容器三把斧之 | OverlayFS原理与实现
Docker 底层有三驾马车,Namespace、CGroup 和 UnionFS(联合文件系统),UnionFS 是 Docker 镜像的基础。前面我们介绍过 Namespace 和 CGroup,接下来将会介绍 UnionFS 的实现原理。
UnionFS(联合文件系统)是一种分层、轻量级并且高性能的文件系统,它支持对文件系统的修改作为一次提交来一层层的叠加,同时可以将不同目录挂载到同一个虚拟文件系统下。
UnionFS 是 Docker 镜像的基础,镜像可以通过分层来进行继承,基于基础镜像(没有父镜像),可以制作各种具体的应用镜像。由于 Linux 下有多种的 UnionFS (如 AUFS、OverlayFS 和 Btrfs 等),所以我们以实现相对简单的 OverlayFS 作为分析对象。
OverlayFS 使用
我们先来看看 OverlayFS 基本原理(图片来源于网络):
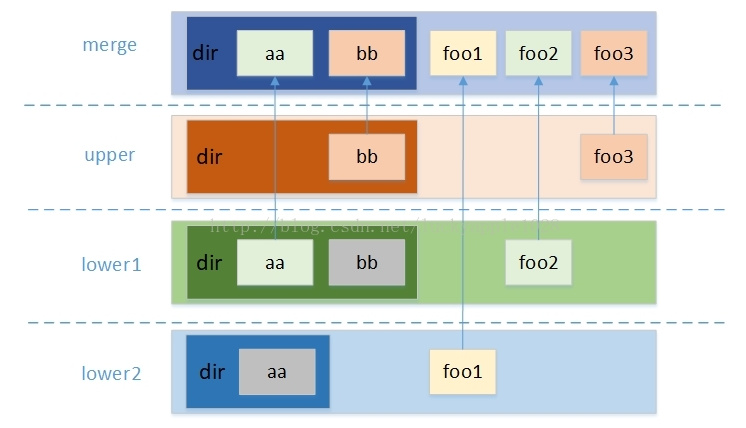
从上图可知,OverlayFS 文件系统主要有三个角色,lowerdir、upperdir 和 merged。lowerdir 是只读层,用户不能修改这个层的文件;upperdir 是可读写层,用户能够修改这个层的文件;而 merged 是合并层,把 lowerdir 层和 upperdir 层的文件合并展示。
使用 OverlayFS 前需要进行挂载操作,挂载 OverlayFS 文件系统的基本命令如下:
$ mount -t overlay overlay -o lowerdir=lower1:lower2,upperdir=upper,workdir=work merged
参数 -t 表示挂载的文件系统类型,这里设置为 overlay 表示文件系统类型为 OverlayFS,而参数 -o 指定的是 lowerdir、upperdir 和 workdir,最后的 merged 目录就是最终的挂载点目录。下面说明一下 -o 参数几个目录的作用:
lowerdir:指定用户需要挂载的lower层目录,指定多个目录可以使用:来分隔(最大支持500层)。upperdir:指定用户需要挂载的upper层目录。workdir:指定文件系统的工作基础目录,挂载后内容会被清空,且在使用过程中其内容用户不可见。
OverlayFS 实现原理
下面我们开始分析 OverlayFS 的实现原理。
OverlayFS 文件系统的作用是合并 upper 目录和 lower 目录的中的内容,如果 upper 目录与 lower 目录同时存在同一文件或目录,那么 OverlayFS 文件系统怎么处理呢?
- 如果
upper和lower目录下同时存在同一文件,那么按upper目录的文件为准。比如upper与lower目录下同时存在文件a.txt,那么按upper目录的a.txt文件为准。 - 如果
upper和lower目录下同时存在同一目录,那么把upper目录与lower目录的内容合并起来。比如upper与lower目录下同时存在目录test,那么把upper目录下的test目录中的内容与lower目录下的test目录中的内容合并起来。
为了简单起见,本文使用的是 Linux 3.18.3 版本,此版本的 OverlayFS 文件系统只支持一层的 lower 目录,所以简化了多层 lower 合并的逻辑。
OverlayFS 文件系统挂载
前面介绍过挂载 OverlayFS 文件系统的命令,挂载 OverlayFS 文件系统会触发系统调用 sys_mount(),而 sys_mount() 会执行 虚拟文件系统 的通用挂载过程,如申请和初始化 超级块对象(super block)(可参考:虚拟文件系统)。然后调用具体文件系统的 fill_super() 接口来填充 超级块对象,对于 OverlayFS 文件系统而言,最终会调用 ovl_fill_super() 函数来填充 超级块对象。
我们来分析一下 ovl_fill_super() 函数的主要部分:
static int ovl_fill_super(struct super_block *sb, void *data, int silent)
{
struct path lowerpath;
struct path upperpath;
struct path workpath;
struct inode *root_inode;
struct dentry *root_dentry;
struct ovl_entry *oe;
...
oe = ovl_alloc_entry(); // 新建一个ovl_entry对象
...
