扒开 Linux 中断的底裤之 workqueue
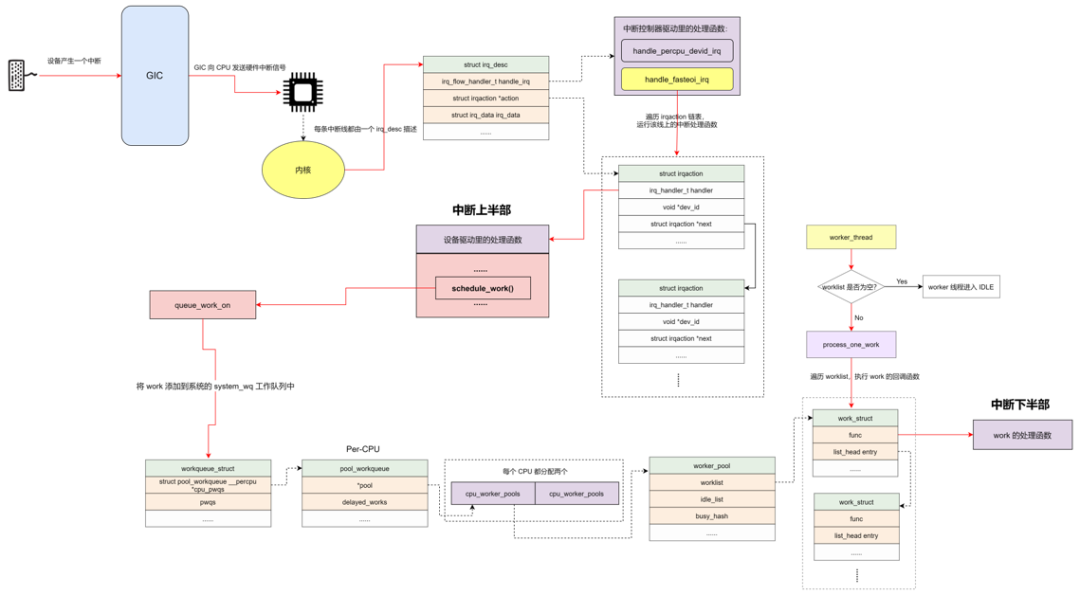
workqueue 是除了 softirq 和 tasklet 以外最常用的下半部机制之一。workqueue 的本质是把 work 交给一个内核线程,在进程上下文调度的时候执行。因为这个特点,所以 workqueue 允许重新调度和睡眠,这种异步执行的进程上下文,能解决因为 softirq 和 tasklet 执行时间长而导致的系统实时性下降等问题。
当驱动程序在进程上下文中有异步执行的工作任务时,可以用 work 来描述工作任务。把 work 添加到一个链表 worklist 中,然后由一个内核线程 worker 遍历链表,串行地执行挂入 worklist 中的所有 work。如果 worklist 中没有 work,那么内核线程 worker 就会变成 IDLE 状态;如果有 work,则执行 work 中的回调函数。
workqueue 相关的数据结构
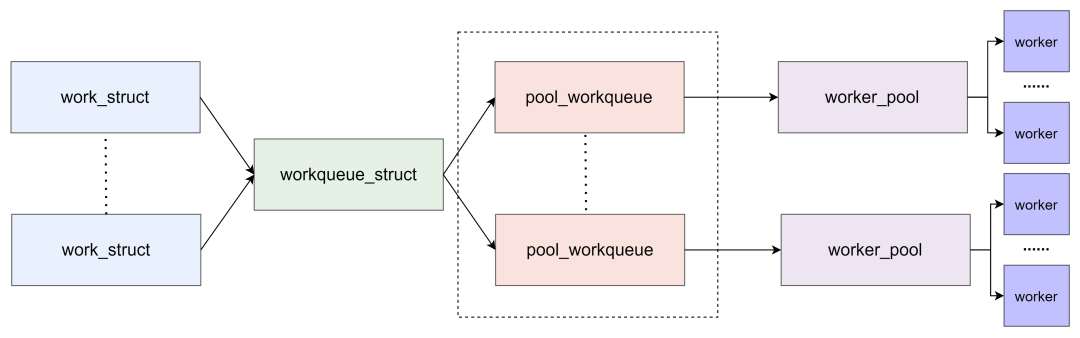
关于 workqueue 中几个概念都是 work 相关的数据结构非常容易混淆,大概可以这样来理解:
work_struct :
工作。初始化一个 work 并添加到工作队列后,将会将其传递到合适的内核线程来进行处理,它是用于调度的最小单位。
struct work_struct {
atomic_long_t data;
struct list_head entry;
work_func_t func;
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
};- data:低比特存放状态位,高比特存放 worker_pool 的ID或者 pool_workqueue 的指针
- entry:用于添加到其他队列上
- func:工作任务的处理函数,在内核线程中回调
