Objective-C Method Swizzling 最佳实践
Objective-C 中的 Hook 又被称作 Method Swizzling,这是动态语言大都具有的特性。在 Objective-C 中经常会把 Hook 的逻辑写在 + load 方法中,这是利用它调用时机较提前等性质。
有时候需要 Hook 子类和父类的同一个方法,但是它们的 + load 方法调用顺序不同。一个常见的顺序可能是:父类->子类->子类类别->父类类别。所以 Hook 的顺序并不能保证,就不能保证 Hook 后方法调用的顺序是对的。而且使用不同方法 Method Swizzling 也会带来不同的结果。本文将会对这些情况下的 Hook 结果进行分析和总结。
Method Swizzling 常用实现方案
目前有两类常用的 Method Swizzling 实现方案,诸如 RSSwizzle 和 jrswizzle 这种较为复杂且周全的一些实现方案这里暂且不提。
方案 A
如果类中没有实现 Original selector 对应的方法,那就先添加 Method,并将其 IMP 映射为 Swizzle 的实现。然后替换 Swizzle selector 的 IMP 为 Original 的实现;否则交换二者 IMP。
+ (void)load
{
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Class aClass = [self class];
SEL originalSelector = @selector(method_original:);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(method_swizzle:);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, swizzledSelector);
BOOL didAddMethod =
class_addMethod(aClass,
originalSelector,
method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod),
method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(aClass,
swizzledSelector,
method_getImplementation(originalMethod),
method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
});
}有时为了避免方法命名冲突和参数 _cmd 被篡改,也会使用下面这种『静态方法版本』的 Method Swizzle。CaptainHook 中的宏定义也是采用这种方式,比较推荐:
typedef IMP *IMPPointer;
static void MethodSwizzle(id self, SEL _cmd, id arg1);
static void (*MethodOriginal)(id self, SEL _cmd, id arg1);
static void MethodSwizzle(id self, SEL _cmd, id arg1) {
// do custom work
MethodOriginal(self, _cmd, arg1);
}
BOOL class_swizzleMethodAndStore(Class class, SEL original, IMP replacement, IMPPointer store) {
IMP imp = NULL;
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(class, original);
if (method) {
const char *type = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
imp = class_replaceMethod(class, original, replacement, type);
if (!imp) {
