小小的宏 大大的世界
小小的宏,大大的世界
题记:用最通俗的语言,描述最难懂的技术
目录表
-
关于UIKITEXTERN
-
UIKITEXTERN代码解读
-
原理
-
应用场景
-
扩展
-
宏
-
extern
-
static
-
const
-
iOS下的extern
-
参考文档
-
结束语
关于UIKITEXTERN
在开发中大家难免会声明很多的全局常量,以确保在整个项目中可用,在这里这个全局常量的值一般不会变,且全局有效,在iOS中的表现方式就是这样的,这段代码既保证了全局可用,又防止了不同动态库之间的引用冲突
1.0 eg
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define UIKIT_EXTERN extern "C" __attribute__((visibility ("default")))
#else
#define UIKIT_EXTERN extern __attribute__((visibility ("default")))
#endif同样也被很多优秀的框架引用,比如YYKit
1.1 eg
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define YY_EXTERN_C_BEGIN extern "C" {
#define YY_EXTERN_C_END }
#else
#define YY_EXTERN_C_BEGIN
#define YY_EXTERN_C_END
#endi那么为什么这么写?这么写会有什么作用?适用于那种场景?以及它的原理,接下来我们一步一步揭开神秘的面纱,Let's go.. UIKITEXTERN代码解读
- 解读1.0 eg
如果是C++语言
那么就声明此宏定义,在C++语言里面写C需要加上C的说明,设置编译器属性为default,保证对外部的类可见
否则
就声明此宏定义,设置编译器属性为default,保证对外部的类可见
在这里,宏仅仅是对象宏,等量替换,后者替换前者原理
__attribute____attribute__是一个编译属性,用于向编译器描述特殊的标识,错误检查或者高级优化。同时它是GNU C的特色之一,在iOS和Mac OS中有许多地方使用到。它可以设置函数属性,变量属性以及类型属性等
__attribute__格式
__attribute__ ((attribute-list))
这两个括号是一定要带上的,千万记得,千万记得,千万记得-
visibility用于设置动态链接库中函数或者变量的可见性,将变量设置为hidden,则该符号仅在当前动态库可见,在其他库不可见;g++(GNU C&C++编译器)在编译时,可用参数-fvisbility指定所有符号的可见性,不加此参数默认外部可见;如果需要对特定函数的可见性进行设置,需要在代码中使用__attribute__设置visibility属性。如上面的1.0 eg中使用__attribute__ ((visibility("default")))令该符号外部可见,这种方法也有效避免动态库之间的符号冲突。 -
举例说明
test2.cc 可以调用func1,原因是test1.o和test2.o同属于一个so文件(so文件是Linux下的动态库文件,等同于iOS下的动态库UIKit等)
// test1.cc file
# include <stdio.h>
extern "C" void func1();
{
printf("in %s\n,__FUNCTION__);
}
// 如果编译的时候设置了参数-fvisibility=hidden,下面可以省略设置
// compile
__attribute__ ((visibility("hidden"))) void func1();
// test2.cc file
# include <stdio.h>
extern "C" void func1();
extern "C" void func2()
{
func1();
printf("in %s\n,__FUNCTION__);
}
// compile
__attribute__ ((visibility("default"))) void func2();
// main.cc file
extern "C" void func1();
extern "C" void func2();
int main ()
{
func1();
func2();
return 0;
}
// compile result
ll:test
test:main.o libvisibility.so
g++ -o test main.o -lvisibility -L .
main.o::main.cc
g++ -c main.cc
libvisibility.so:test1.o test2.o
g++ -shared -o libvisibility.so test1.o test2.o
test1.o:test1.cc
g++ -fvisibility=hidden -fPIC -c test1.cc
test2.o:test2.cc
g++ -fvisibility=hidden -fPIC -c test2.cc
clean:
rm -f *.o *.so test
$ make
g++ -c main.cc
g++ -fvisibility=hidden -fPIC -c test1.cc
g++ -fvisibility=hidden -fPIC -c test2.cc
g++ -shared -o libvisibility.so test1.o test2.o
g++ -o test main.o -lvisibility -L .