// 新建一个inode对象
root_inode = ovl_new_inode(sb, S_IFDIR, oe);
// 新建一个dentry对象, 并且指向新建的inode对象root_inode
root_dentry = d_make_root(root_inode);
...
oe->__upperdentry = upperpath.dentry; // 指向upper目录的dentry对象
oe->lowerdentry = lowerpath.dentry; // 指向lower目录的dentry对象
root_dentry->d_fsdata = oe; // 保存ovl_entry对象到新建dentry对象的d_fsdata字段中
...
sb->s_root = root_dentry; // 保存新建的dentry对象到超级块的s_root字段中
...
return 0;
}ovl_fill_super() 函数主要完成以下几个步骤:
- 调用
ovl_alloc_entry()创建一个ovl_entry对象oe。 - 调用
ovl_new_inode()创建一个inode对象root_inode。 - 调用
d_make_root()创建一个dentry对象root_dentry,并且将其指向root_inode。 - 将
oe的__upperdentry字段指向upper目录的dentry,而将lowerdentry字段指向lower目录的dentry。 - 将
root_dentry的d_fsdata字段指向oe。 - 将
超级块对象的s_root字段指向root_dentry。
最后,其各个数据结构的关系如下图:
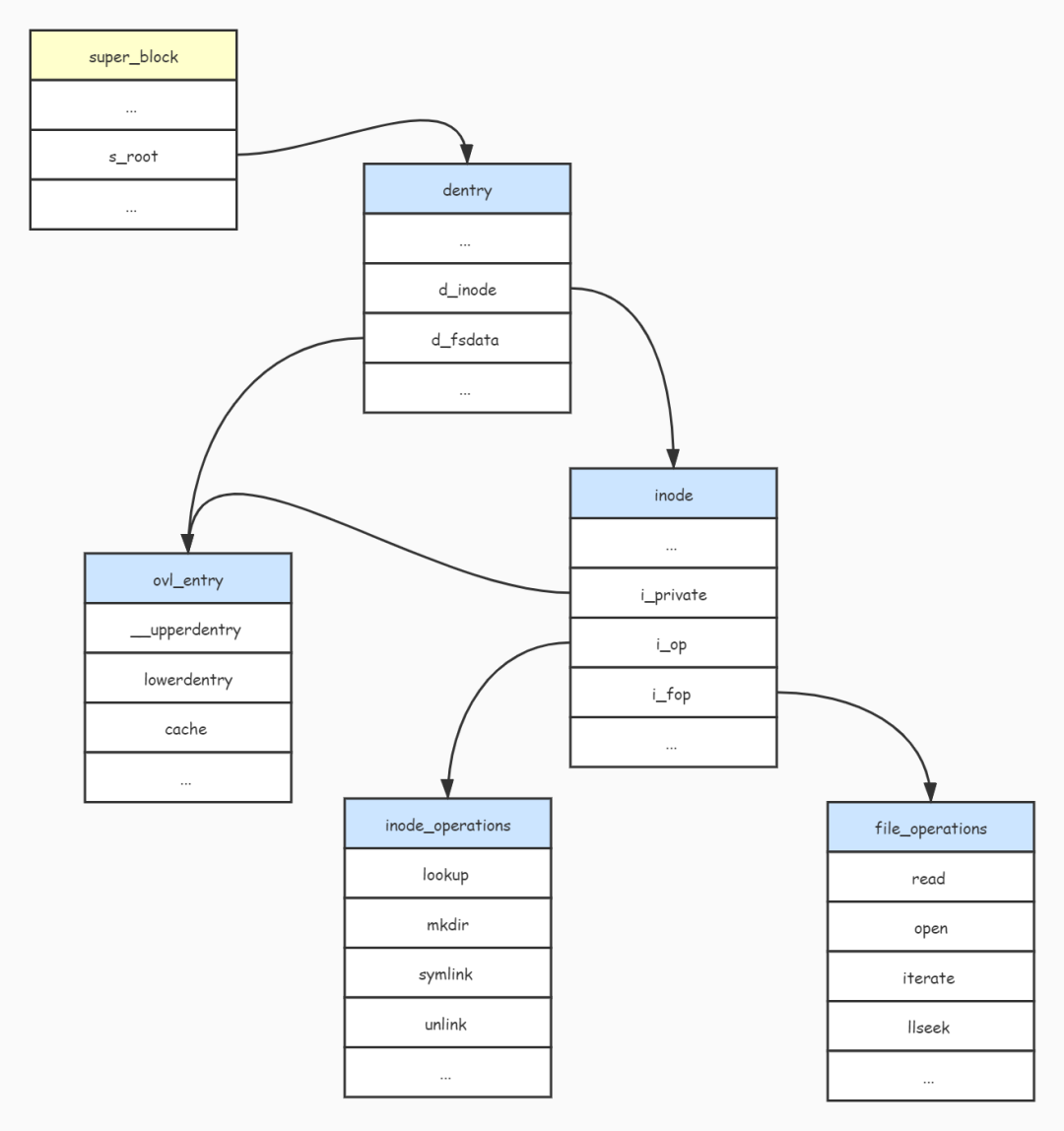
在上面的代码中出现的 ovl_entry 结构用于记录 OverlayFS 文件系统中某个文件或者目录所在的真实位置,由于 OverlayFS 文件系统是一个联合文件系统,并不是真正存在于磁盘的文件系统,所以在 OverlayFS 文件系统中的文件都要指向真实文件系统中的位置。
而 ovl_entry 结构就是用来指向真实文件系统的位置,其定义如下:
struct ovl_entry {
struct dentry *__upperdentry;
struct dentry *lowerdentry;
struct ovl_dir_cache *cache;
union {
struct {
u64 version;
bool opaque;
};
struct rcu_head rcu;
};
};下面解析一下 ovl_entry 结构各个字段的作用:
__upperdentry:如果文件存在于upper目录中,那么指向此文件的dentry对象。lowerdentry:如果文件存在于lower目录中,那么指向此文件的dentry对象。cache:如果指向的目录,那么缓存此目录的文件列表。version:用于记录此ovl_entry结构的版本。opaque:此文件或目录是否被隐藏。
__upperdentry 和 lowerdentry 是 ovl_entry 结构比较重要的两个字段,一个指向文件所在 upper 目录中的dentry对象,另外一个指向文件所在 lower 目录中的dentry对象,如下图:
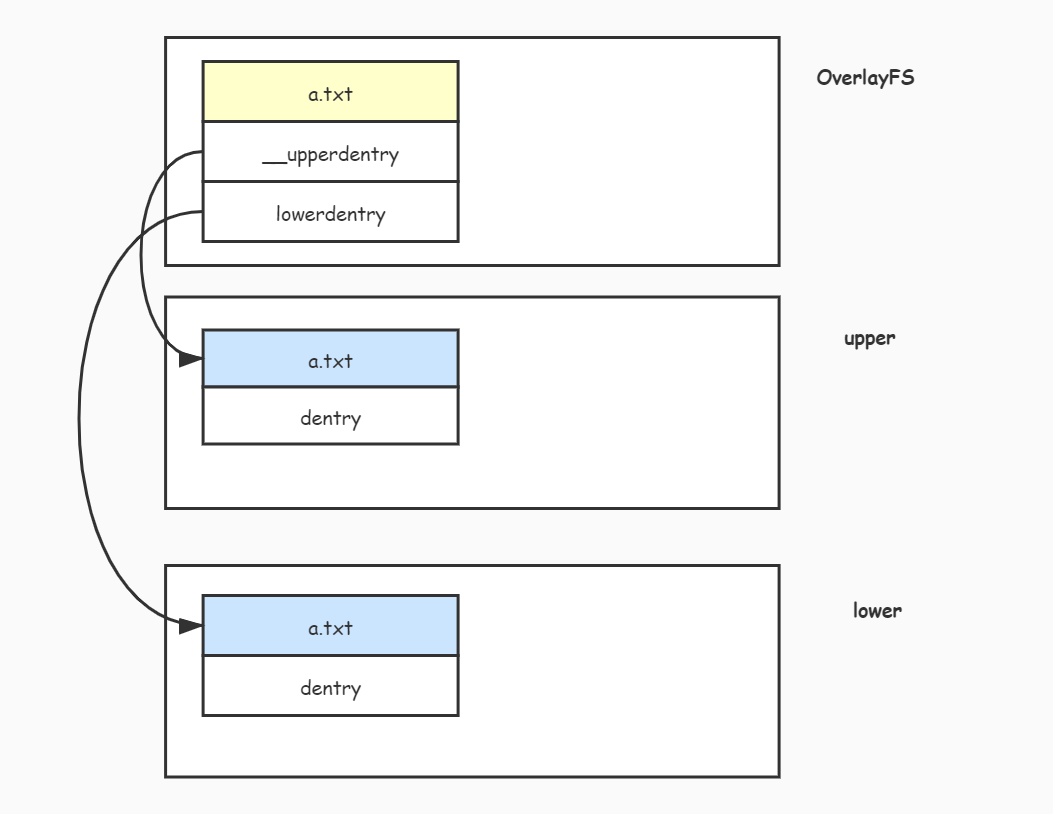
在 OverlayFS 文件系统中,每个文件或目录都由一个 ovl_entry 结构管理。如果我们把 dentry 结构当成是文件或目录的实体,那么 __upperdentry 指向的就是文件或目录所在 upper 目录中的实体,而 lowerdentry 指向的就是文件或目录所在 lower 目录的实体。