imp = method_getImplementation(method);
}
}
if (imp && store) { *store = imp; }
return (imp != NULL);
}
+ (BOOL)swizzle:(SEL)original with:(IMP)replacement store:(IMPPointer)store {
return class_swizzleMethodAndStore(self, original, replacement, store);
}
+ (void)load {
[self swizzle:@selector(originalMethod:) with:(IMP)MethodSwizzle store:(IMP *)&MethodOriginal];
}然而上面的代码依然不是 Method Swizzling 的最佳实现。
方案 B
其实就是方案 A 的阉割版:
+ (void)load
{
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Class aClass = [self class];
SEL originalSelector = @selector(method_original:);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(method_swizzle:);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(aClass, swizzledSelector);
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
});
}直接交换 IMP 是很危险的。因为如果这个类中没有实现这个方法,class_getInstanceMethod() 返回的是某个父类的 Method 对象,这样 method_exchangeImplementations() 就把父类的原始实现(IMP)跟这个类的 Swizzle 实现交换了。这样其他父类及其其他子类的方法调用就会出问题,最严重的就是 Crash。
但如果这个类中实现了此方法,那么方案 A 等价于方案 B。
研究背景
这里对本文的研究背景进行一些假设和约定:
- 有三个类,Child 类继承 Super 类,Super 类继承 Base 类。
- 我们 Hook 了 Child 和 Super 的某个方法(而且是同一个方法)。
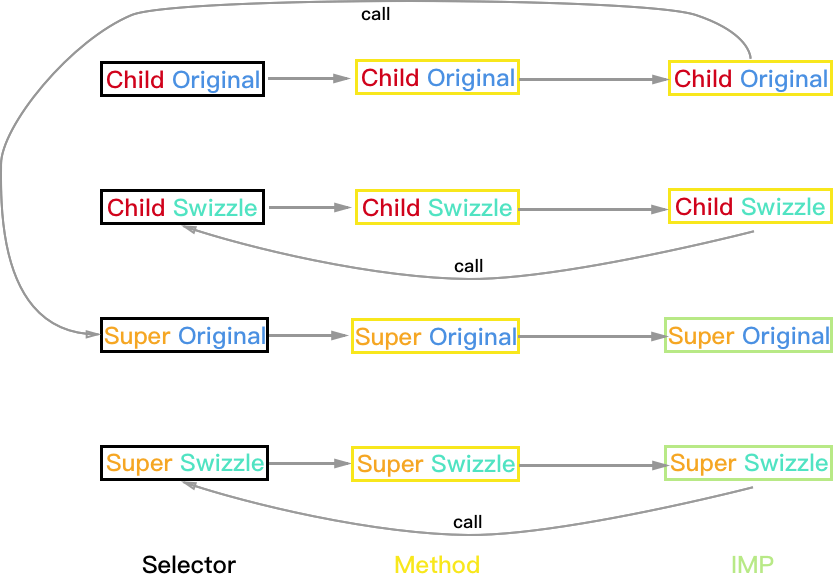
- 为了方便表示,Child 的原始方法被称作 Child_Original,Hook 后的方法被称作 Child_Swizzle。Super 以此类推。
- 为了让 Swizzle 的实现调用 Original 实现,Child_Swizzle 的 IMP 中会调用 Child_Swizzle 的 selector。Super 以此类推。
- 我们期望执行 Child 对象的 Child_Original 方法时的 IMP 执行顺序是:Child_Swizzle->Child_Original->Super_Swizzle->Super_Original->Base。我们只需关注其中 Swizzle 的部分,所以约定简写为:Child->Super->Base。
- 本文会按 Hook 顺序、类是否实现方法、Hook 方案(A/B) 来细分不同情况下的结果。一共细分为 18 种情况。
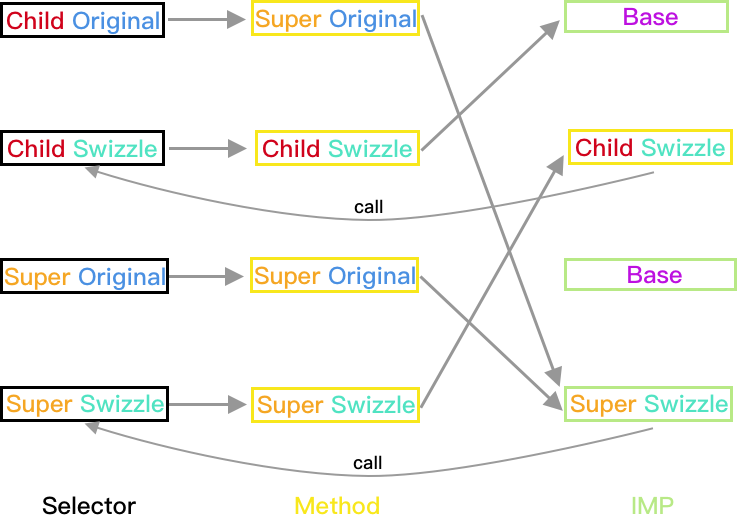
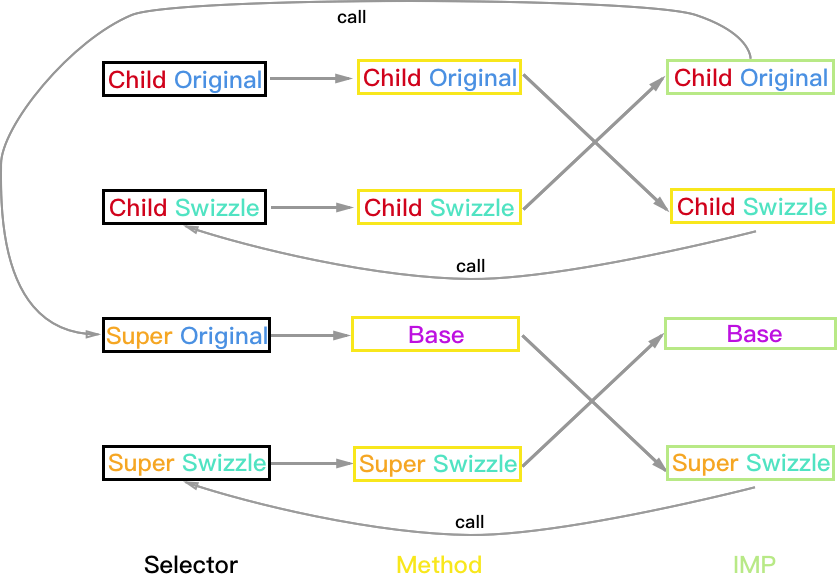
- 本文会使用图例表示每种情况下的方法调用和映射关系,分为三个维度(Super/Child;Original/Swizzle;Selector/Method/IMP)
下文中的图例均为 Hook 后的结果(Hook 前的太简单了懒得画)。如果不理解 Selector,Method 与 IMP 三者的关系,甚至不理解 Method Swizzling 原理,请先阅读 Objective-C Runtime!如果还是看不懂,那就再看一遍吧!
