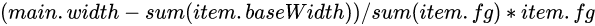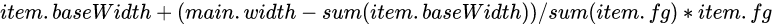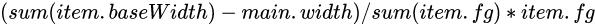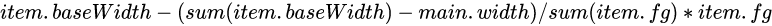从零开始深入理解 CSS — Flex 布局
1 . css 布局方式
1.1 css 2.1
CSS2.1定义了四种布局方式,由一个盒与其兄弟,祖先盒的关系决定其尺寸与位置的算法。
- 块布局:呈现文档的布局模式。
- 行内布局:呈现文本的布局模式。
- 表格布局:用表格呈现2D数据的布局模式。
- 定位布局:能够直接地定位元素的布局模式,定位元素奴基本与其他元素没有任何关系。
1.2 css 3
引入的flex布局,主要思想是让容器有能力控制子项目的高度,宽度(设置顺序)。以最佳方式填充可用空间(主要是为了适应所有类型的显示设备和屏幕大小)。flex容器会使子项目扩展来填满可用空间,或者缩小以防止溢出容器。
最重要的是flex布局方向不可预知,不像常规的布局(块就是从上到下,内联就是从左到右),常规布局适合页面布局,但是对于支持大型或者复杂的应用程序(特别是涉及方向布局方向的改变,缩放或者收缩)就缺乏灵性。
2 . flex
2.1 最新版本的浏览器的兼容性
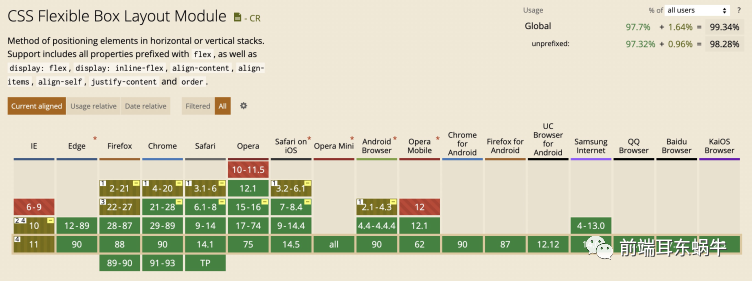
详情可以访问flex的兼容性 这里兼容性的主要问题是IE,IE10需要使用-ms-。至于IE8和IE9的兼容性,需要使用flex.js。
2.2 术语介绍
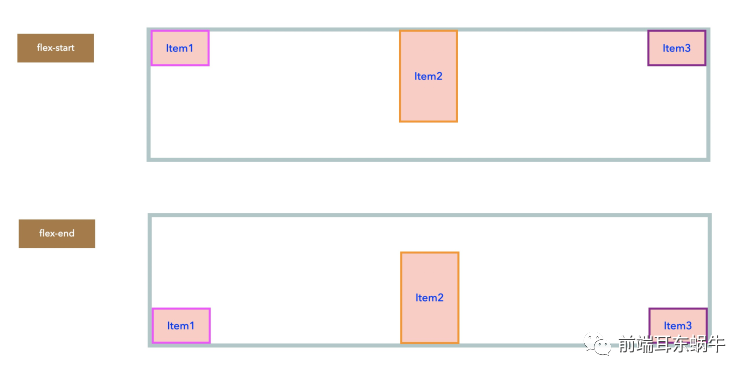
2.2.1 主轴&侧轴
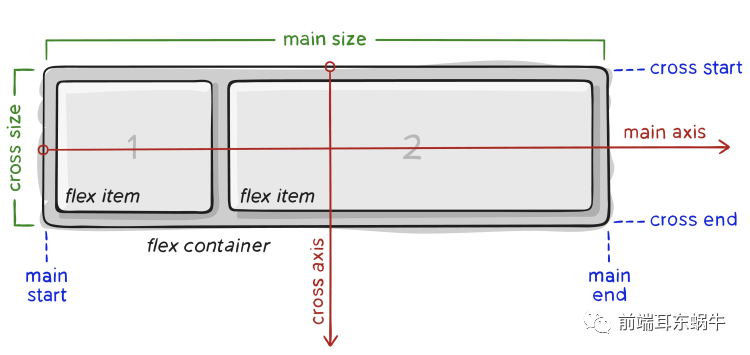
图片来源:https://css-tricks.com/snippets/css/a-guide-to-flexbox/#basics-and-terminology
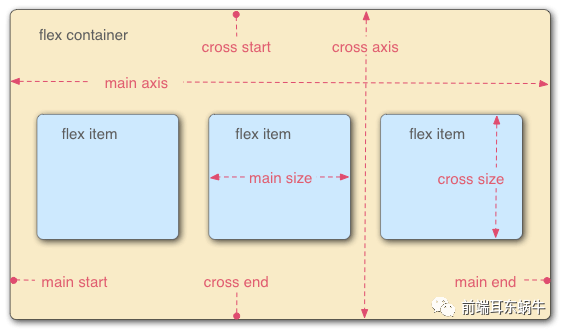
图片来源:https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2015/07/flex-grammar.html
- 主轴(main axis):Flex容器的主轴主要用来配置Flex项目。注意,它不一定是水平,这主要取决于flex-direction属性。
- 主轴开始(main-start) | 主轴结束(main-end):Flex项目的配置从容器的主轴起点边开始,往主轴终点边结束。
- 主轴长度(main size):Flex项目的在主轴方向的宽度或高度就是项目的主轴长度,Flex项目的主轴长度属性是width或height属性,由哪一个对着主轴方向决定 【这里可能存有一些歧义,说的是总长度,还是flex项目长度】。
- 侧轴(cross axis):与主轴垂直的轴称作侧轴,是侧轴方向的延伸。
- 侧轴开始(cross-start) | 侧轴结束(cross-end):伸缩行的配置从容器的侧轴起点边开始,往侧轴终点边结束。
- 侧轴长度(cross size):Flex项目的在侧轴方向的宽度或高度就是项目的侧轴长度,Flex项目的侧轴长度属性是width或height属性,由哪一个对着侧轴方向决定。
2.2.2.1 问题残留:
关于main size的描述:这里可能根据上提有一些歧义,说的是总长度,还是flex item长度
2.2.2 伸缩容器和伸缩项目
- 通过display显示地给一个元素设置为flex或者inline-flex,这个容器就是一个伸缩容器。伸缩容器回为其内容创建新的伸缩格式化上下文,其中设置为flex的容器被渲染为一个块级元素,设置为inline-flex的容器被渲染为一个行内元素。
- 元素display为inline-flex且元素是一个浮动或者绝对定位,则display的计算值是flex。