workqueue_struct :
工作的集合。workqueue 和 work 是一对多的关系。内核中工作队列分为两种:
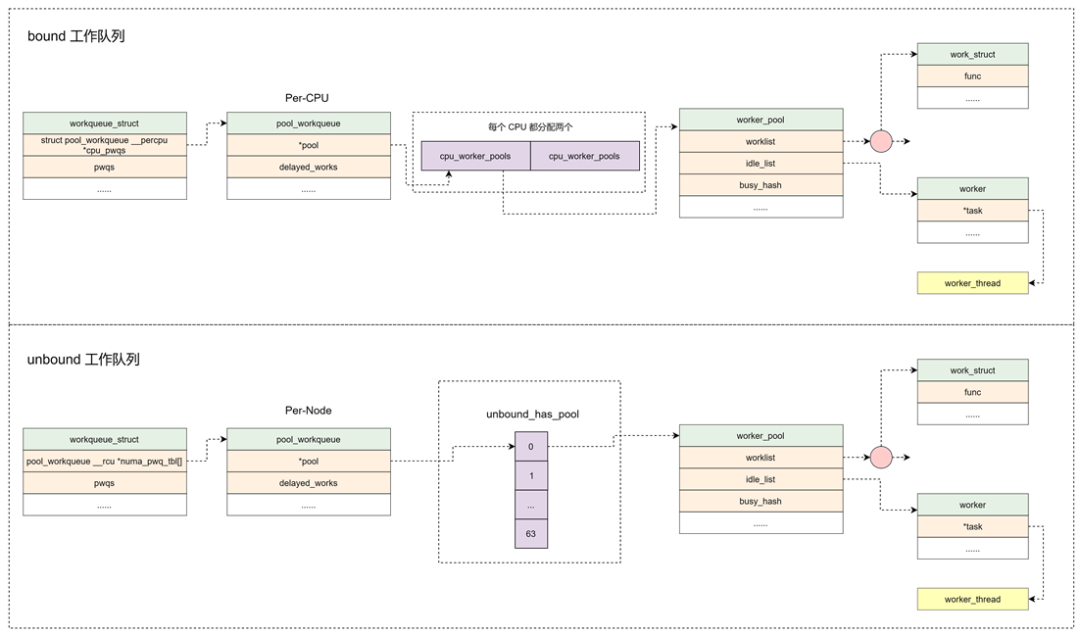
- bound:绑定处理器的工作队列,每个 worker 创建的内核线程绑定到特定的 CPU 上运行。
- unbound:不绑定处理器的工作队列,创建的时候需要指定 WQ_UNBOUND 标志,内核线程可以在处理器间迁移。
struct workqueue_struct {
struct list_head pwqs; /* WR: all pwqs of this wq */
struct list_head list; /* PR: list of all workqueues */
struct list_head maydays; /* MD: pwqs requesting rescue */
struct worker *rescuer; /* I: rescue worker */
struct pool_workqueue *dfl_pwq; /* PW: only for unbound wqs */
char name[WQ_NAME_LEN]; /* I: workqueue name */
/* hot fields used during command issue, aligned to cacheline */
unsigned int flags ____cacheline_aligned; /* WQ: WQ_* flags */
struct pool_workqueue __percpu *cpu_pwqs; /* I: per-cpu pwqs */
struct pool_workqueue __rcu *numa_pwq_tbl[]; /* PWR: unbound pwqs indexed by node */ //Per-Node创建pool_workqueue
...
