造一个 react-error-boundary 轮子
| 导语 捕获和处理前端组件异常是个十分重要且必要的操作。对于 React 来说,一般用 ErrorBoundary 来实现,今天就带大家一起造一个 react-error-boundary 的轮子吧~。
发生甚么事了
朋友们好,我是 ABCMouse 的一位前端开发,刚才老板对我说:海怪,发生甚么事了,怎么页面白屏了?我说:怎么回事?给我发了几张截图。我打开控制台一看:
哦!原来是昨天,有个后端年轻人,说要和我联调接口,我说:可以。然后,我说:小兄弟,你的数据尽量按我需要的格式来:
interface User {
name: string;
age: number;
}
interface GetUserListResponse {
retcode: number;
data: User[]
}他不服气,他说:你这个没用。我说:我这个有用,这是规范,传统前后端联调返回数据是要讲规范的,对项目质量的提高可以起到四两拨千斤的作用。100多万行代码的系统,只要有了类型规范,都不会轻易崩溃。他说试试,我说行。
我请求刚发出去,他的数据,啪!一下就返回了!很快啊!!
{
retcode: 0,
data: [
{name: '张三', age: 11},
undefined,
null
]
}上来先是一个 retcode: 0,然后数组里一个 User 对象,一个 undefined,一个 null,我全部用判断 falsy 值防过去了啊。防过去之后自然是正常处理业务逻辑和页面展示。我笑一下把代码发到线上,准备收工。然后,现在线上突然白屏,我一看返回的数据:
{
retcode: 0,
data: [
{name: '张三', age: 11},
'找不到此用户',
'找不到此用户',
'找不到此用户'
]
}我大意了啊!没有做类型判断!虽然这个是后端的异常问题,但是前端也不应该出现白屏。对于这种异常情况,应该使用 React 提供的 “Error Boundary 错误便捷特性” 来处理。下面来说说怎么打好这一套 Error Boundary。
第一步:抄
直接把官网例子抄下来,将 ErrorBoundary 组件输出:
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// 更新 state 使下一次渲染能够显示降级后的 UI
return { hasError: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
// 你同样可以将错误日志上报给服务器
logger.error(error, errorInfo);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// 你可以自定义降级后的 UI 并渲染
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}然后将业务组件包裹:
<ErrorBoundary> // 捕获错误
<UserList /> // 使劲报错
</ErrorBoundary>如果 UserList 里报错,ErrorBoundary 就会捕获,然后在 getDerivedStateFromError 里更新组件状态,render 里就会显示 Something went wrong,不会渲染 this.props.children。
总结:
- 将 ErrorBoundary 包裹可能出错的业务组件;
- 当业务组件报错时,会调用 componentDidCatch 钩子里的逻辑,将 hasError 设置 true,直接展示 。
第二步:造个灵活的轮子
上面只是解决了燃眉之急,如果真要造一个好用的轮子,不应直接写死 return Something went wrong,应该添加 props 来传入报错显示内容(以下统称为 fallback):
// 出错后显示的元素类型
type FallbackElement = React.ReactElement<unknown, string | React.FC | typeof React.Component> | null;
// 出错显示组件的 props
export interface FallbackProps {
error: Error;
}
// 本组件 ErrorBoundary 的 props
interface ErrorBoundaryProps {
fallback?: FallbackElement;
onError?: (error: Error, info: string) => void;
}
// 本组件 ErrorBoundary 的 props
interface ErrorBoundaryState {
error: Error | null; // 将 hasError 的 boolean 改为 Error 类型,提供更丰富的报错信息
}
// 初始状态
const initialState: ErrorBoundaryState = {
error: null,
}
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component<React.PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>, ErrorBoundaryState> {
state = initialState;
static getDerivedStateFromError(error: Error) {
return {error};
}
componentDidCatch(error: Error, errorInfo: React.ErrorInfo) {
if (this.props.onError) {
this.props.onError(error, errorInfo.componentStack);
}
}
render() {
const {fallback} = this.props;
const {error} = this.state;
if (error !== null) {