- 一个伸缩容器的每一个子元素都会成为一个伸缩项目。
2.2.2.1 特别说明上面第二条:
元素display为inline-flex且元素是一个浮动或者绝对定位,则display的计算值是flex。规则和之前学习的视觉格式化类似。当存在浮动和绝对定位的时候,inline-* =》 *。下面的图表可以新增一条。
css - 视觉格式化模型 (visual formatting model )
- 如果’display’值为’none’,同时不设置’position’和’float’,那么该元素不生成框。
- 否则,如果’positon’值为’absolute’或’fixed’,即框为绝对定位,’float’的计算值为’none’,并且’display’根据下表设置。那么该框的位置由’top’,’right’,’bottom’,’left’和框的包含块决定。
- 否则,如果’float’的值不为’none’,那么该框会浮动,’display’根据下表设置。
- 否则,如果该元素为根元素,’display’根据下表设置。
- 否则,剩余的’display’属性值与指定值相同。
| Specified value | Computed value |
|---|---|
| inline-table | table |
| inline, table-row-group, table-column, table-column-group, table-header-group, table-footer-group, table-row, table-cell, table-caption, inline-block | block |
| inline-flex | flex |
| others | same as specified |
2.3 flex模型的功能
- 屏幕和浏览器窗口大小发生改变也可以灵活调整布局。
- 指定伸缩项目沿着主轴或者侧轴按比例分配额外空间(伸缩容器额外空间),从而调整伸缩项目的大小。
- 指定伸缩项目沿着主轴或者侧轴将伸缩容器额外空间,分配到伸缩项目之前,之后或者之间。
- 指定如何将垂直于元素布局轴的额外空间分配到该元素的周围。
- 控制元素在页面上的布局方向
- 按照不同与文档对象模型(DOM)所指定排序方式对屏幕上的元素重新排序。
- 设为Flex布局以后,子元素的float、clear和vertical-align属性将失效。
3 . 伸缩容器属性
- flex-direction
- flex-wrap
- flex-flow
- justify-content
- align-items
- align-content
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.parent-flex {
width: 800px;
height: 400px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
.child-flex {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent-flex">
<div class="child-flex">
flex item1
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex item2
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex item3
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html> 3.1 flex-direction
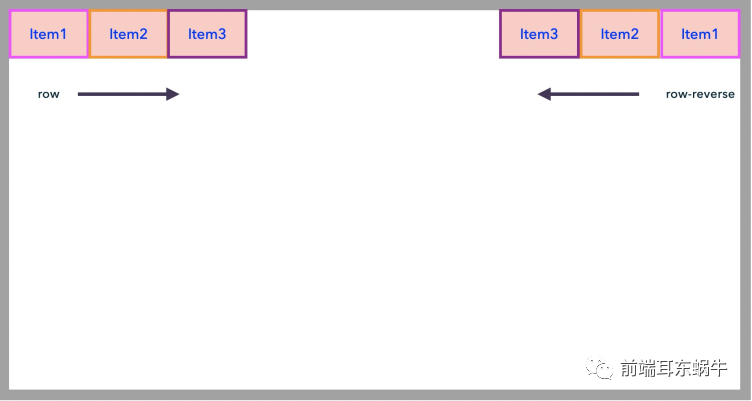
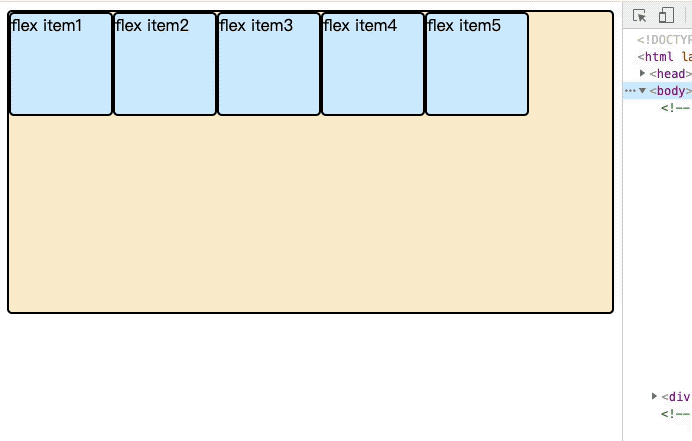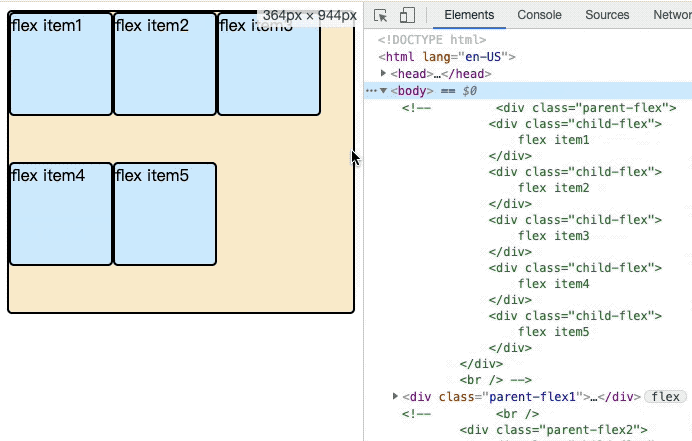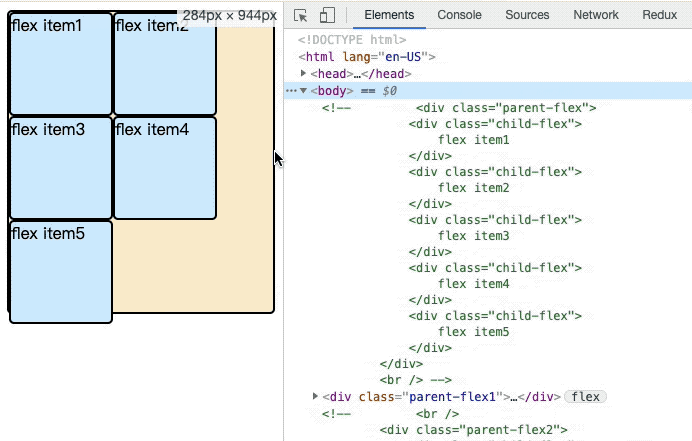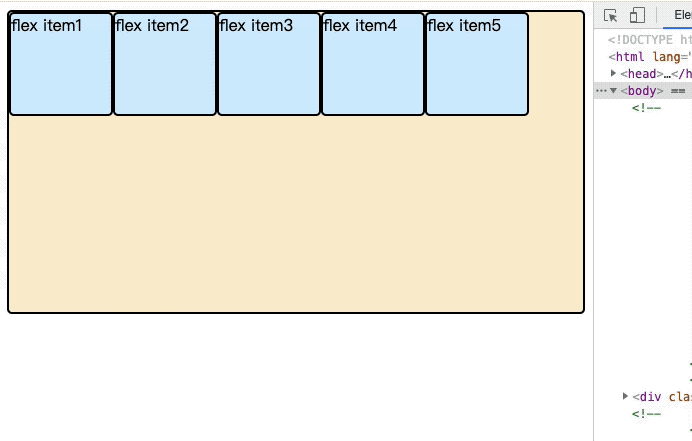