Hook 顺序:先 Child 后 Super
这个顺序本身就不被大众认可却又不得不广泛被使用,因为很多想 Hook 系统 API 只能从 Category 下手。当子类同样的方法也被 Hook 后,奇怪的事情便发生了。
Super 未实现方法, Child 未实现方法
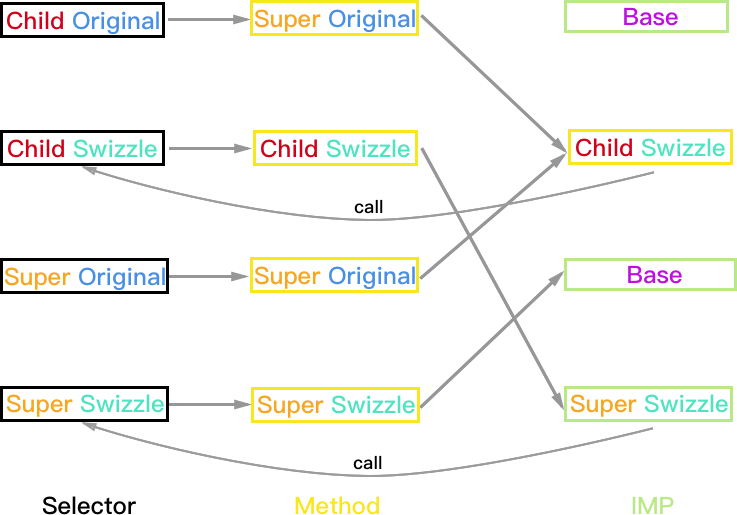
Super:PlanA, Child:PlanA
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:Child_Swizzle->Base (Super_Swizzle 被忽略)
- Super 和 Base 对象均正常
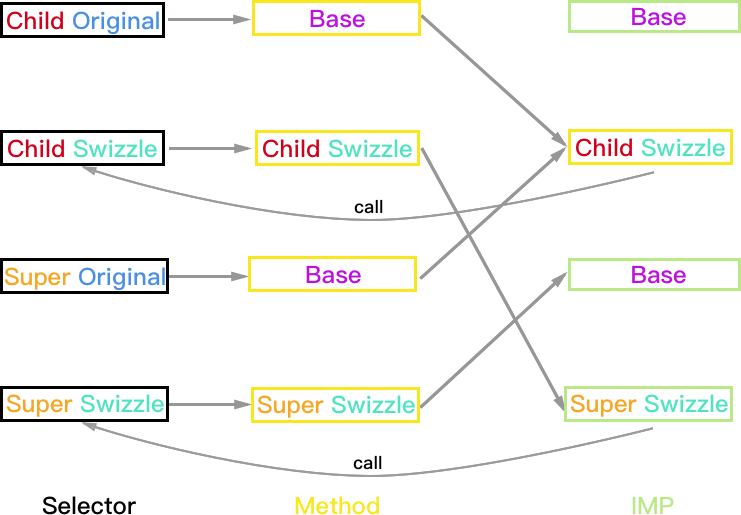
Super:PlanB, Child:PlanA
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:Child_Swizzle->Base (Super_Swizzle 被忽略)
- Super 对象正常:Super_Swizzle->Base
- Base 对象:产生 unrecognized selector 异常,此情况亦等同于:在子类类别中 Hook 了子类未实现而父类实现了的方法。(Super 是 Base 的子类)
Super:PlanA, Child:PlanB
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,结果是 Super_Swizzle->Child_Swizzle->Base (顺序错误);如果两个 selector 相同,则导致 Super_Swizzle 调用的是 Child_Swizzle 方法,结果是 Super_Swizzle->Base (Child_Swizzle 被忽略)。
- Super 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则会产生 unrecognized selector 异常;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child_Swizzle 进入死循环。
- Base 对象产生 unrecognized selector 异常,此情况亦间接等同于:在子类类别中 Hook 了子类未实现而父类实现了的方法。
Super:PlanB, Child: PlanB