读取 OverlayFS 文件系统的目录
一般来说,我们调用 ls 命令读取目录的列表时,会触发内存以下过程:
- 调用
openat()系统调用打开目录。 - 调用
getdents()系统调用读取目录的列表。
打开目录
open() 系统调用最终会调用具体文件系统的 open() 方法来打开文件,对于 OverlayFS 文件系统调用的是 ovl_dir_open() 函数,其实现如下:
static int ovl_dir_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct path realpath;
struct file *realfile;
struct ovl_dir_file *od;
enum ovl_path_type type;
// 申请一个 ovl_dir_file 对象
od = kzalloc(sizeof(struct ovl_dir_file), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!od)
return -ENOMEM;
type = ovl_path_real(file->f_path.dentry, &realpath);
realfile = ovl_path_open(&realpath, file->f_flags);
if (IS_ERR(realfile)) {
kfree(od);
return PTR_ERR(realfile);
}
// 初始化 ovl_dir_file 对象
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&od->cursor.l_node);
od->realfile = realfile;
od->is_real = (type != OVL_PATH_MERGE);
od->is_upper = (type != OVL_PATH_LOWER);
od->cursor.is_cursor = true;
file->private_data = od; // 保存到 file 对象的 private_data 字段中
return 0;
}ovl_dir_open() 函数主要完成的工作包括:
-
创建一个
ovl_dir_file对象od。 -
调用
ovl_path_real()函数分析当前文件或目录所属的类型:
a . 如果是一个目录,并且 upper 目录和 lower 目录同时存在,那么返回 OVL_PATH_MERGE,表示需要对目录进行合并。
b . 如果是一个目录,并且只存在于 upper 目录中。或者是一个文件,并且存在于 upper 目录中,那么返回 OVL_PATH_UPPER,表示从 upper 目录中读取。
c . 否则返回 OVL_PATH_LOWER,表示从 lower 目录中读取。
3 . 把 ovl_dir_file 对象保存到 file 对象的 private_data 字段中。
ovl_dir_file 对象用于描述 OverlayFS 文件系统的目录或文件的信息,其定义如下:
struct ovl_dir_file {
bool is_real;
bool is_upper;
struct ovl_dir_cache *cache;
struct ovl_cache_entry cursor;
struct file *realfile;
struct file *upperfile;
};
struct ovl_dir_cache {
long refcount;
u64 version;
struct list_head entries;