伸缩器容器的主轴方向,其决定了伸缩项目放置在伸缩容器的方向。伸缩流方向通过flex-direction属性来设置,其默认值为row。
.box {
flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse;
}- row(默认值):主轴为水平方向,起点在左端。
- row-reverse:主轴为水平方向,起点在右端。
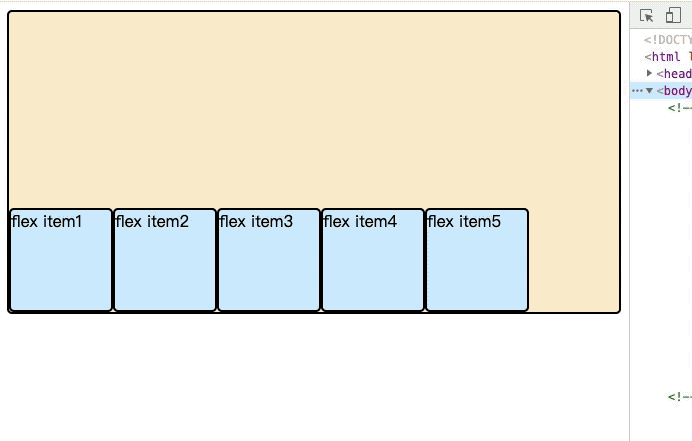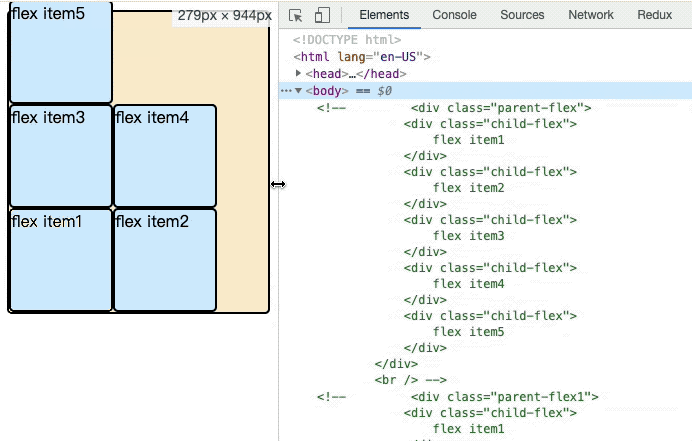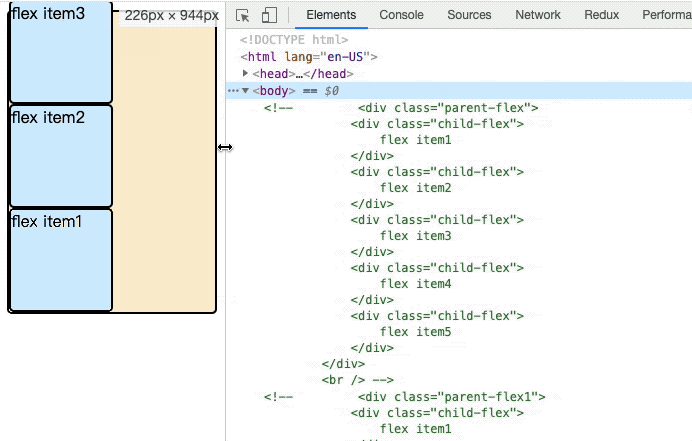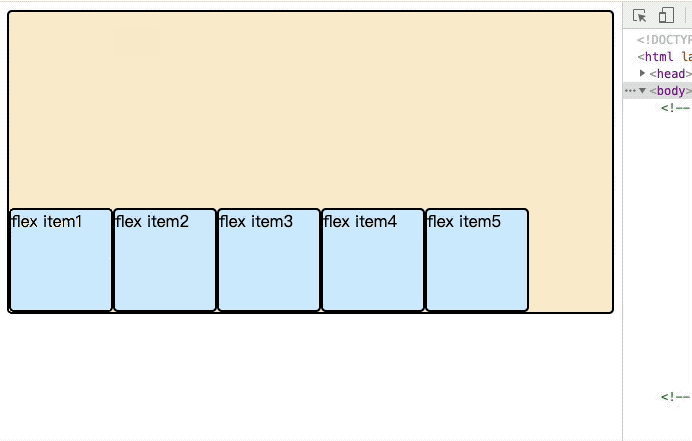
- column:主轴为垂直方向,起点在上沿。
- column-reverse:主轴为垂直方向,起点在下沿。
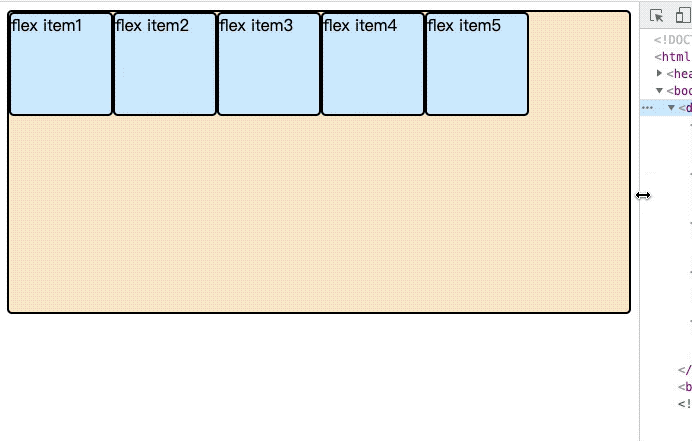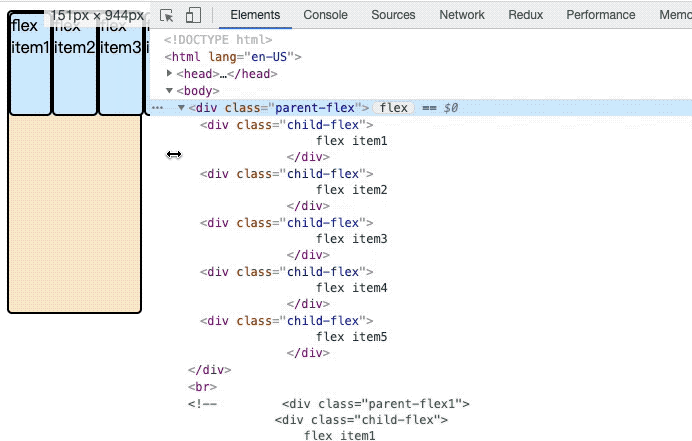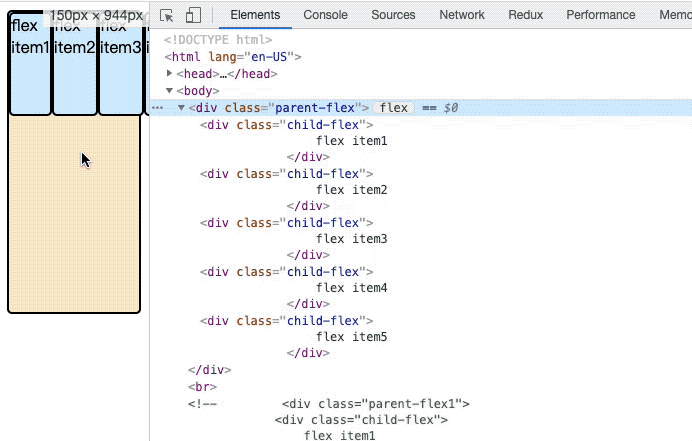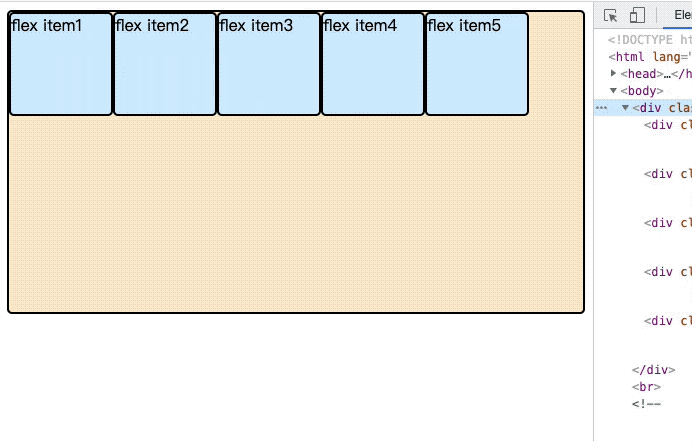
3.2 flex-wrap
默认情况下,子元素项目都排在一条线。但是许多情况下子元素的排列不仅一行。在伸缩容器中有一个伸缩换行属性,主要用来设置伸缩容器的伸缩项目是当行还是多行显示,以及决定侧轴的方向。
.box{
flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse;
}- nowrap(默认):不换行。
- wrap:换行,第一行在上方。
- wrap-reverse:换行,第一行在下方。
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.parent-flex {
height: 400px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: nowrap;
}
.child-flex {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
}
</style><div class="parent-flex">
<div class="child-flex">
flex item1
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex item2
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex item3
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex item4
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex item5
</div>
</div>下面为动态图,如果看不到效果,刷新页面,到此处查看。
3.3 flex-flow
伸缩流方向与伸缩换行的结合物。也就是说flex-flow同时设定了flex-direction和flex-wrap两个属性,也就是这两个属性的缩写,决定了伸缩容器的主轴和侧轴。
.box {
flex-flow: <flex-direction> || <flex-wrap>;
}flex-flow:row wrap;
/* 两种方式都可以 */
flex-flow:wrap row;3.4 justify-content
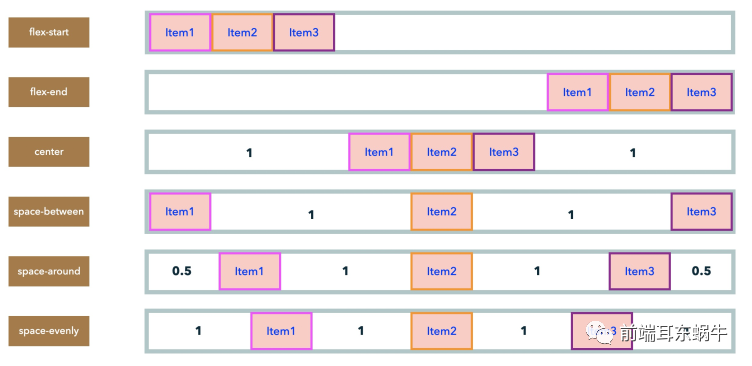