if (React.isValidElement(fallback)) {
return fallback;
}
throw new Error('ErrorBoundary 组件需要传入 fallback');
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary上面提供 onError 和 fallback 两个 props,前者为出错的回调,可以做错误信息上报或者用户提示,后者则传入错误提示内容,像下面这样:
const App = () => {
return (
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<div>出错啦</div>} onError={logger.error('出错啦')}>
<UserList />
</ErrorBoundary>
)
}这已经让 ErrorBoundary 变得稍微灵活一点了。但是有人就喜欢把 fallback 渲染函数、Fallback 组件作为 props 传入 ErrorBoundary,而不传一段 ReactElement,所以为了照顾更多人,将 fallback 进行扩展:
export declare function FallbackRender (props: FallbackProps): FallbackElement;
// 本组件 ErrorBoundary 的 props
interface ErrorBoundaryProps {
fallback?: FallbackElement; // 一段 ReactElement
FallbackComponent?: React.ComponentType<FallbackProps>; // Fallback 组件
fallbackRender?: typeof FallbackRender; // 渲染 fallback 元素的函数
onError?: (error: Error, info: string) => void;
}
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component<React.PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>, ErrorBoundaryState> {
...
render() {
const {fallback, FallbackComponent, fallbackRender} = this.props;
const {error} = this.state;
// 多种 fallback 的判断
if (error !== null) {
const fallbackProps: FallbackProps = {
error,
}
// 判断 fallback 是否为合法的 Element
if (React.isValidElement(fallback)) {
return fallback;
}
// 判断 render 是否为函数
if (typeof fallbackRender === 'function') {
return (fallbackRender as typeof FallbackRender)(fallbackProps);
}
// 判断是否存在 FallbackComponent
if (FallbackComponent) {
return <FallbackComponent {...fallbackProps} />
}
throw new Error('ErrorBoundary 组件需要传入 fallback, fallbackRender, FallbackComponent 其中一个');
}
return this.props.children;
}
}上面提供 3 种方式来传入出错提示组件:fallback(元素)、FallbackComponent(组件),fallbackRender(render 函数)。现在使用轮子就更灵活了:
const App = () => {
const onError = () => logger.error('出错啦')
return (
<div>
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<div>出错啦</div>} onError={onError}>
<UserList />
</ErrorBoundary>
<ErrorBoundary FallbackComponent={ErrorFallback} onError={onError}>
<UserList />
</ErrorBoundary>
<ErrorBoundary
fallbackRender={(fallbackProps) => <ErrorFallback {...fallbackProps} />}
onError={onError}
>
<UserList />
</ErrorBoundary>
</div>
)
}总结:
- 将原来的 hasError 转为 error,从 boolean 转为 Error 类型,有利于获得更多的错误信息,上报错误时很有用;
- 添加 fallback, FallbackComponent, fallbackRender 3个 props,提供多种方法来传入展示 fallback。
第三步:添加重置回调
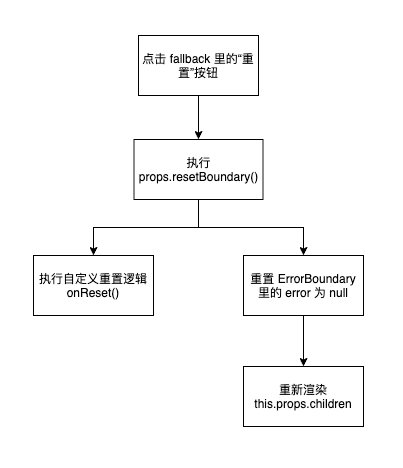
有时候会遇到这种情况:服务器突然抽风了,503、502了,前端获取不到响应,这时候某个组件报错了,但是过一会又正常了。比较好的方法是允许用户点一下 fallback 里的一个按钮来重新加载出错组件,不需要重刷页面,这样的操作下面称为“重置”。
同时,有些开发者也需要在重置里添加自己逻辑,比如弹提示、日志上报等。
图解:
下面给出上面两个需求的实现:
const App = () => {
const onError = () => logger.error('出错啦')
const onReset = () => {