};ovl_dir_file 对象各个字段的含义如下:
is_real:如不需要合并,设置为true。is_upper:是否需要从upper目录中读取。cache:用于缓存目录的文件列表。cursor:用于迭代目录列表时的游标。realfile:真实文件或目录的dentry对象。upperfile:指向文件或目录所在upper目录中的dentry对象。
读取目录列表
读取目录中的文件列表是通过 getdents() 系统调用,而 getdents() 系统调用最终会调用具体文件系统的 iterate() 接口,对于 OverlayFS 文件系统而言,调用的就是 ovl_iterate() 函数。其实现如下:
static int ovl_iterate(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx)
{
struct ovl_dir_file *od = file->private_data;
struct dentry *dentry = file->f_path.dentry;
if (!ctx->pos)
ovl_dir_reset(file);
if (od->is_real) // 如果不需要合并, 直接调用 iterate_dir() 函数读取真实的目录列表即可
return iterate_dir(od->realfile, ctx);
if (!od->cache) { // 如果还没有创建缓存对象
struct ovl_dir_cache *cache;
cache = ovl_cache_get(dentry); // 读取合并后目录的文件列表, 并且缓存起来
if (IS_ERR(cache))
return PTR_ERR(cache);
od->cache = cache; // 保持缓存对象
ovl_seek_cursor(od, ctx->pos); // 移动游标
}
while (od->cursor.l_node.next != &od->cache->entries) { // 遍历合并后的目录中的文件列表
struct ovl_cache_entry *p;
p = list_entry(od->cursor.l_node.next, struct ovl_cache_entry, l_node);
if (!p->is_cursor) {
if (!p->is_whiteout) {
if (!dir_emit(ctx, p->name, p->len, p->ino, p->type)) // 写到用户空间的缓冲区中
break;
}
ctx->pos++;
}
list_move(&od->cursor.l_node, &p->l_node); // 移动到下一个文件
}
return 0;
}ovl_iterate() 函数的主要工作有以下几个步骤:
- 如果不需要合并目录(就是
is_real为true),那么直接调用iterate_dir()函数读取真实的目录列表。 - 如果
ovl_dir_file对象的缓存没有被创建,那么调用ovl_cache_get()创建缓存对象,ovl_cache_get()除了创建缓存对象外,还会读取合并后的目录中的文件列表,并保存到缓存对象的entries链表中。 - 遍历合并后的目录中的文件列表,并把文件列表写到用户空间的缓存中,这样用户就可以获取合并后的文件列表。
我们主要来分析一下怎么通过 ovl_cache_get() 函数来读取合并后的目录中的文件列表:
static struct ovl_dir_cache *ovl_cache_get(struct dentry *dentry)
{
int res;
struct ovl_dir_cache *cache;