main.o: In function `main':
main.cc:(.text+0x5): undefined reference to `fun1'
collect2: ld returned 1 exit status
make: *** [test] Error 1
结论:main()中不可以调用func1,可以调用func2
原因:func1设置了对外不可见,func2设置对外部可见
查看:使用readelf对各个.o文件(可执行文件)分析
$ readelf -s test1.o | grep fun
6: 0000000000000007 5 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 6 _ZZ4fun1E12__FUNCTION__
12: 0000000000000000 30 FUNC GLOBAL HIDDEN 2 func1
$ readelf -s test2.o | grep fun
6: 0000000000000007 5 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 6 _ZZ4fun2E12__FUNCTION__
12: 0000000000000000 35 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 2 func2
15: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT UND fun1
$ readelf -s libvisibility.so | grep fun
9: 00000000000006ac 35 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 12 func2
41: 000000000000071d 5 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 14 _ZZ4fun1E12__FUNCTION__
43: 0000000000000729 5 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 14 _ZZ4fun2E12__FUNCTION__
48: 000000000000068c 30 FUNC LOCAL HIDDEN 12 func1
54: 00000000000006ac 35 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 12 func2
结果:func1的visibility属性是HIDDEN,func2的visibility的属性DEFAULT应用场景
- 编译优化
- 进行全局变量声明
- 进行不同库之间的冲突解决
扩展
宏
这个题是喵神文章的题目,仅供参考
// concat two params
#define __SN_PASTE__(A,B) A##B
// main macro
#define SNSquare(A) __SNSQUARE_IMPL__(A,__COUNTER__)
// param counter
#define __SNSQUARE_IMPL__(A,L) ({ __typeof__(A) __SN_PASTE__(__a,L) = (A); \
(__SN_PASTE__(__a,L)) * (__SN_PASTE__(__a,L)); }) \
// eg
int res = SNSquare(3);
NSLog(@"3 square is %d",res);❝关于宏,喵神写了一篇非常好的文章,这里就不再赘述,链接见文章底部
extern
- 字面意思,外部的,对外的;对外声明全局变量,只用于声明,不可定义
// 在"ViewController.h" 中进行定义全局变量
#import "ViewController.h"
int x = 24;
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation TestViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor purpleColor];;
}
@end
// 在BViewController.m中进行声明全局变量
#import "BViewController.h"
@interface BViewController ()
@end
@implementation BViewController
extern int x;
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
NSLog(@"x is:%d",x);// x is 24
}
@end- 查找流程 首先会去当前文件下去查找对应的全局变量,如果没有,就去其他文件下查找
static
- 修饰局部变量
static int a = 3;
++a;
NSLog(@"a is %d",a); // a is 4局部变量会被延长生命周期,不再跟大括号有关系,直到程序结束才会被销毁,下面的例子除非程序终止,否则a一直有值- 内存只存在一份
static int a = 3;
++a;
NSLog(@"a is %d and addr is %p",a,&a); // a is 4
// printf result
a is 4 and addr is 0x106012954
a is 5 and addr is 0x106012954
a is 6 and addr is 0x106012954
a is 7 and addr is 0x106012954- 修饰全局变量
#import "ViewController.h"
static int a = 24;
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation TestViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// a is visibility in ViewController.m
}
@end
- 被修饰的全局变量只在当前文件下有效
const
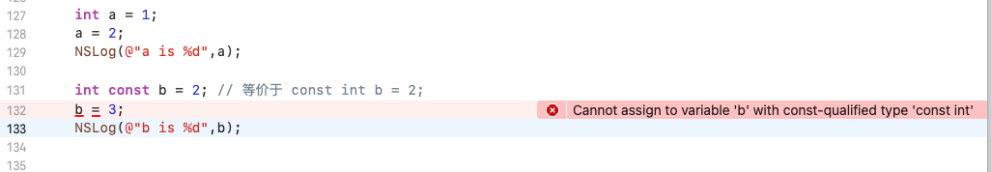
- 修饰基本变量
const修饰基本变量
- 修饰指针变量
注释:const修饰右侧的变量
Line:150 152 154是等价的,修饰的都是*q
Line:153 修饰的是q- iOS中的应用
- 修饰全局变量,保证外部无法修改变量,只读变量,提高预编译(刚打开Xcode的时候Xcode进行的加载)速度
// in ViewController.m
NSString * const kTableViewCell = @"kTableViewCell";- static & const
- static:修饰变量,修改作用域
- const:修饰变量,值不会被更改
static NSString * const kTableViewCell = @"kTableViewCell";
❝结论:使用static和const修饰的变量的作用域是在当前文件,且不会被更改
- extern&const
- extern:修饰变量,声明一个全局变量
- const:修饰变量,值不会被更改
// in BViewController.h file
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
// Read news event
extern NSString * const SNNewsReadNewsEvent;
@interface BViewController : UIViewController
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
// in BViewController.m file
#import "BViewController.h"
NSString * const SNNewsReadNewsEvent = @"SNNewsReadNewsEvent";
@interface BViewController ()
@end
@implementation BViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
}iOS下的extern
- extern
可以修饰任何的变量,字符串,整型,浮点型;多处声明,一处实现-
UIKIT_EXTERN
在UIKIT框架处理,通过文章开头的例子概括就是将函数修饰以兼容C++编译方式的,具有extern属性的(对外部文件可见)一个宏字段
UIKIT_EXTERN是在UIKit框架里面UIKitDefines.h中定义的- FOUNDATION_EXTERN
- 在
Foundation框架处理,兼容C++的extern的宏 FOUNDATION_EXTERN是在Foundation框架里面NSObjCRuntime.h中定义的。
// in BViewController.h file
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
// UIKIT_EXTERN eg
UIKIT_EXTERN const CGFloat kAnimationInterval;
// FOUNDATION_EXTERN eg
FOUNDATION_EXTERN NSString * const kAnimationKey;
@interface BViewController : UIViewController
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
// in BViewController.m file
#import "BViewController.h"
const CGFloat kAnimationInterval = 0.5f;
NSString * const kAnimationKey = @"kAnimationKey";
@interface BViewController ()
@end
@implementation BViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
}
@end参考文档
- 宏定义的黑魔法:https://onevcat.com/2014/01/black-magic-in-macro/
- YYKit的应用场景:https://github.com/ibireme/YYKit/blob/master/YYKit/Base/YYKitMacro.h
- G++ Attributes of Variables:https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Variable-Attributes.html
- G++ AAttributes of Functions:https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Function-Attributes.html
结束语
❝关于一个小小的宏字段,引发了很多的畅想,还有一些更高级的用法,感兴趣的作者可以搜索下ReactiveCocoa这个框架,作者把宏应用到出神入化的地步,简直出天际!!!技术之路需要不断输入输出,我们都是平凡人,只不过看谁坚持的久而已。