console.log('已重置')
message.info('刚刚出错了,不好意思,现在已经重置好了,请找老板锤这个开发')
}
// fallback 组件的渲染函数
const renderFallback = (props: FallbackProps) => {
return (
<div>
出错啦,你可以<button onClick={props.resetErrorBoundary}>重置</button>
</div>
)
}
return (
<div>
<ErrorBoundary
fallbackRender={renderFallback}
onReset={onReset}
onError={onError}
>
<UserList />
</ErrorBoundary>
</div>
)
}上面例子中,在 onReset 里自定义想要重试的逻辑,然后在 renderFallback 里将 props.resetErrorBoudnary 绑定到重置即可,当点击“重置”时,就会调用 onReset ,同时将 ErrorBoundary 组件状态清空(将 error 设为 null)。
总结:
- 添加onReset来实现重置的逻辑;
- 在fallback组件里找个按钮绑定 props.resetErrorBoundary 来触发重置逻辑。
第四步:监听渲染以重置
上面的重置逻辑简单也很实用,但是有时也会有局限性:触发重置的动作只能在 fallback 里面。假如我的重置按钮不在 fallback 里呢?或者 onReset 函数根本不在这个 App 组件下那怎么办呢?难道要将 onReset 像传家宝一路传到这个 App 再传入 ErrorBoundary 里?
这时,我们就会想:能不能监听状态的更新,只要状态更新就重置,反正就重新加载组件也没什么损失,这里的状态完全用全局状态管理,放到 Redux 中。
上面的思路听起来不就和 useEffect 里的依赖项 deps 数组一样嘛,不妨在 props 提供一个 resetKeys 数组,如果这个数组里的东西变了,ErrorBoundary 就重置,这样一控制是否要重置就更灵活了。马上动手实现一下:
// 本组件 ErrorBoundary 的 props
interface ErrorBoundaryProps {
...
resetKeys?: Array<unknown>;
}
// 检查 resetKeys 是否有变化
const changedArray = (a: Array<unknown> = [], b: Array<unknown> = []) => {
return a.length !== b.length || a.some((item, index) => !Object.is(item, b[index]));
}
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component<React.PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>, ErrorBoundaryState> {
...
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: Readonly<React.PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>>) {
const {error} = this.state;
const {resetKeys, onResetKeysChange} = this.props;
// 只要 resetKeys 有变化,直接 reset
if (changedArray(prevProps.resetKeys, resetKeys)) {
// 重置 ErrorBoundary 状态,并调用 onReset 回调
this.reset();
}
}
render() {
...
}
}首先,在 componentDidupdate 里去做 resetKeys 的监听,只要组件有 render 就看看 resetKeys 里面的元素是否改过了,改过了就会重置。但这里又会有一个问题:万一 resetKeys 里元素是个 Date 或者一个对象怎么办?所以,我们还需要给开发者提供一种判断 resetKeys 元素是否改变的方法,这里就添加一个 onResetKeysChange 的 props 就好了:
// 本组件 ErrorBoundary 的 props
interface ErrorBoundaryProps {
...
resetKeys?: Array<unknown>;
onResetKeysChange?: (
prevResetKey: Array<unknown> | undefined,
resetKeys: Array<unknown> | undefined,
) => void;
}
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component<React.PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>, ErrorBoundaryState> {
...
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: Readonly<React.PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>>) {
const {resetKeys, onResetKeysChange} = this.props;
if (changedArray(prevProps.resetKeys, resetKeys)) {
if (onResetKeysChange) {
onResetKeysChange(prevProps.resetKeys, resetKeys);
}
// 重置 ErrorBoundary 状态,并调用 onReset 回调
this.reset();
}
}
render() {
...