...
cache = kzalloc(sizeof(struct ovl_dir_cache), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cache)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
cache->refcount = 1;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cache->entries);
res = ovl_dir_read_merged(dentry, &cache->entries);
...
cache->version = ovl_dentry_version_get(dentry);
ovl_set_dir_cache(dentry, cache);
return cache;
}ovl_cache_get() 函数首先创建一个 ovl_dir_cache 缓存对象,并且调用 ovl_dir_read_merged() 函数读取合并目录的文件列表,ovl_dir_read_merged() 函数实现如下:
static int ovl_dir_read_merged(struct dentry *dentry, struct list_head *list)
{
int err;
struct path lowerpath;
struct path upperpath;
struct ovl_readdir_data rdd = {
.ctx.actor = ovl_fill_merge,
.list = list,
.root = RB_ROOT,
.is_merge = false,
};
ovl_path_lower(dentry, &lowerpath); // 获取lower目录
ovl_path_upper(dentry, &upperpath); // 获取upper目录
if (upperpath.dentry) { // 如果upper目录存在, 读取upper目录中的文件列表
err = ovl_dir_read(&upperpath, &rdd);
if (err)
goto out;
if (lowerpath.dentry) {
err = ovl_dir_mark_whiteouts(upperpath.dentry, &rdd);
if (err)
goto out;
}
}
if (lowerpath.dentry) { // 如果lower目录存在, 读取lower目录中的文件列表
list_add(&rdd.middle, rdd.list);
rdd.is_merge = true;
err = ovl_dir_read(&lowerpath, &rdd);
list_del(&rdd.middle);
}
out:
return err;
}ovl_dir_read_merged() 函数的实现比较简单,调用了 ovl_dir_read() 函数读取 lower 和 upper 目录中的文件列表,并保存到 list 参数中。
这里有个问题,就是如果 lower 目录和 upper 目录同时存在相同的文件怎办?
在调用 ovl_dir_read() 函数读取 lower 和 upper 目录中的文件列表时会调用 ovl_fill_merge() 函数过滤相同的文件。过滤操作通过红黑树来实现,过滤过程如下:
- 读取
upper目录中的文件列表,保存到list列表中,并且保存到红黑树中。 - 读取
lower目录中的文件列表,查询红黑树中是否已经存在此文件,如果存在,那么跳过此文件,否则添加到list列表中