};- pwqs:所有的 pool_workqueue 都添加到本链表中
- list:用于将工作队列添加到全局链表 workqueues 中
- maydays:rescue状态下的 pool_workqueue 添加到本链表中
- rescuer:rescuer 内核线程,用于处理内存紧张时创建工作线程失败的情况
- cpu_pwqs:Per-CPU 创建 pool_workqueue
- numa_pwq_tbl[]:Per-Node 创建 pool_workqueue
pool_workqueue:
中间人 / 中介,负责建立起 workqueue 和 worker_pool 之间的关系。workqueue 和 pool_workqueue 是一对多的关系。
struct pool_workqueue {
struct worker_pool *pool; /* I: the associated pool */
struct workqueue_struct *wq; /* I: the owning workqueue */
int nr_active; /* L: nr of active works */
int max_active; /* L: max active works */
struct list_head delayed_works; /* L: delayed works */
struct list_head pwqs_node; /* WR: node on wq->pwqs */
struct list_head mayday_node; /* MD: node on wq->maydays */ //用于添加到workqueue链表中
...
} __aligned(1 << WORK_STRUCT_FLAG_BITS);- pool:指向 worker_pool
- wq:指向所属的 workqueue
- nr_active:活跃的 work 数量
- max_active:活跃的最大 work 数量
- delayed_works:延迟执行的 work 挂入本链表
- pwqs_node:用于添加到 workqueue 链表中
- mayday_node:用于添加到 workqueue 链表中
worker_pool:
工人的集合。pool_workqueue 和 worker_pool 是一对一的关系,worker_pool 和 worker 是一对多的关系。
- bound 类型的工作队列:worker_pool 是 Per-CPU 创建,每个 CPU 都有两个 worker_pool,对应不同的优先级,nice 值分别为 0 和 -20。
- unbound 类型的工作队列:worker_pool 创建后会添加到 unbound_pool_hash 哈希表中。
struct worker_pool {
spinlock_t lock; /* the pool lock */
int cpu; /* I: the associated cpu */
int node; /* I: the associated node ID */
int id; /* I: pool ID */
unsigned int flags; /* X: flags */
unsigned long watchdog_ts; /* L: watchdog timestamp */
struct list_head worklist; /* L: list of pending works */
int nr_workers; /* L: total number of workers */
/* nr_idle includes the ones off idle_list for rebinding */
int nr_idle; /* L: currently idle ones */
struct list_head idle_list; /* X: list of idle workers */
struct timer_list idle_timer; /* L: worker idle timeout */
struct timer_list mayday_timer; /* L: SOS timer for workers */
/* a workers is either on busy_hash or idle_list, or the manager */
DECLARE_HASHTABLE(busy_hash, BUSY_WORKER_HASH_ORDER); /* L: hash of busy workers */
/* see manage_workers() for details on the two manager mutexes */
struct worker *manager; /* L: purely informational */
struct mutex attach_mutex; /* attach/detach exclusion */
struct list_head workers; /* A: attached workers */
struct completion *detach_completion; /* all workers detached */
struct ida worker_ida; /* worker IDs for task name */
struct workqueue_attrs *attrs; /* I: worker attributes */
struct hlist_node hash_node; /* PL: unbound_pool_hash node */
...
} ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;- cpu:绑定到 CPU 的 workqueue,代表 CPU ID
- node:非绑定类型的 workqueue,代表内存 Node ID
- worklist:pending 状态的 work 添加到本链表
- nr_workers:worker 的数量
- idle_list:处于 IDLE 状态的 worker 添加到本链表
- busy_hash:工作状态的 worker 添加到本哈希表中
- workers:worker_pool 管理的 worker 添加到本链表中
- hash_node:用于添加到 unbound_pool_hash 中
worker :
工人。在代码中 worker 对应一个 work_thread() 内核线程。
struct worker {
/* on idle list while idle, on busy hash table while busy */
union {
struct list_head entry; /* L: while idle */
struct hlist_node hentry; /* L: while busy */
};
struct work_struct *current_work; /* L: work being processed */
work_func_t current_func; /* L: current_work's fn */
struct pool_workqueue *current_pwq; /* L: current_work's pwq */
struct list_head scheduled; /* L: scheduled works */
/* 64 bytes boundary on 64bit, 32 on 32bit */
struct task_struct *task; /* I: worker task */
struct worker_pool *pool; /* I: the associated pool */
/* L: for rescuers */
struct list_head node; /* A: anchored at pool->workers */ //添加到worker_pool->workers链表中
/* A: runs through worker->node */
...