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,结果是 Super_Swizzle->Child_Swizzle->Base (顺序错误);如果两个 selector 相同,则导致 Super_Swizzle 调用的是 Child_Swizzle 方法,结果是 Super_Swizzle->Base (Child_Swizzle 被忽略)。
- Super 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则会产生 unrecognized selector 异常;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child_Swizzle 进入死循环
- Base 对象产生 unrecognized selector 异常,此情况亦间接等同于:在子类类别中 Hook 了子类未实现而父类实现了的方法。
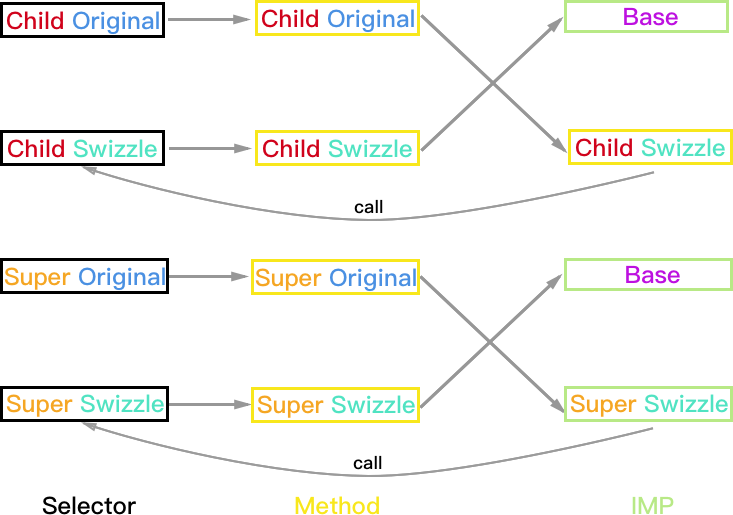
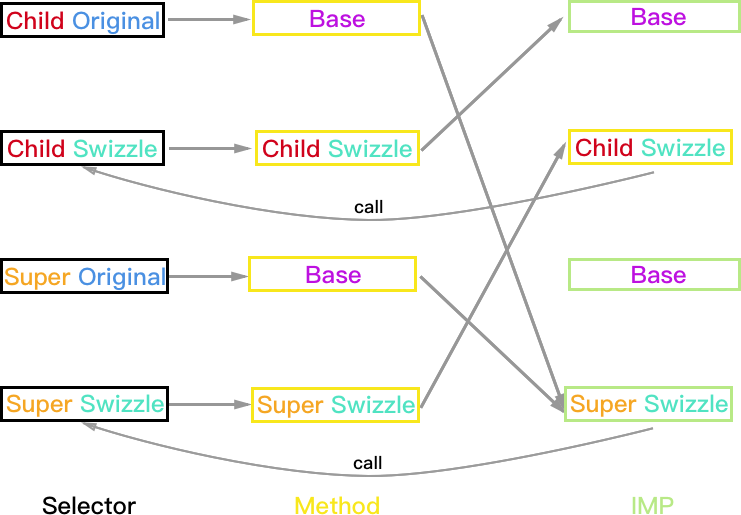
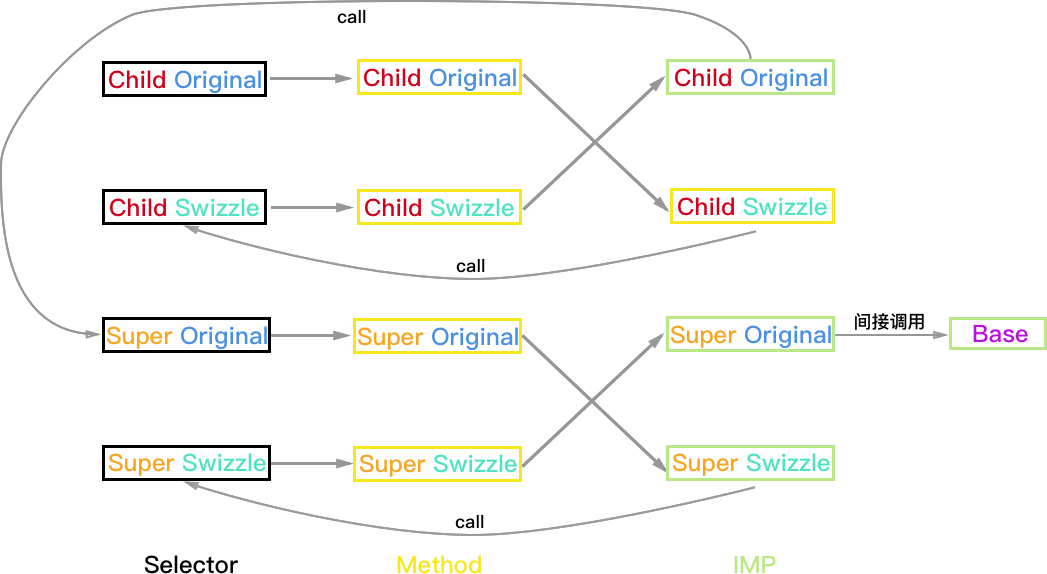
Super 实现方法, Child 未实现方法
由于 Super 类被 Hook 的方法已经被实现,所以只需区分 Child 的 Hook 方案。
Child:PlanA
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:Child_Swizzle->Super->Base (Super_Swizzle 被忽略)
- Super 和 Base 对象均正常
Child:PlanB
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果为 Super_Swizzle->Child_Swizzle->Super->Base (顺序错误);如果两个 selector 相同则结果为 Super_Swizzle->Super->Base (Child_Swizzle 被忽略)
- Super 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则会产生 unrecognized selector 异常;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child_Swizzle 进入死循环