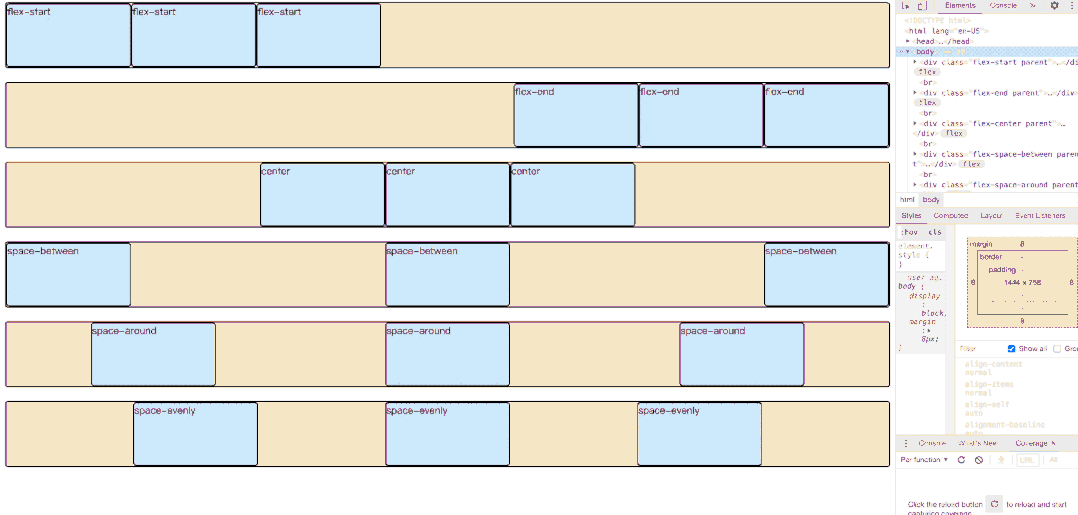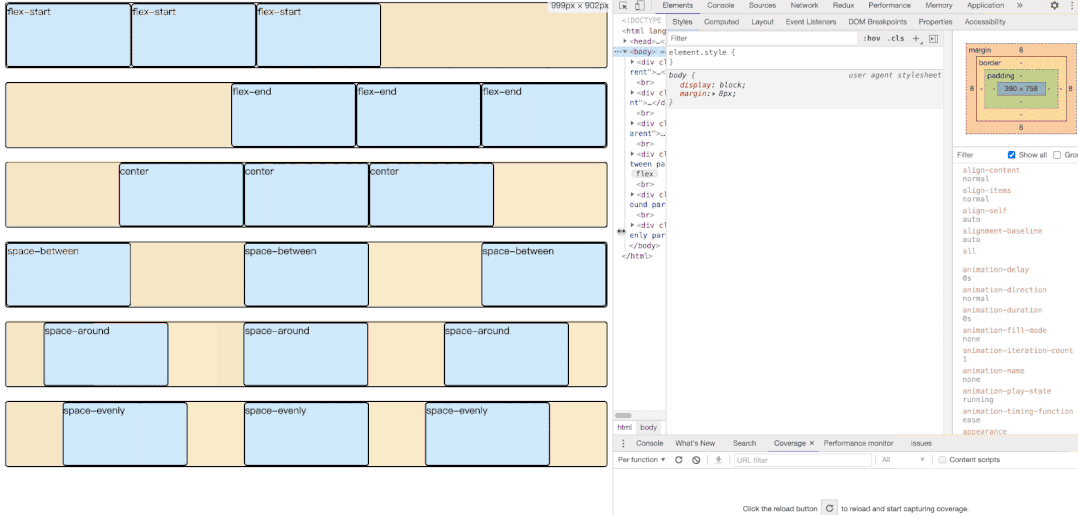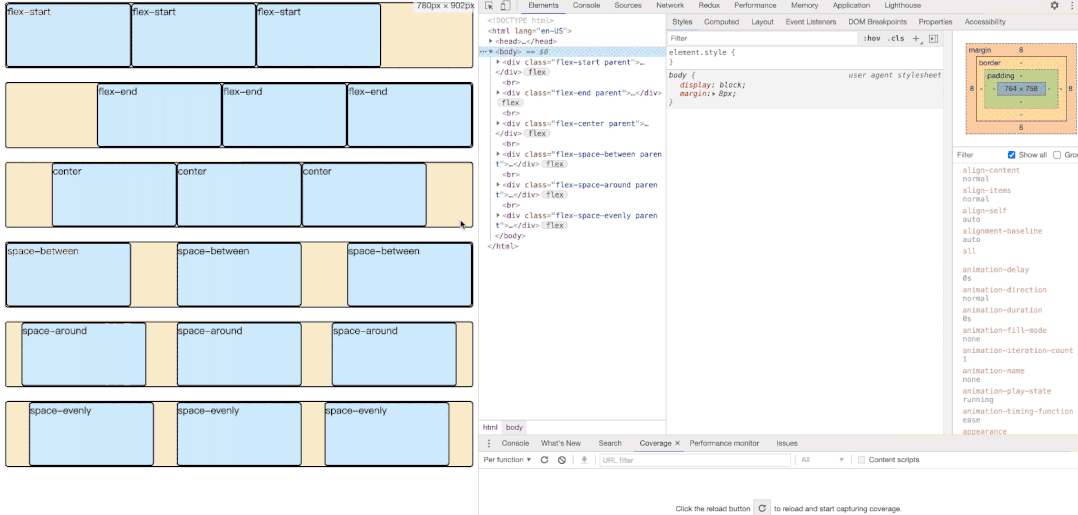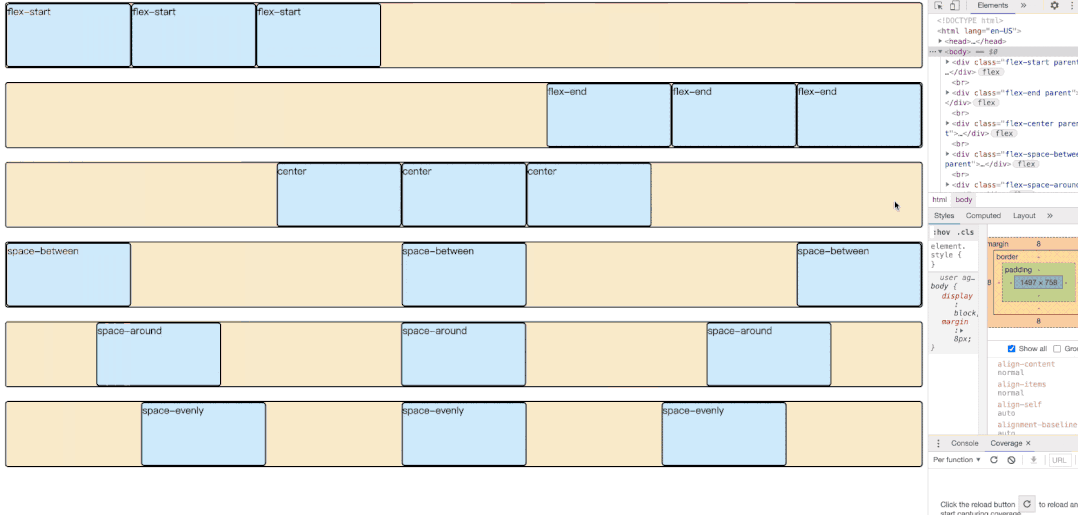
用来设置伸缩容器内当前伸缩项目在主轴方向的对齐方式,指定如何在伸缩项目之间分布伸缩容器额外空间。当伸缩项目溢出某一行时,这一属性也会在项目的对以上增加一些控制。
.box {
justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around |space-evenly;
}- flex-start(默认值):左对齐
- flex-end:右对齐
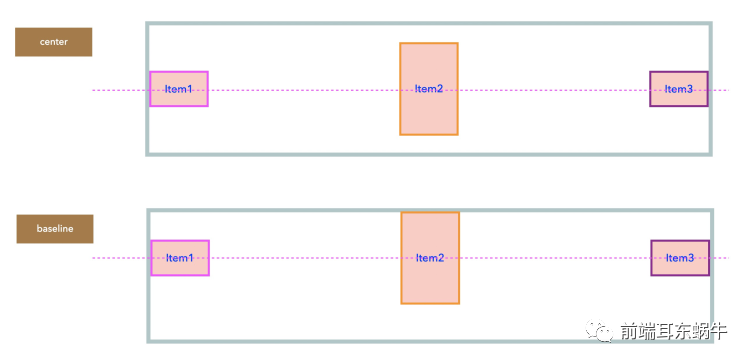
- center:居中
- space-between:两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等。
- space-around:每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍。
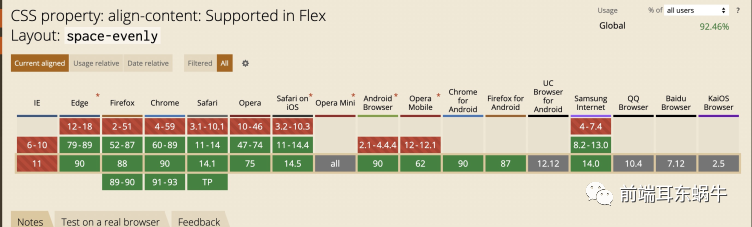
- space-evenly:每个子项目均分容器空间。但是存在兼容性问题。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.child-flex {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
}
.parent {
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
}
.flex-start {
justify-content: flex-start;
}
.flex-end {
justify-content: flex-end;
}
.flex-center {
justify-content: center;
}
.flex-space-between {
justify-content: space-between;
}
.flex-space-around {
justify-content: space-around;
}
.flex-space-evenly {
justify-content: space-evenly;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-start parent">
<div class="child-flex">
flex-start
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex-start
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex-start
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="flex-end parent">
<div class="child-flex">
flex-end
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex-end
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
flex-end
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="flex-center parent">
<div class="child-flex">
center
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
center
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
center