}
}在 changedArray 判定后,再次使用 props.onResetKeysChange 再次自定义判断(如果有的话)resetKeys 里的元素值是否有更新。还有没有问题呢?嗯,还有问题。这里注意这里的 componentDidUpdate 钩子逻辑,假如某个 key 是触发 error 的元凶,那么就有可能触发二次 error 的情况:
- xxxKey 触发了 error,组件报错;
- 组件报错导致 resetKeys 里的一些东西改了;
- componentDidUpdate 发现 resetKeys 里有东西更新了,不废话,马上重置;
- 重置完了,显示报错的组件,因为 error 还存在(或者还未解决),报错的组件又再次触发了 error;
- ...
所以要区分出来这一次到底是因为 error 才 render 还是普通组件的 render,而且还需要确保当前有错误才重置,都没错误还重置个毛。具体实现思路如图所示:
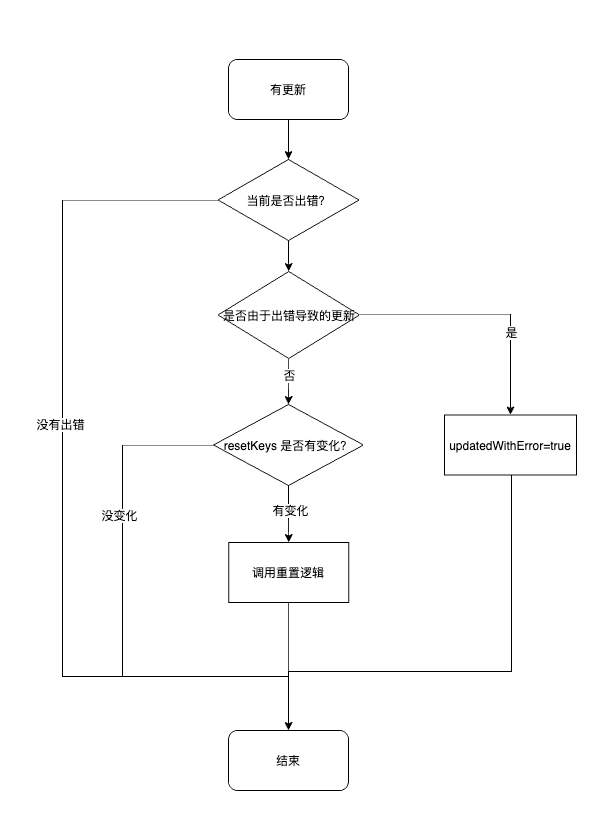
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component<React.PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>, ErrorBoundaryState> {
state = initialState;
// 是否已经由于 error 而引发的 render/update
updatedWithError = false;
static getDerivedStateFromError(error: Error) {
return {error};
}
componentDidCatch(error: Error, errorInfo: React.ErrorInfo) {
if (this.props.onError) {
this.props.onError(error, errorInfo.componentStack);
}
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps: Readonly<React.PropsWithChildren<ErrorBoundaryProps>>) {
const {error} = this.state;
const {resetKeys, onResetKeysChange} = this.props;
// 已经存在错误,并且是第一次由于 error 而引发的 render/update,那么设置 flag=true,不会重置
if (error !== null && !this.updatedWithError) {
this.updatedWithError = true;
return;
}
// 已经存在错误,并且是普通的组件 render,则检查 resetKeys 是否有改动,改了就重置
if (error !== null && changedArray(prevProps.resetKeys, resetKeys)) {
if (onResetKeysChange) {
onResetKeysChange(prevProps.resetKeys, resetKeys);
}
this.reset();
}
}
reset = () => {
this.updatedWithError = false;
this.setState(initialState);
}
resetErrorBoundary = () => {
if (this.props.onReset) {
this.props.onReset();
}
this.reset();
}
render() {
...