};- entry:用于添加到 worker_pool 的空闲链表中
- hentry:用于添加到 worker_pool 的忙碌列表中
- current_work:当前正在处理的 work
- current_func:当前正在执行的 work 回调函数
- current_pwq:指向当前 work 所属的 pool_workqueue
- scheduled:所有被调度执行的 work 都将添加到该链表中
- task:指向内核线程
- pool:该 worker 所属的 worker_pool
- node:添加到 worker_pool->workers 链表中
可以用下图来总结:
workqueue 的初始化
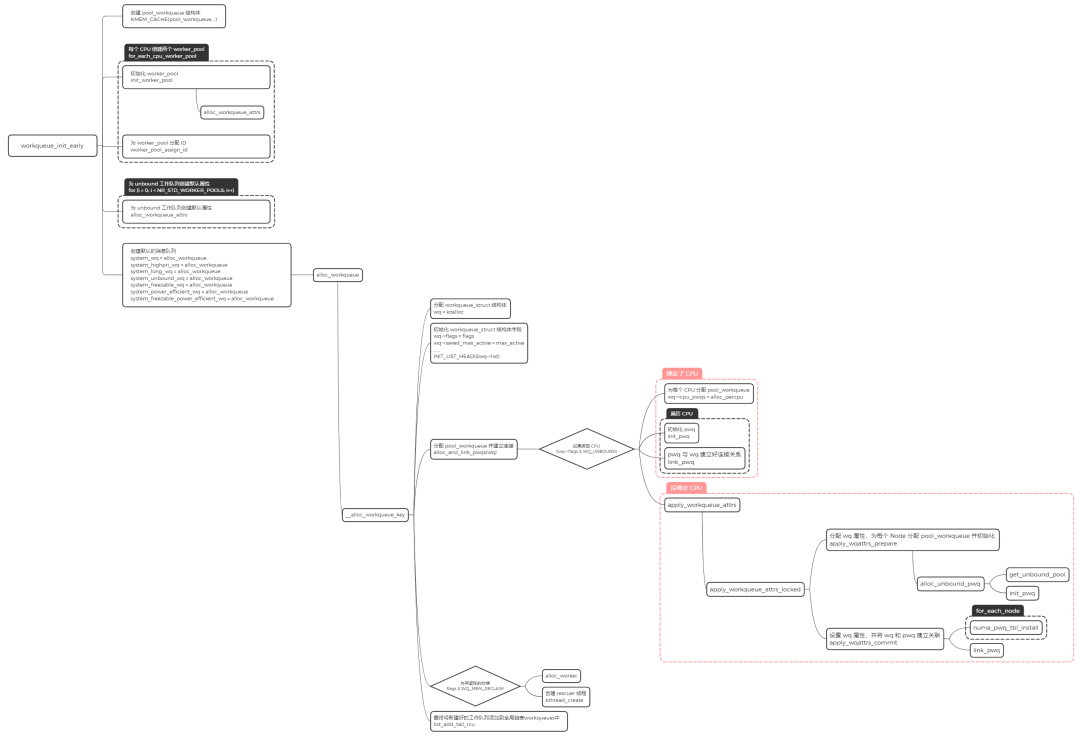
内核在启动的时候会对 workqueue 做初始化,workqueue 的初始化包含两个阶段,分别是 workqueue_init_early 和 workqueue_init。
workqueue_init_early
- 分配 worker_pool,并且对该结构中的字段进行初始化操作
- 分配 workqueue_struct,并且对该结构中的字段进行初始化操作
- alloc_and_link_pwqs:分配 pool_workqueue,将 workqueue_struct 和 worker_pool 关联起来