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="flex-space-between parent">
<div class="child-flex">
space-between
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
space-between
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
space-between
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex">
space-around
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
space-around
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
space-around
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="flex-space-evenly parent">
<div class="child-flex">
space-evenly
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
space-evenly
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
space-evenly
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>3.4.1 space-evenly兼容性问题
通过space-between代替,前后各加一个空元素进行占位。
.flex-space-evenly {
justify-content: space-between;
}
.flex-space-evenly::before, .flex-space-evenly::after {
display: block;
content: ''
}3.5 align-items
文章开头说过flex布局的主轴方向和侧轴方向,justify-content说的是主轴,align-items则是侧轴。如文字描述,侧轴对齐方式说的是侧轴方向对齐方式。
.box {
align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;
}- flex-start:交叉轴的起点对齐。
- flex-end:交叉轴的终点对齐。
- center:交叉轴的中点对齐。
- baseline: 项目的第一行文字的基线对齐。
- stretch(默认值):如果项目未设置高度或设为auto,将占满整个容器的高度。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.child-flex {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
}
.parent {
height: 600px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
}
.flex-space-around {
justify-content: space-around;
align-items: stretch;
align-items: flex-start;
align-items: flex-end ;
align-items: center;
align-items: baseline;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex" style="height: 300px; padding-top: 40px;">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html> 3.6 align-content