- Base 对象正常
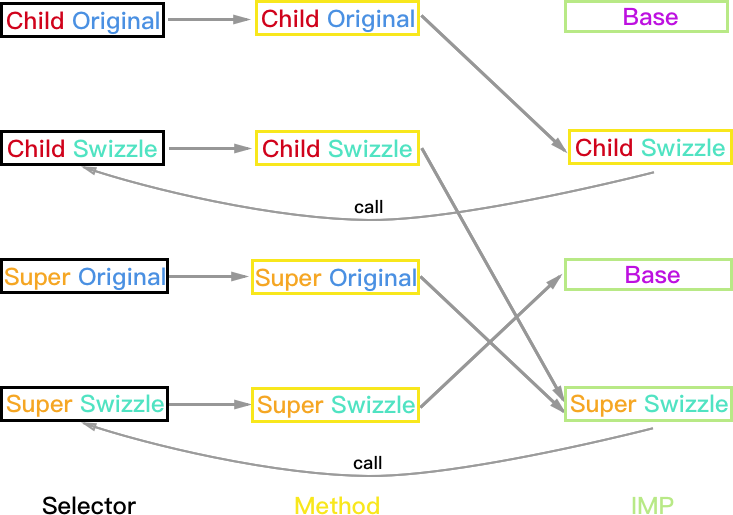
Super 未实现方法, Child 实现方法
由于 Child 类被 Hook 的方法已经被实现,所以只需区分 Super 的 Hook 方案。
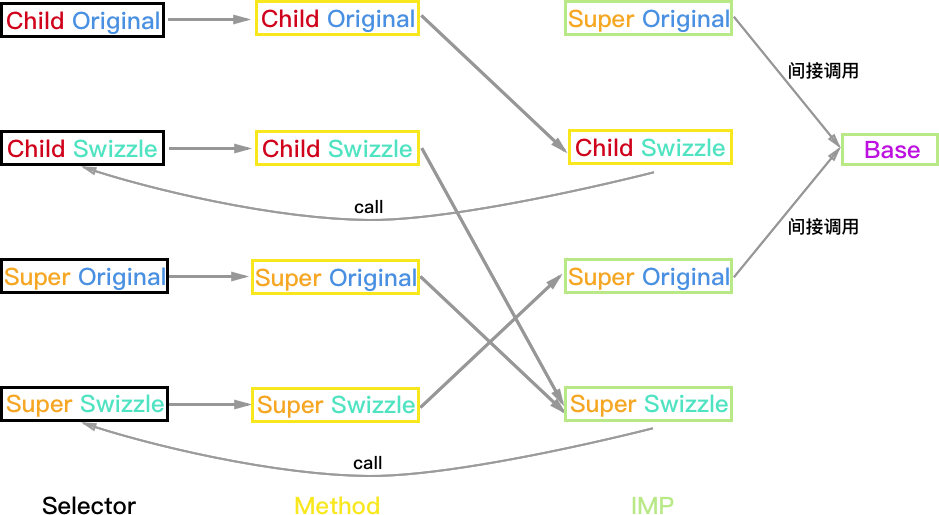
Super:PlanA
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Child->Super_Swizzle->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child 和 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 和 Base 对象均正常
Super:PlanB
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Child->Super_Swizzle->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child 和 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 对象正常:Super_Swizzle->Base
- Base 对象产生 unrecognized selector 异常,此情况亦等同于:在子类类别中 Hook 了子类未实现而父类实现了的方法。(Super 是 Base 的子类)
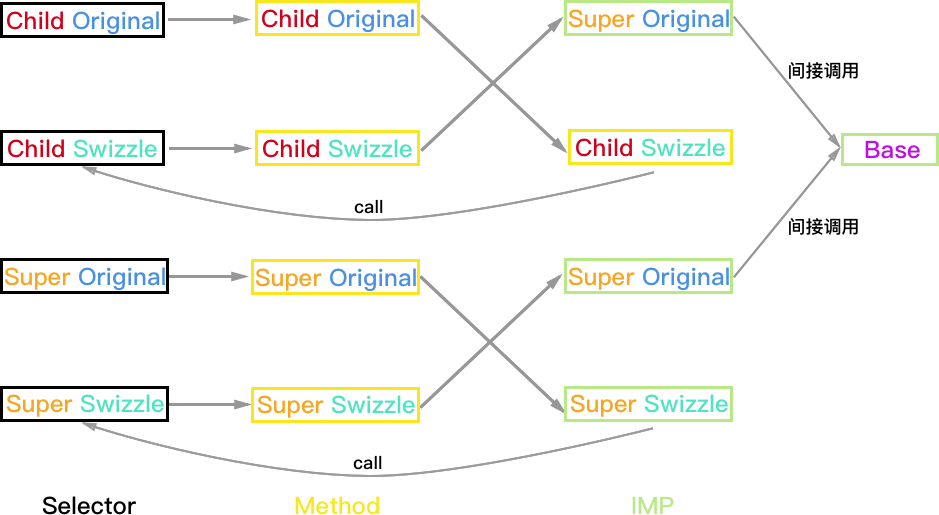
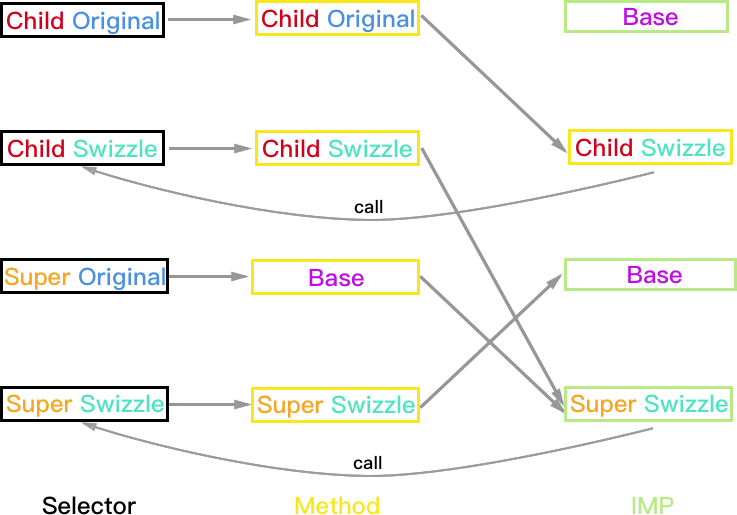
Super 实现方法, Child 实现方法
相当于 Super 和 Child 都使用方案 B 进行 Hook,所以只有一种情况。
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Child->Super_Swizzle->Super->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child 和 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 和 Base 对象均正常
Hook 顺序:先 Super 后 Child