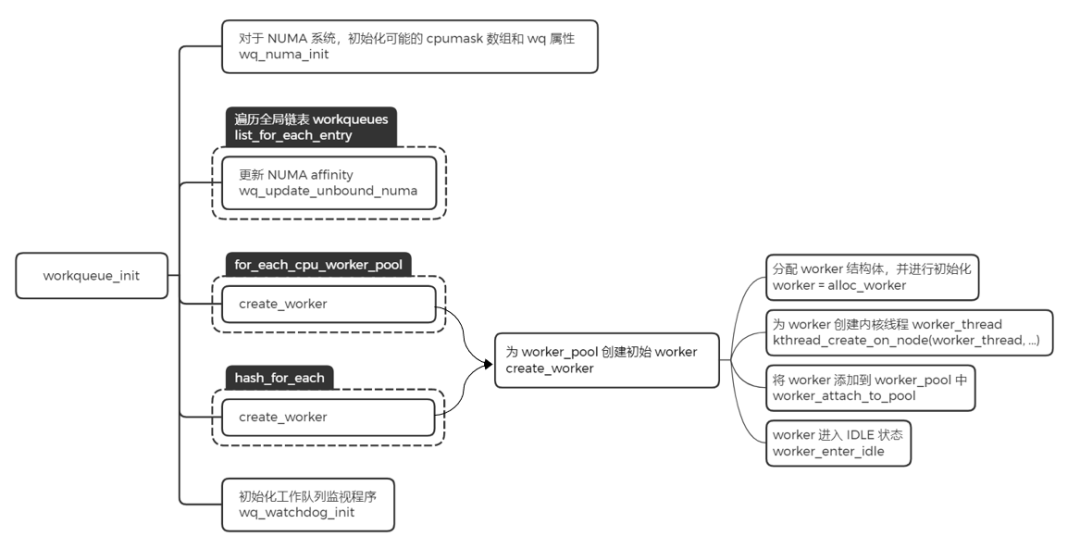
workqueue_init
这里主要完成的工作是给之前创建好的 worker_pool,添加一个初始的 worker,然后利用函数 create_worker,创建名字为 kworker/XX:YY 或者 kworker/uXX:YY 的内核线程。其中 XX 表示 worker_pool 的编号,YY 表示 worker 的编号,u 表示unbound。
- 分配 worker,并且对该结构中的字段进行初始化操作
- 为 worker 创建内核线程 worker_thread
- 将 worker 添加到 worker_pool 中
- worker 进入 IDLE 状态
经过上面两个阶段的初始化,workqueue 子系统基本就已经将数据结构的关联建立好了,当有 work 来进行调度的时候,就可以进行处理了。
使用 workqueue
内核推荐驱动开发者使用默认的 workqueue,而不是新建 workqueue。要使用系统默认的 workqueue,首先需要初始化 work,内核提供了相应的宏 INIT_WORK。
初始化 work
#define INIT_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 0)