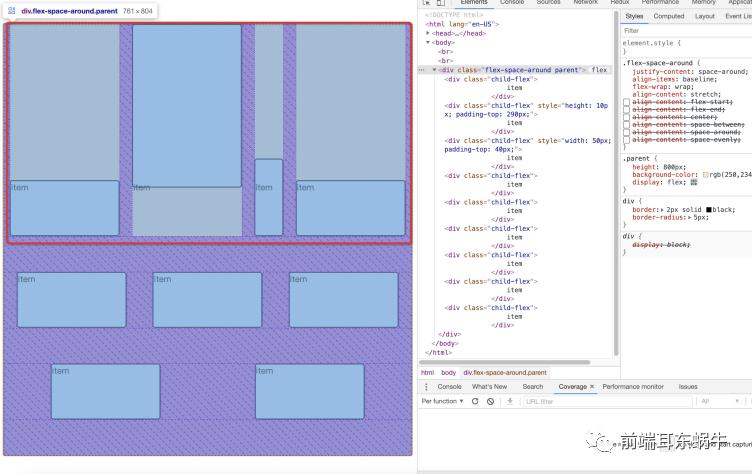
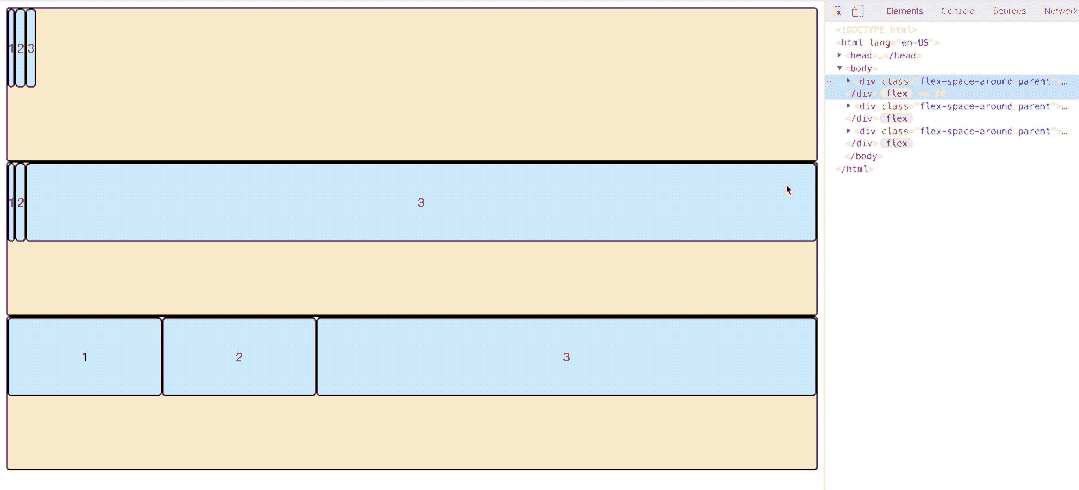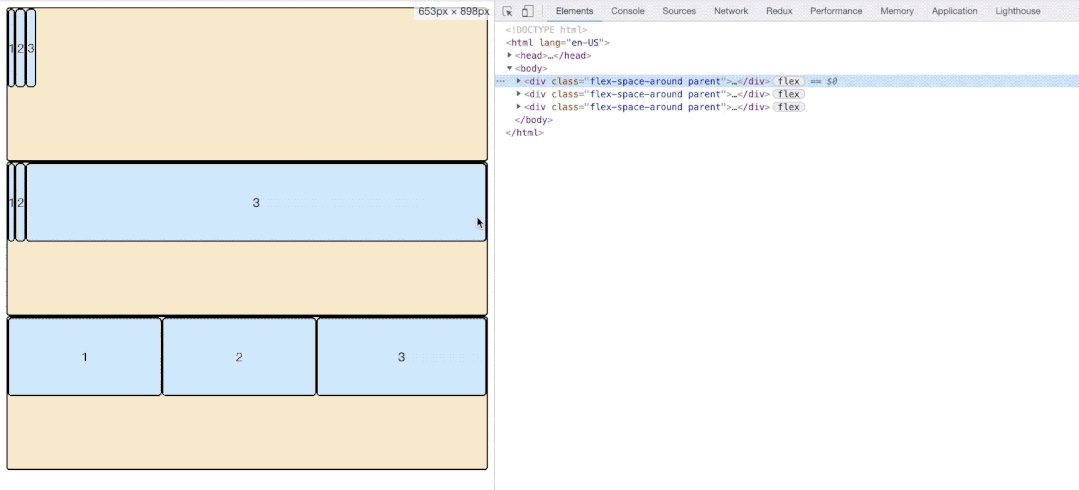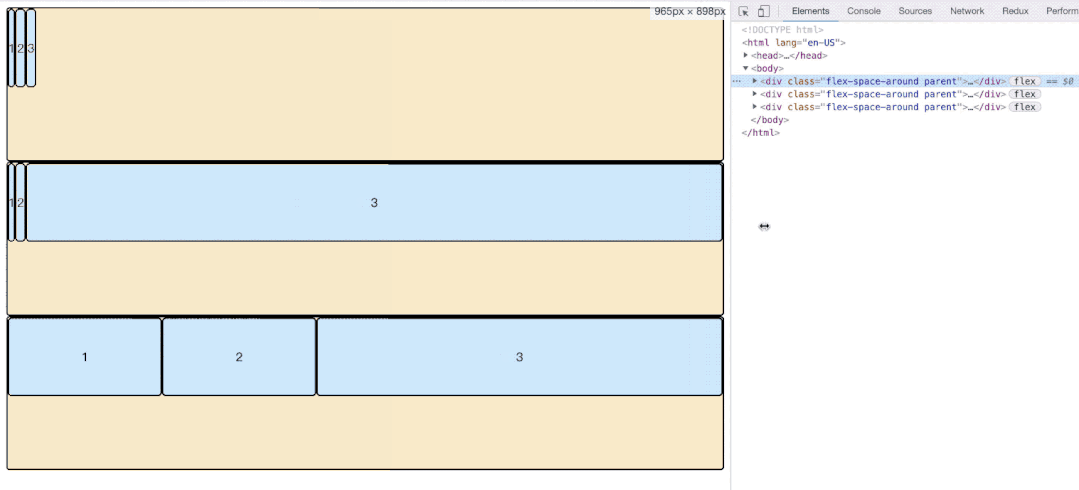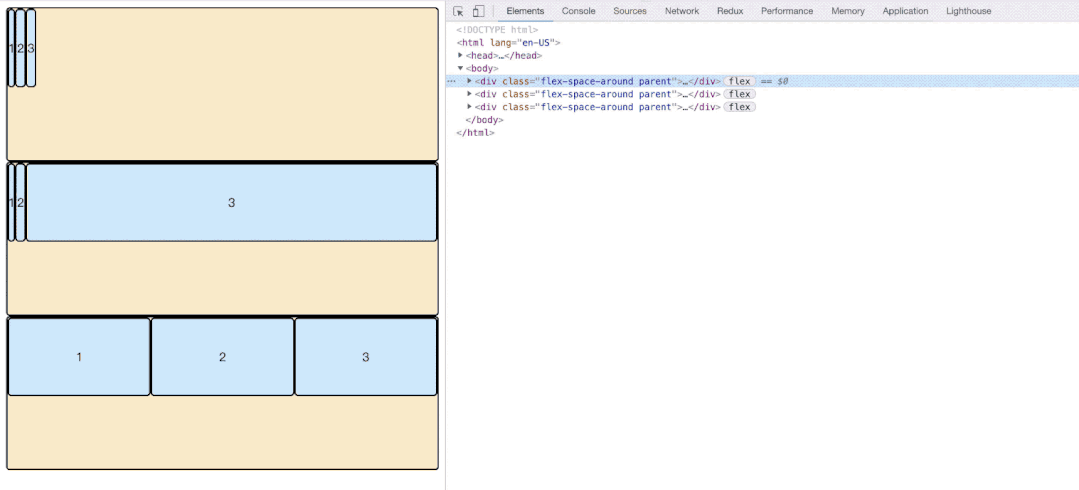
align-content属性定义了多根轴线的对齐方式。如果项目只有一根轴线,该属性不起作用。
.box {
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | stretch;
}- flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐。
- flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐。
- center:与交叉轴的中点对齐。
- space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。
- space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。
- space-evenly:每根轴线均分容器空间。但是存在兼容性问题。
- stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.child-flex {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
}
.parent {
height: 800px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
}
.flex-space-around {
justify-content: space-around;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: stretch;
align-content: flex-start;
align-content: flex-end;
align-content: center;
align-content: space-between;
align-content: space-around;
align-content: space-evenly;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<br /><br />
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex" style="height: 10px; padding-top: 290px;">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex" style="width: 50px; padding-top: 40px;">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
item
</div>
</div>
</body>
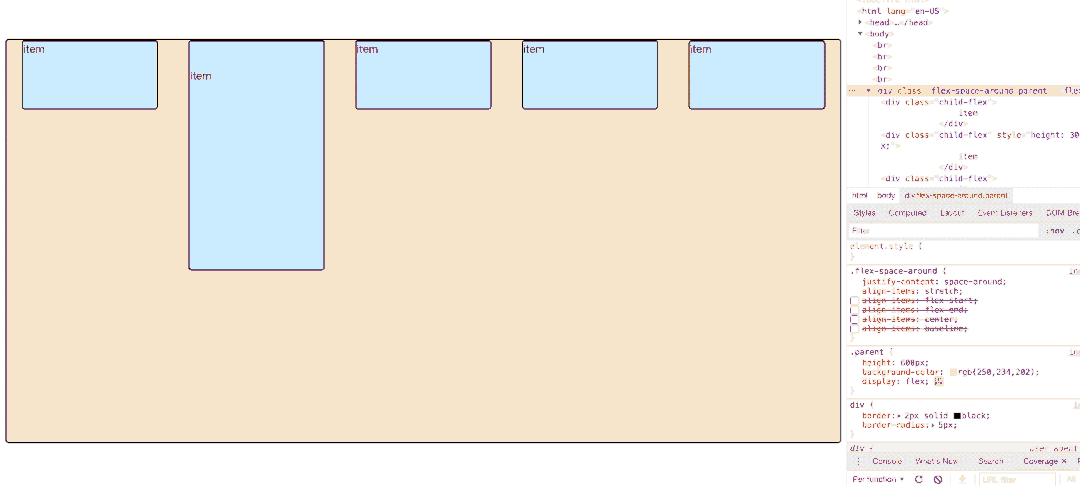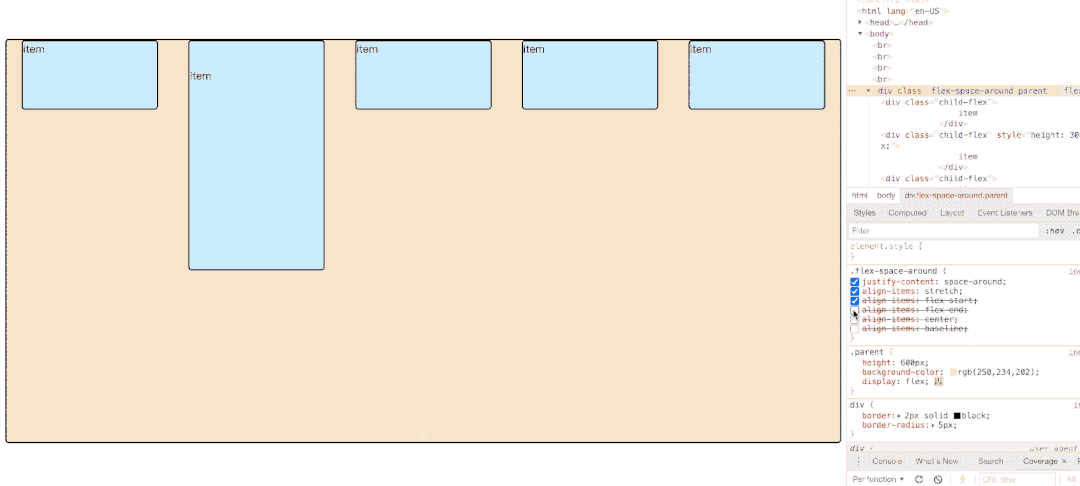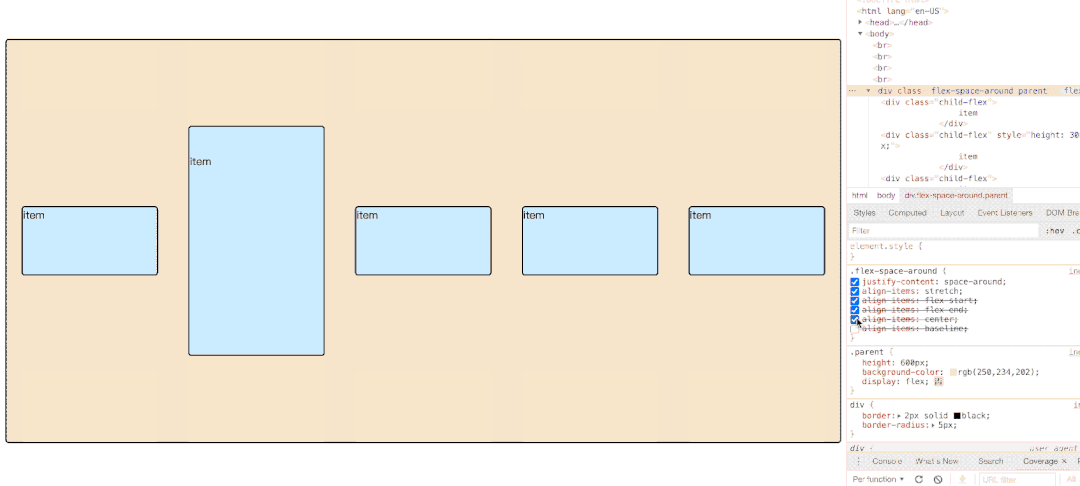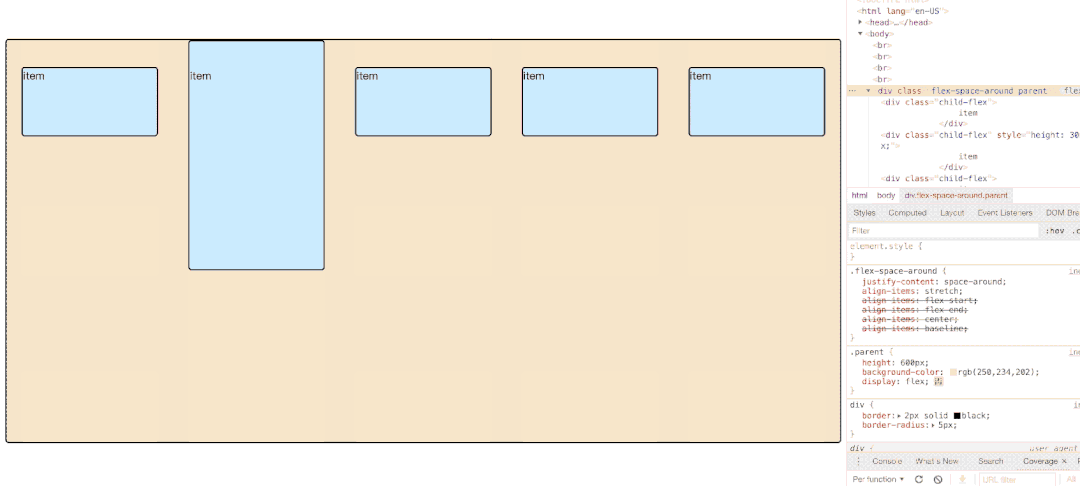
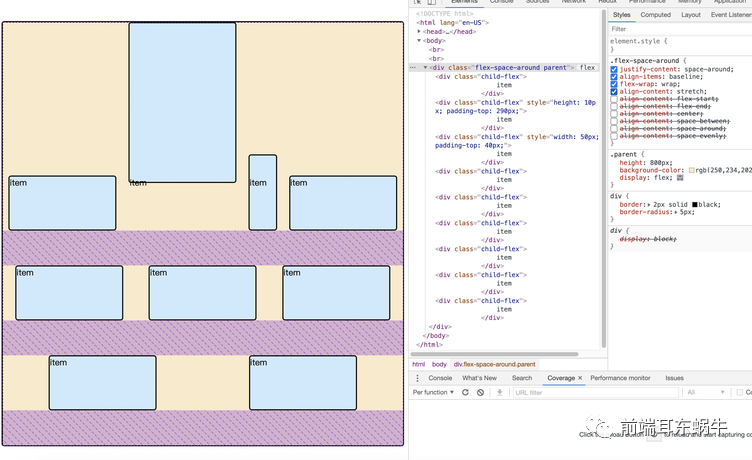
</html> 3.6.1 先明确一个概念:flex每一行item在flex计算的时候所占高度【默认direction】是多少?