并不是 Hook 顺序对了就能保平安,姿势也同样重要。
Super 未实现方法, Child 未实现方法
Super:PlanA, Child:PlanA
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Super_Swizzle->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 和 Base 对象均正常
Super:PlanB, Child:PlanA
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Super_Swizzle->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 对象正常:Super_Swizzle->Base
- Base 对象产生 unrecognized selector 异常,此情况亦等同于:在子类类别中 Hook 了子类未实现而父类实现了的方法。(Super 是 Base 的子类)
Super:PlanA, Child PlanB
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常:Child_Swizzle->Super_Swizzle->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则会产生 unrecognized selector 异常;如果两个 selector 相同则 Child_Swizzle->Base (Super_Swizzle 被忽略)
- Base 对象正常
Super:PlanB, Child PlanB
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常为 Child_Swizzle->Super_Swizzle->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则会产生 unrecognized selector 异常;如果两个 selector 相同则 Child_Swizzle->Base (Super_Swizzle 被忽略)
- Base 对象产生 unrecognized selector 异常
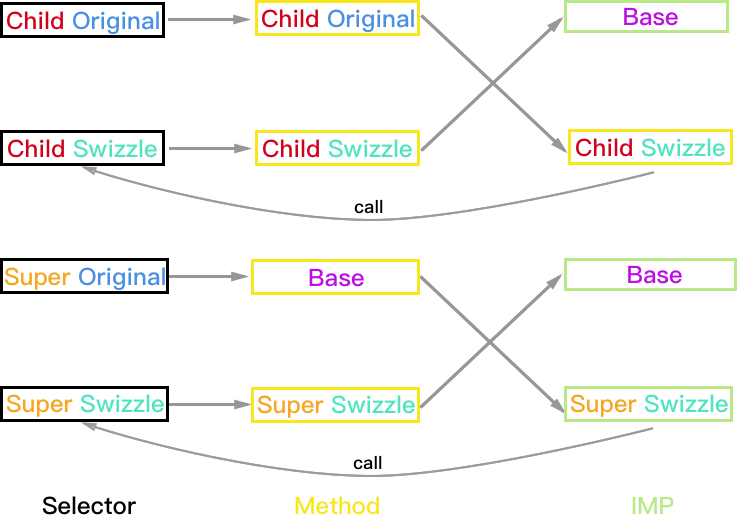
Super 实现方法, Child 未实现方法