#define __INIT_WORK(_work, _func, _onstack) \
do { \
__init_work((_work), _onstack); \
(_work)->data = (atomic_long_t) WORK_DATA_INIT(); \
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&(_work)->entry); \
(_work)->func = (_func); \
} while (0)初始化 work 后,就可以调用 shedule_work 函数把 work 挂入系统默认的 workqueue 中。
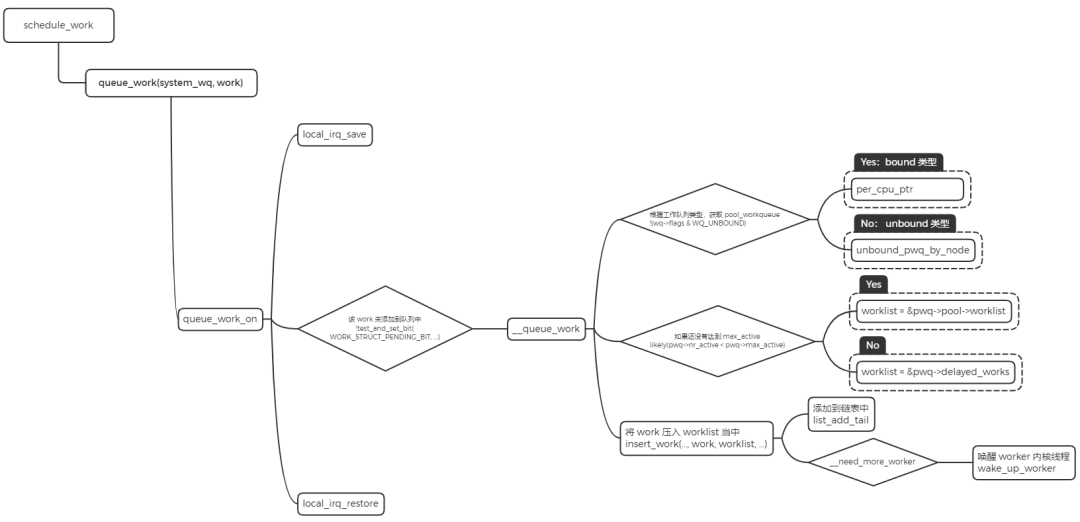
work 调度
- 将 work 添加到系统的 system_wq 工作队列中。
- 判断 workqueue 的类型,如果是 bound 类型,根据 CPU 来获取 pool_workqueue。如果是 unbound 类型,通过 node 号来获取 pool_workqueue。
- 判断 pool_workqueue 活跃的 work 数量,少于最大限值则将 work 加入到 pool->worklist 中,否则加入到 pwq->delayed_works 链表中。