如图所示,第一排三个item因为baseline侧轴排列方式导致极为不规则,他们每排之间的空格高度为:

3.6.2 属性值图示展示
3.6.3 space-evenly兼容性问题
通过space-between代替。和上面类似。
4 . 伸缩item属性
一个伸缩容器项目是一个伸缩容器的子元素。伸缩容器的文本也是被认为是一个伸缩项目。伸缩项目中内容与普通流一样。伸缩项目都有一个主轴长度和一个侧轴长度。主轴长度是伸缩项目在主轴上的尺寸,侧轴长度是伸缩项目在侧轴上的尺寸。 默认情况下侧轴长度和父元素的侧轴的长度相同。之前说到的align-items: stretch已经说过。
- order
- flex-grow
- flex-shrink
- flex-basis
- flex
- align-self
4.1 order
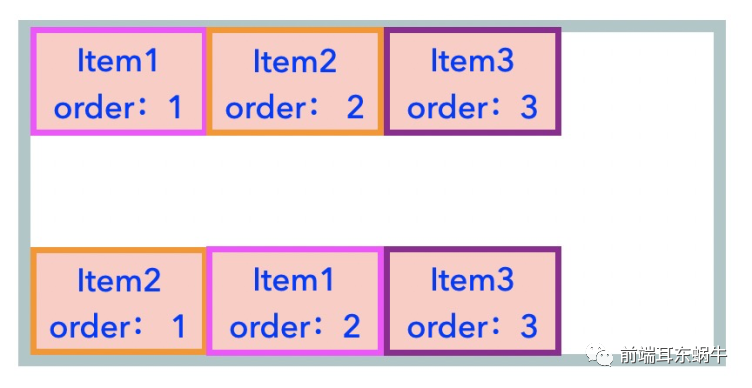
伸缩容器中的伸缩项目默认显示顺序是遵守文档在源码中出现的先后顺序。我们可以通过伸缩项目的显示顺序修改伸缩项目在页面中的显示顺序。order属性定义项目的排列顺序。数值越小,排列越靠前,默认为0。
.item {
order: <integer>;
}html元素位置相同,flex布局下的item会根据order的顺序进行排列
4.2 flex-grow
flex-grow属性定义项目的放大比例,默认为0,即如果存在剩余空间,也不放大。
.item {
flex-grow: <number>; /* default 0 */
}4.2.1 明确概念:放大不是针对伸缩项目,是针对空余空间的处理
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.child-flex {
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.child-flex1 {
}
.child-flex2 {
}
.child-flex3 {
width: 200px;
}
.child-flex2:nth-child(3) {
flex-grow: 1;
}
.child-flex3:nth-child(3) {
flex-grow: 1;
}
.parent {
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex child-flex1">
1
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex1">
2
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex1">
3
</div>
</div>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex child-flex2">
1
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex2">
2
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex2">
3
</div>
</div>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex child-flex3">
1
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex3">
2
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex3">
3
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>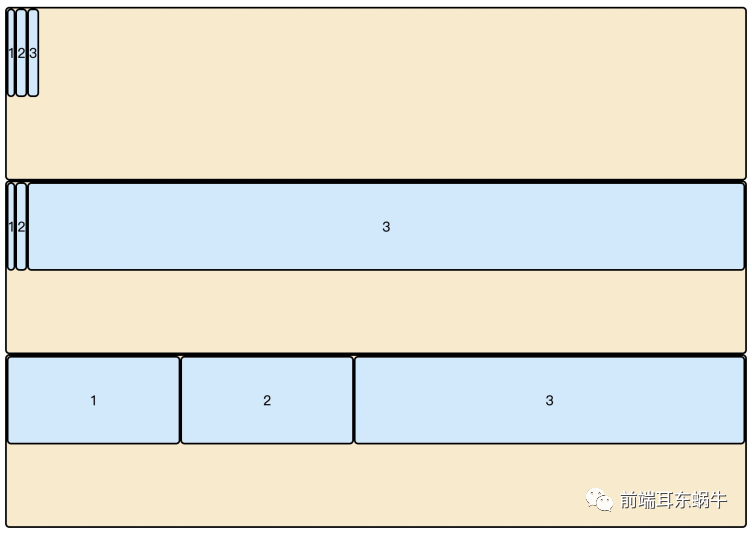