由于 Super 类被 Hook 的方法已经被实现,所以只需区分 Child 的 Hook 方案。
Child:PlanA
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Super_Swizzle->Super->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 和 Base 对象均正常
Child:PlanB
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Super_Swizzle->Super->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则会产生 unrecognized selector 异常;如果两个 selector 相同则结果为 Child_Swizzle->Super->Base (Super_Swizzle 被忽略)
- Base 对象正常
Super 未实现方法, Child 实现方法
由于 Child 类被 Hook 的方法已经被实现,所以只需区分 Super 的 Hook 方案。
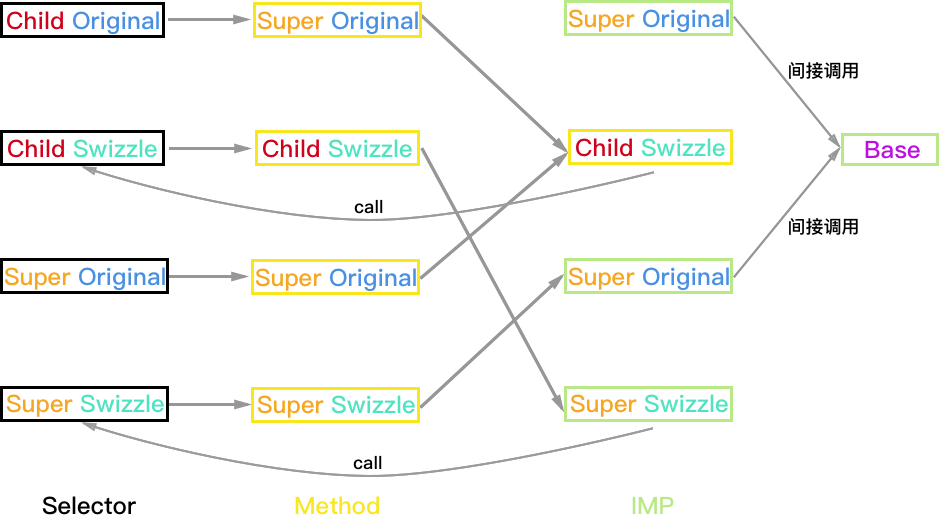
Super:PlanA
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Child->Super_Swizzle->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child 和 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 和 Base 对象均正常
Super:PlanB
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Child->Super_Swizzle->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child 和 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 对象正常:Super_Swizzle->Base
- Base 对象产生 unrecognized selector 异常,此情况亦等同于:在子类类别中 Hook 了子类未实现而父类实现了的方法。(Super 是 Base 的子类)
