手撕源码系列:80行代码实现express框架
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
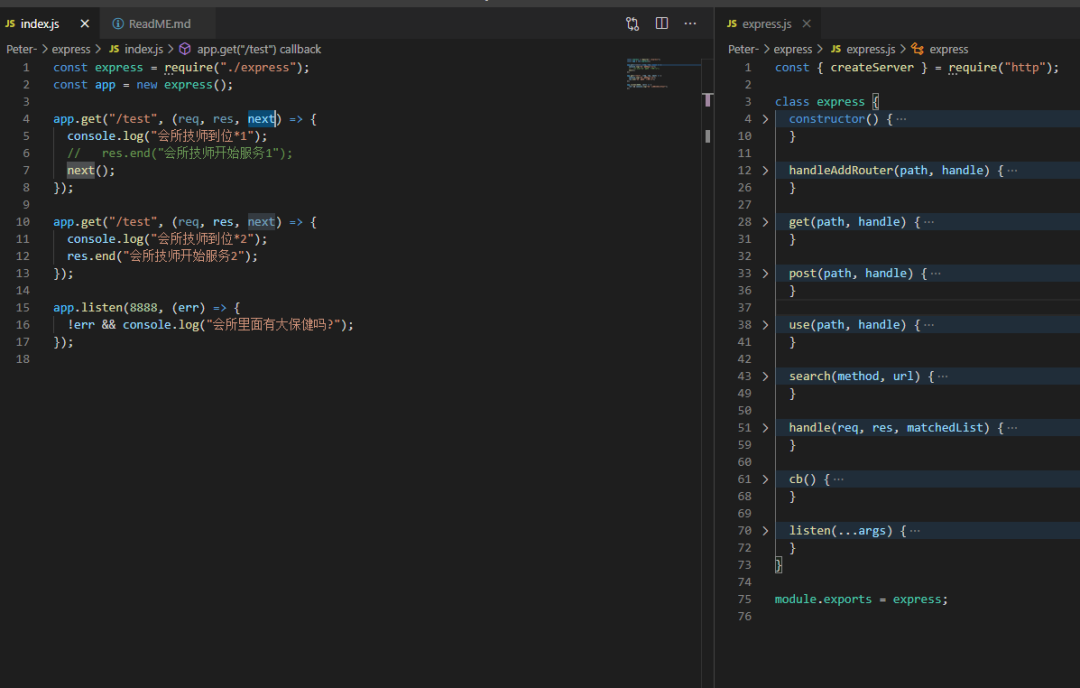
app.get("/test", (req, res, next) => {
console.log("会所技师到位*1");
// res.end("会所技师开始服务1");
next();
});
app.get("/test", (req, res, next) => {
console.log("会所技师到位*2");
res.end("会所技师开始服务2");
});
app.listen(8888, (err) => {
!err && console.log("会所里面有大保健吗?");
});
- 以上为express的基本用法
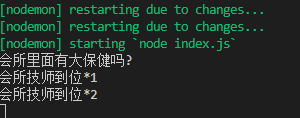
- 当我访问
localhost:8888/test时候,返回了:会所技师开始服务 2,服务端打印了
会所技师到位*1
会所技师到位*2- 从上面可以看到什么?
app.listen会启动进程监听端口- 每次收到请求,对应的
url和method会触发相应挂载在app上对应的回调函数 - 调用
next方法,会触发下一个 express默认引入调用后返回一个app对象
一起来实现一个简单的express框架
- 定义属于我们的
express文件入口,这里使用class来实现
class express {
}
module.exports = express;- 需要的原生模块
http,创建进程监听端口
const { createServer } = require("http");
- 给 class 定义
listen方法,监听端口
class express {
listen(...args) {
createServer(cb).listen(...args);
}
}- 这样就可以通过调用
class的listen去调用http模块的listen了,这里的cb我们可以先不管,你要知道每次接受到请求,必然会调用cb函数,这个是createServer原生模块帮我们封装好的
实现接收到请求触发
- 实现
app.get app.post等方法 - 目前我们接受到响应,就会触发 cb 这个回调函数,那我们打印下,看看是什么参数?
class express {
cb() {
return (req, res) => {
console.log(res, res, "来客人了");
};
}
listen(...args) {
createServer(this.cb()).listen(...args);
}
}- 发现此时的
req和res正是我们想要的可读流和可写流.