}
}上面的改动有:
- 用updatedWithError 作为 flag 判断是否已经由于 error 出现而引发的 render/update;
- 如果当前没有错误,无论如何都不会重置;
- 每次更新:当前存在错误,且第一次由于 error 出现而引发的 render/update,则设置 updatedWithError= true,不会重置状态;
- 每次更新:当前存在错误,且如果 updatedWithError 为 true 说明已经由于 error 而更新过了,以后的更新只要 resetKeys 里的东西改了,都会被重置;
至此,我们拥有了两种可以实现重置的方式了:
| 方法 | 触发范围 | 使用场景 | 思想负担 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 手动调用 resetErrorBoundary | 一般在 fallback 组件里 | 用户可以在 fallback 里手动点击“重置”实现重置 | 最直接,思想负担较轻 |
| 更新 resetKeys | 哪里都行,范围更广 | 用户可以在报错组件外部重置、resetKeys 里有报错组件依赖的数据、渲染时自动重置 | 间接触发,要思考哪些值放到 resetKeys 里,思想负担较重 |
总结:
- 添加resetKeys和onResetKeysChange两个props,为开发者提供监听值变化而自动重置的功能;
- 在 componentDidUpdate 里,只要不是由于 error 引发的组件渲染或更新,而且 resetKeys 有变化了,那么直接重置组件状态来达到自动重置;
这里自动重置还有一个好处:假如是由于网络波动引发的异常,那页面当然会显示 fallback 了,如果用上面直接调用 props.resetErrorBoundary 方法来重置,只要用户不点“重置”按钮,那块地方永远不会被重置。又由于是因为网络波动引发的异常,有可能就那0.001 秒有问题,别的时间又好了,所以如果我们将一些变化频繁的值放到 resetKeys 里就很容易自动触发重置。例如,报错后,其它地方的值变了从而更改了 resetKeys 的元素值就会触发自动重置。对于用户来说,最多只会看到一闪而过的 fallback,然后那块地方又正常了。这样一来,用户也不需要亲自触发重置了。
第五步:输出轮子
上面第四步里,到最后都是 export default ErrorBoundary 将组件输出,如果代理里很多个地方都要 catch error,就有这样很啰嗦的代码:
<div>
<ErrorBoundary>
<AAA/>
</ErrorBoundary>
<ErrorBoundary>
<BBB/>
</ErrorBoundary>
<ErrorBoundary>
<CCC/>
</ErrorBoundary>
<ErrorBoundary>
<DDD/>
</ErrorBoundary>
</div>要处理这样啰嗦的包裹,可以借鉴 React Router 的 withRouter 函数,我们也可以输出一个高阶函数 withErrorBoundary :
/**
* with 写法
* @param Component 业务组件
* @param errorBoundaryProps error boundary 的 props
*/
function withErrorBoundary<P> (Component: React.ComponentType<P>, errorBoundaryProps: ErrorBoundaryProps): React.ComponentType<P> {
const Wrapped: React.ComponentType<P> = props => {
return (
<ErrorBoundary {...errorBoundaryProps}>
<Component {...props}/>
</ErrorBoundary>
)
}
// DevTools 显示的组件名
const name = Component.displayName ||Component.name || 'Unknown';
Wrapped.displayName = `withErrorBoundary(${name})`;
return Wrapped;
}使用的时候就更简洁了一些了:
// 业务子组件
const User = () => {
return <div>User</div>
}
// 在业务组件加一层 ErrorBoundary
const UserWithErrorBoundary = withErrorBoundary(User, {
onError: () => logger.error('出错啦'),
onReset: () => console.log('已重置')
})
// 业务父组件
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<UserWithErrorBoundary/>
</div>
)
}其实 withXXX 这种写法还可以写成装饰其,将 @withXXX 放到 class component 上也很方便,这里就不展开了。
还有没有更好的设计呢?我们观察到只有一些比较“严重的异常”浏览器才会报错,比如开头提到的 TypeError: xxx is not a function。JS 是个动态类型语言,在浏览器里你可以:NaN + 1,可以 NaN.toString(),可以 '1' + 1 都不报任何错误。其实官网也说了,对于一些错误 componenDidCatch 是不能自动捕获的:

- 有错误的时候,开发者自己调用 handleError(error) 将错误传入函数中;
- handleError 将错误 throw new Error(error);
- ErrorBoundary 发现有上面抛出的 Error,调用 componentDidCatch 处理错误;
- ...