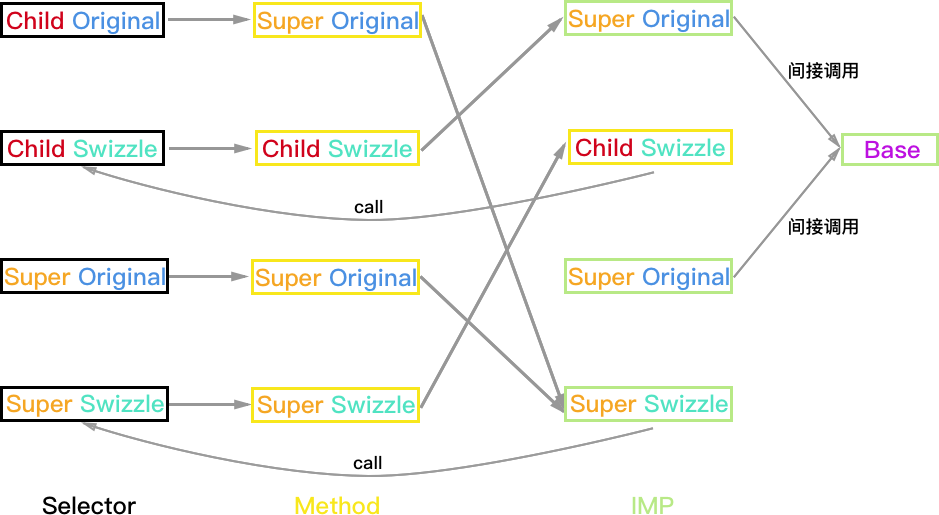
Super 实现方法, Child 实现方法
相当于 Super 和 Child 都使用方案 B 进行 Hook,所以只有一种情况。
方法执行结果:
- Child 对象:如果 Super_Swizzle 与 Child_Swizzle 的 selector 不同,则结果正常 Child_Swizzle->Child->Super_Swizzle->Super->Base;如果两个 selector 相同则会一直调用 Child 和 Super_Swizzle 死循环。
- Super 和 Base 对象均正常
结论
Hook 顺序:先 Child 类后 Super 类
为了保证 Hook 后方法调用顺序是对的,需要同时满足以下三个条件:
- Child 类实现被 Hook 的方法
- Super 和 Child 中用于 Swizzle 新增的方法命名不同
- Super 类实现被 Hook 的方法或使用 A 方案 Hook
Hook 顺序:先 Super 类后 Child 类
虽然 Hook 的顺序是正确的,也需要同时满足以下两个条件才能保证调用顺序也是对的:
- Super 类和 Child 类中用于 Swizzle 新增的方法命名不同
- 类实现了被 Hook 的方法或使用方案 A 来 Hook
Objective-C Method Swizzling 最佳实践
- Hook 顺序并不能保证结果一定正确,但先 Super 后 Child 更加安全
- 如果 Hook 父类和子类的同一个方法,用于 Swizzle 的方法名需要保持唯一。如果子类用于 Hook 的新增方法名与父类相同,则会导致调用逻辑错误或死循环。
- 方案 A 明显优于方案 B。方案 A 中的『静态方法版本』固然更缜密,但操作复杂。为了提升开发效率,建议参考 CaptainHook 的宏定义实现。
- RSSwizzle 被很多人推荐,它用很复杂的方式解决了 What are the Dangers of Method Swizzling in Objective C? 中提到的一系列问题。不过引入它还是有一些成本的,建议在本文列举的那些极端特殊情况下才使用它,毕竟方案 A 已经能 Cover 到大部分情况了。
- jrswizzle 尝试解决在不同平台和系统版本上的 Method Swizzling 与类继承关系的冲突。对各平台低版本系统兼容性较强。
我觉得最适合项目的方案才是最佳实践。