- 如果 __need_more_worker 判断没有 worker 在执行,则通过 wake_up_worker 唤醒 worker 内核线程。
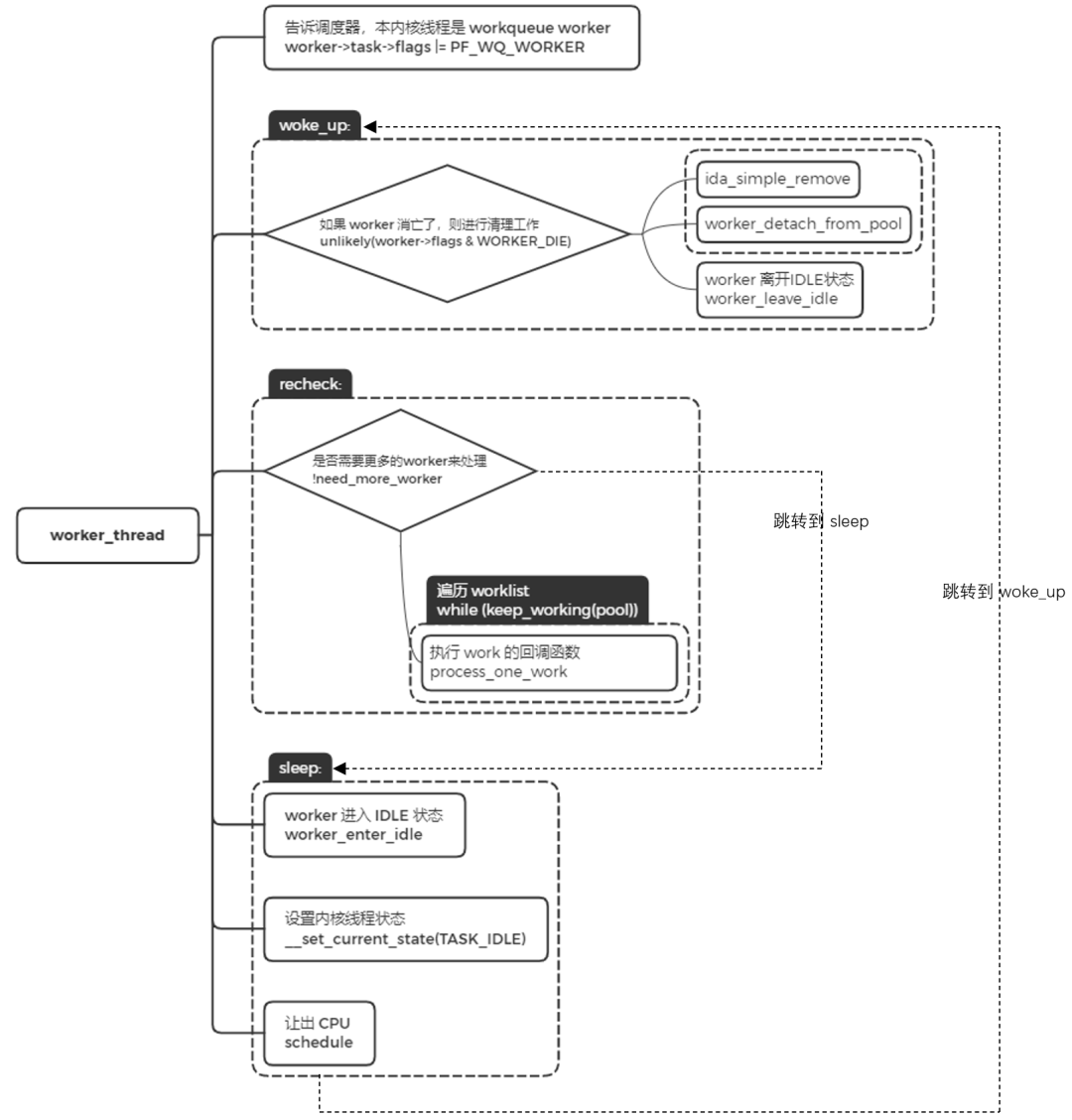
worker_thread
worker 内核线程的执行函数是 worker_thread。
- 设置标志位 PF_WQ_WORKER,调度器在进行调度处理时会对 task 进行判断,针对 workerqueue worker 有特殊的处理。
- worker 被唤醒的时候,跳转到 woke_up 执行。
- woke_up 中,如果此时 worker 是需要销毁的,那就进行清理工作并返回。否则,离开 IDLE 状态,并进入 recheck 模块执行。
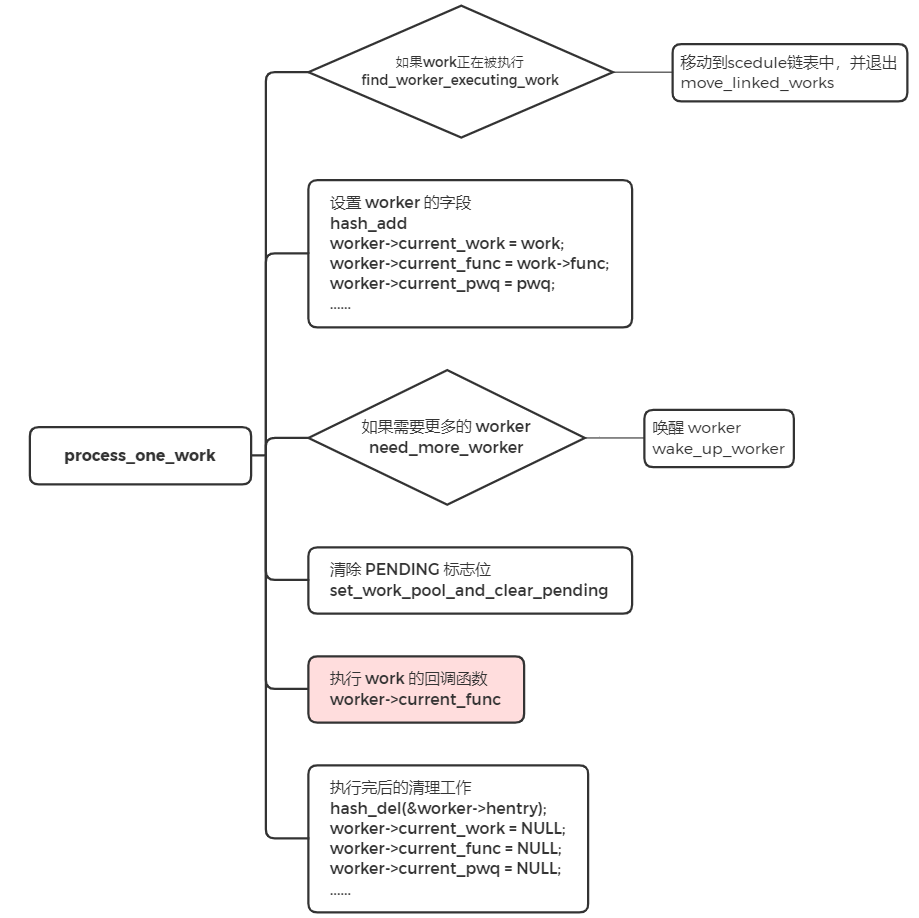
- recheck 中,判断是否需要更多的 worker 来处理,如果没有任务处理,跳转到 sleep 地方进行睡眠。如果有任务需要处理时,遍历工作链表,对链表中的每个节点调用 process_one_work 来执行 work 的回调函数,即 INIT_WORK 里的回调函数。
- sleep 中,没有任务处理时,worker 进入空闲状态,并将当前的内核线程设置成睡眠状态,让出 CPU。
总结