我来提供一种使用 React Hook 的实现方式:
/**
* 自定义错误的 handler
* @param givenError
*/
function useErrorHandler<P=Error>(
givenError?: P | null | undefined,
): React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<P | null>> {
const [error, setError] = React.useState<P | null>(null);
if (givenError) throw givenError; // 初始有错误时,直接抛出
if (error) throw error; // 后来再有错误,也直接抛出
return setError; // 返回开发者可手动设置错误的钩子
}使用上面的 hook,对于一些需要自己处理的错误,可以有两种处理方法:
- const handleError = useErrorHandler(),然后 handleError(yourError);
- useErrorHandler(otherHookError),如果别的 hooks 里有 export error,完全可以直接将这个 error 传入 useErrorHandler,直接处理;
比如:
function Greeting() {
const [greeting, setGreeting] = React.useState(null)
const handleError = useErrorHandler()
function handleSubmit(event) {
event.preventDefault()
const name = event.target.elements.name.value
fetchGreeting(name).then(
newGreeting => setGreeting(newGreeting),
handleError, // 开发者自己处理错误,将错误抛出
)
}
return greeting ? (
<div>{greeting}</div>
) : (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<label>Name</label>
<input id="name" />
<button type="submit">get a greeting</button>
</form>
)
}
// 用 ErrorBoundary 包裹,处理手动抛出的错误
export default withErrorBoundary(Greeting)或者:
function Greeting() {
const [name, setName] = React.useState('')
const {greeting, error} = useGreeting(name)
// 开发者自己处理错误,将错误抛出
useErrorHandler(error)
function handleSubmit(event) {
event.preventDefault()
const name = event.target.elements.name.value
setName(name)
}
return greeting ? (
<div>{greeting}</div>
) : (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<label>Name</label>
<input id="name" />
<button type="submit">get a greeting</button>
</form>
)
}
// 用 ErrorBoundary 包裹,处理手动抛出的错误
export default withErrorBoundary(Greeting)总结:
- 提供 withErrorBoundary 方法来包裹业务组件实现异常捕获;
- 提供 useErrorHandler hook 让开发者自己处理/抛出错误。
总结
再次总结一下上面的要点:
- 造一个 ErrorBoundary 轮子;
- componentDidCatch 捕获页面报错,getDerivedStateFromError 更新 ErrorBoundary 的 state,并获取具体 error;
- 提供多种展示错误内容入口:fallback, FallbackComponent, fallbackRender;
- 重置钩子:提供 onReset, resetErrorBoundary 的传值和调用,以实现重置;
- 重置监听数组:监听 resetKeys 的变化来重置。对于拥有复杂元素的 resetKeys 数组提供 onResetKeysChange 让开发者自行判断。在 componentDidUpdate 里监听每次渲染时 resetKeys 变化,并设置 updatedWithError 作为 flag 判断是否由于 error 引发的渲染,对于普通渲染,只要 resetKeys 变化,直接重置;
- 提供 ErrorBoundary 的2种使用方法:嵌套业务组件,将业务组件传入withErrorBoundary 高阶函数。提供 useErrorBoundary 钩子给开发者自己抛出 ErrorBoundary 不能自动捕获的错误;