- 开始编写
get和post方法 - 这里注意,有路由是'/'的,这种是不管任何路由都会触发一次
constructor() {
this.routers = {
get: [],
post: [],
};
}
get(path, handle) {
this.routers.get.push({
path,
handle,
});
}
post(path, handle) {
this.routers.post.push({
path,
handle,
});
}
- 初始化时候定义 get、post 的数组储存对应的
path和handle. - 需要触发路由回调的时候,首先要找到对应的请求方式下对应的
url的handle方法,然后触发回调. - 如何找到对应请求方式下的
url对应的handle方法? 在接到请求时候就要遍历一次 - 这里要考虑匹配多个路由,意味着,我们可能遇到像最开始一样,有两个
get方式的test路由
cb() {
return (req, res) => {
const method = req.method.toLowerCase();
console.log(this.routers[method], ",method");
const url = req.url;
this.routers[method].forEach((item) => {
item.path === url && item.handle(req, res);
});
};
}
listen(...args) {
createServer(this.cb()).listen(...args);
}
- 上面根据 method 找到对应的数组,遍历找到请求的路由,触发回调,此时已经能正常返回数据了
[ { method: 'get', path: '/test', handle: [Function] } ] ,method
- 此时最简单的
express已经完成了,但是我们好像忘了最重要的中间件
完成最重要的中间件功能
- 首先要知道,
express中间件分两种,一种带路由的,那就是根据路由决定是否触发 - 另外一种就是不带路由的,像静态资源这种. 是用户访问任何路由都要触发一次的
- 那我们需要一个
all数组储存这种任意路由都需要匹配触发的
constructor() {
this.routers = {
get: [],
post: [],
all: [],
};
}
- 之前的直接通过 push 方式是太粗暴.如果用户需要中间件功能,不传路由,那就要做特殊处理,这里通过一个中间函数处理下
- 改造
get、post方法,定义handleAddRouter方法
handleAddRouter(path, handle) {
let router = {};
if (typeof path === "string") {
router = {
path,
handle,
};
} else {
router = {
path: "/",
handle: path,
};
}
return router;
}
get(path, handle) {
const router = this.handleAddRouter(path, handle);
this.routers.get.push(router);
}
post(path, handle) {
const router = this.handleAddRouter(path, handle);
this.routers.post.push(router);
}
use(path, handle) {
const router = this.handleAddRouter(path, handle);
this.routers.all.push(router);
}
- 每次添加之前,先触发一次
handleAddRouter,如果是path为空的中间件,直接传入函数的,那么path帮它设置成'/' - 我们还遗留了一个点,
next的实现,因为我们现在加了all这个数组后,意味着可能有多个中间件,那么可能一次请求打过来,就要触发多个路由
❝这里要注意,promise.then 源码实现和 express 的 next、以及 koa 的洋葱圈、redux 的中间件实现,有着一丁点相似,当你能真的领悟前后端框架源码时候,发现大都相似
❞
- 阅读我的文章,足以击破所有前后端源码.而且可以手写出来, 我们只学最核心的,抓重点学习,野蛮生长!
实现next
-
思路:
-
首先要找到所有匹配的路由
-
然后逐个执行(看
next的调用) -
定义
search方法,找到所有匹配的路由
search(method, url) {
const matchedList = [];
[...this.routers[method], ...this.routers.all].forEach((item) => {
item.path === url && matchedList.push(item.handle);
});
return matchedList;
}
cb() {
return (req, res) => {
const method = req.method.toLowerCase();
const url = req.url;
const matchedList = this.search(method, url);
};
}matchedList就是我们想要找到的所有路由- 为了完成
next,我们要将req ,res , matchedList存入闭包中,定义handle方法
handle(req, res, matchedList) {
const next = () => {
const midlleware = matchedList.shift();
if (midlleware) {
midlleware(req, res, next);
}
};
next();
}
cb() {
return (req, res) => {
const method = req.method.toLowerCase();
const url = req.url;
const matchedList = this.search(method, url);
this.handle(req, res, matchedList);
};
}- 这样我们就完成了
next方法,只要手动调用next就会调用下一个匹配到的路由回调函数
- 不到一百行代码,就完成了这个简单的
express框架 - 源码地址:https://github.com/JinJieTan/Peter-/tree/master/express