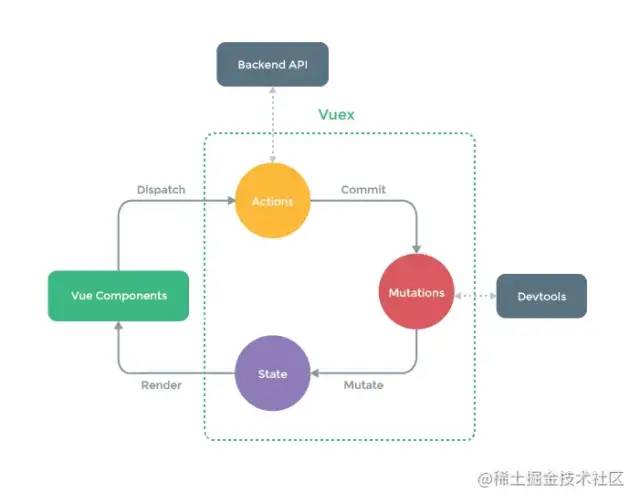
State:定义并初始化全局状态。 Getter: 依赖 State 中的状态,进行二次包装,不会影响 State 源数据。 Mutation: 更改 State 状态的函数,必须是同步。 Action:用于提交 Mutation,可包含任意异步操作。 Module:若应用复杂,Store 会集中一个比较大的对象而显得臃肿,Module允许我们将 Store模块化管理。
当然,若应用比较简单,共享状态也比较少,可以用 Vue.observe 去替代 Vuex,省去安装一个库也挺好。
Vuex 刷新后数据丢失怎么办
持久化缓存:localStorage、sessionStorage
Vuex 如何知道 State 是通过 Mutation 修改还是外部修改?
Vuex 中修改 state 唯一渠道是执行 commit 方法,底层通过执行 this._withCommit(fn),且设置_committing标识符为 true,才能修改 state,修改完还需要将标识符置为 false。外部修改是无法设置标识位的,所以通过 watch 监听 state 变化,来判断修改的合法性。
Vue SSR 了解么
Vue SSR 项目中暂时还没有运用过,后续会写个 Demo 单独成文吧。这边搬运下其他答案。
SSR 服务端渲染,将 HTML 渲染工作放在服务端完成后,将 HTML 返回到浏览器端。
优点:SSR有更好的 SEO,首屏加载更快。 缺点:服务端负载大。
如果是内部系统,SSR其实没有太多必要。如果是对外的项目,维护高可用的node服务器是个难点。
Vue2 与 Vue3 的区别 ?Vue3有哪些优化点?
自产自销:【持续更新】梳理 Vue3 相比于 Vue2 的有哪些 “与众不同” ?[6]
Vue 性能优化
- 非响应式数据通过 Object.freeze 冻结数据
- 嵌套层级不要过深
- computed 和 watch 区别使用
- v-if 和 v-show 区别使用
- v-for 避免和 v-if 一起使用,且绑定 key 值要唯一
- 列表数据过多采用分页或者虚拟列表
- 组件销毁后清除定时器和事件
- 图片懒加载
- 路由懒加载
- 防抖、节流
- 按需引入外部库
- keep-alive缓存使用
- 服务端渲染和预渲染
总结
[1]https://juejin.cn/post/7008476801634680869
[2]https://juejin.cn/post/7001860784586227720
[3]https://juejin.cn/post/7012419511907254308
[4]https://www.zhihu.com/question/419154194
[5]https://juejin.cn/post/6906028995133833230
[6]https://juejin.cn/post/7011372376969445413