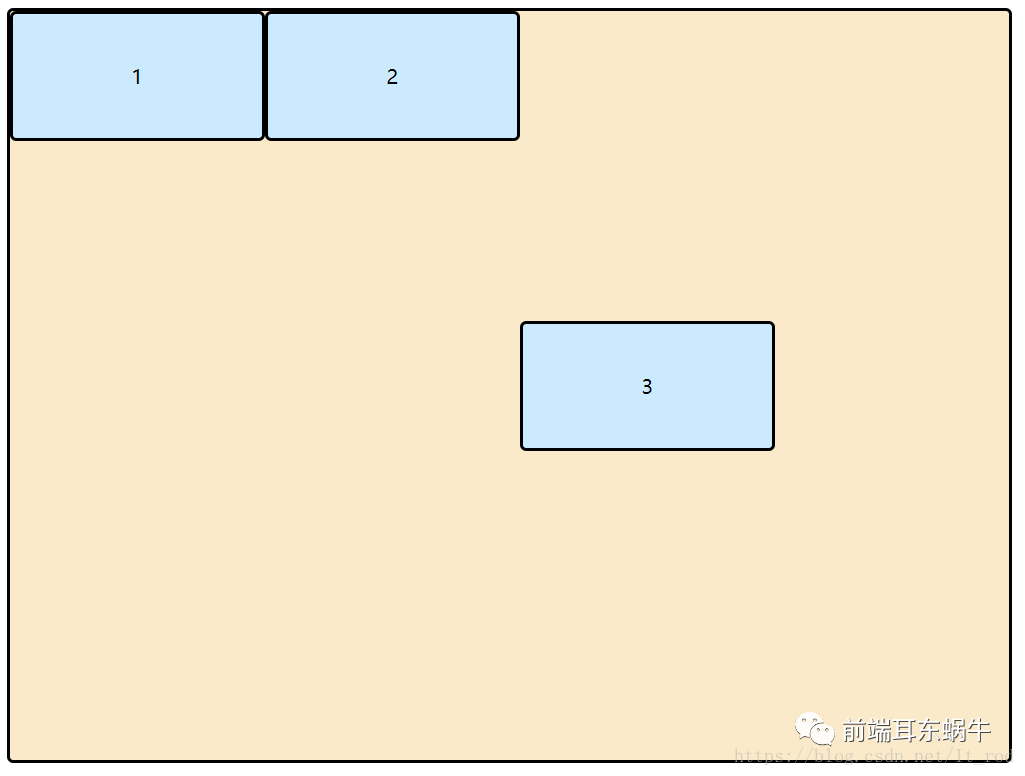
通过上面可以看到三组元素;
- 第一组,没有设置item 宽度和flex-grow
- 第二组,没有设置item 宽度,设置flex-grow
- 第三组,设置item宽度,设置flex-grow
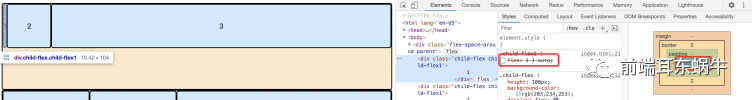
通过1和2可以看出,当设置flex-grow。item3将会占有剩余的空间。 通过3发现,在设置item宽度的时候,flex-grow作用的边界为: 满足item3的宽度并且存在剩余空间。而且缩小的时候,是三者等比缩小。
4.3 flex-shrink
flex-shrink属性定义了项目的缩小比例,默认为1,即如果空间不足,该项目将缩小。
.item {
flex-shrink: <number>; /* default 1 */
}如果所有项目的flex-shrink属性都为1,当空间不足时,都将等比例缩小。如果一个项目的flex-shrink属性为0,其他项目都为1,则空间不足时,前者不缩小。负值对该属性无效。
4.3.1 和flex-grow的区别【杜撰】
| 作用效果 | 默认值 | 实际作用点 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| flex-grow | 放大 | 0 | 空间【项目占用容器剩余空间】 |
| flex-shrink | 缩小 | 1 | 项目【空间缩小导致项目item缩小】 |
4.4 flex-basis
flex-basis属性定义了在分配多余空间之前,项目占据的主轴空间(main size)。浏览器根据这个属性,计算主轴是否有多余空间。它的默认值为auto,即项目的本来大小。
.item {
flex-basis: <length> | auto; /* default auto */
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.child-flex {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.child-flex:nth-child(1) {
flex-basis: 300px;
}
.parent {
height: 600px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex">
1
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
2
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
3
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>4.4.1 结论:
- flex-basis的优先级高于width。从上面的例子中就可以看到。
- 可以设为跟width或height属性一样的值,则项目将占据固定空间。
4.5 flex
flex属性是flex-grow, flex-shrink 和 flex-basis的简写,默认值为0 1 auto。后两个属性可选。
.item {
flex: none | [ <'flex-grow'> <'flex-shrink'>? || <'flex-basis'> ]
}第一个属性是必选。后面两个属性是可选,浏览器会根据参数值自动计算。
4.5.1 浏览器计算
flex: 2
flex: 2 auto
flex: 2 2
flex: 2 2 100
4.5.2 默认值的不同
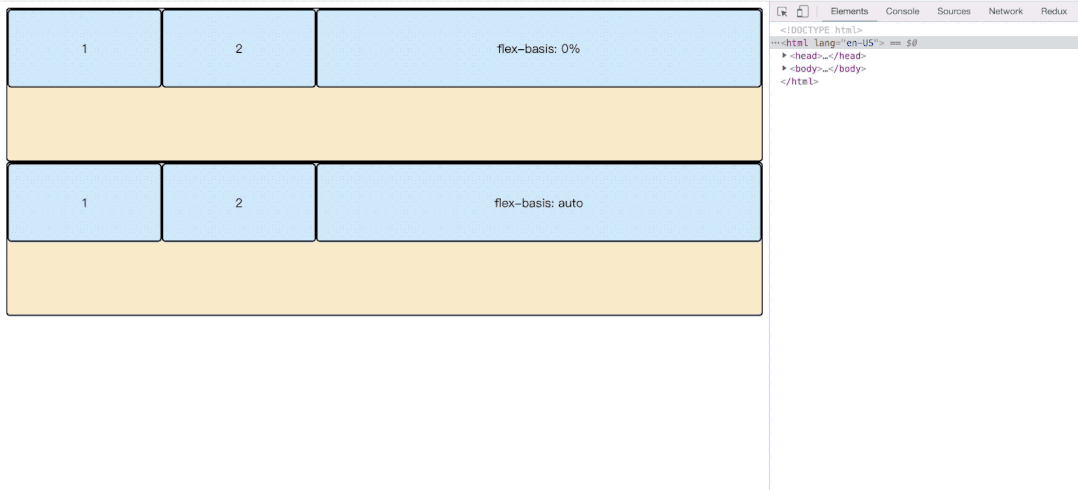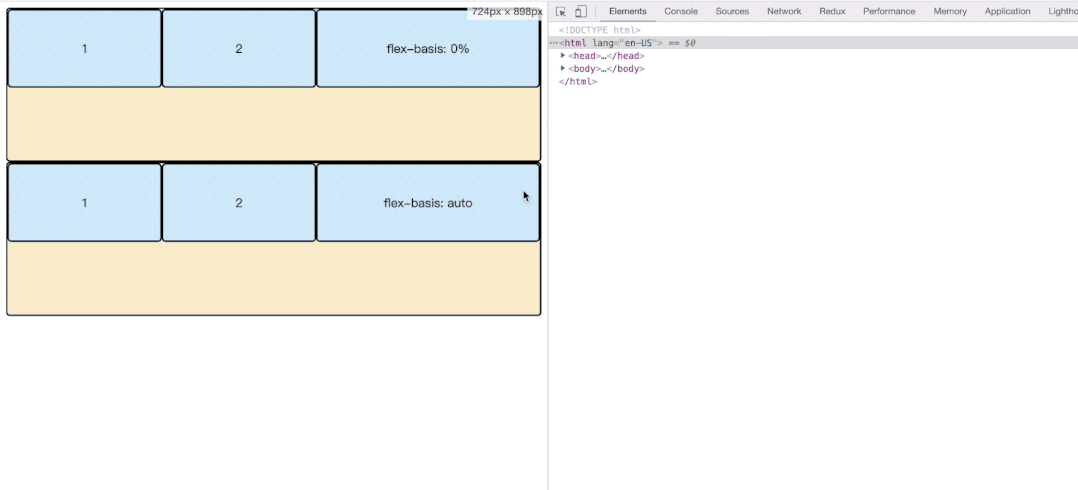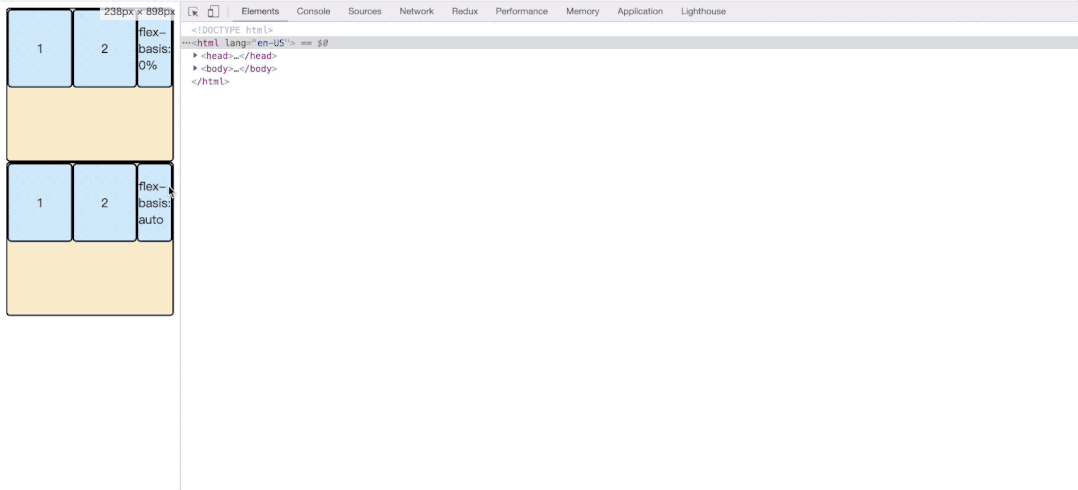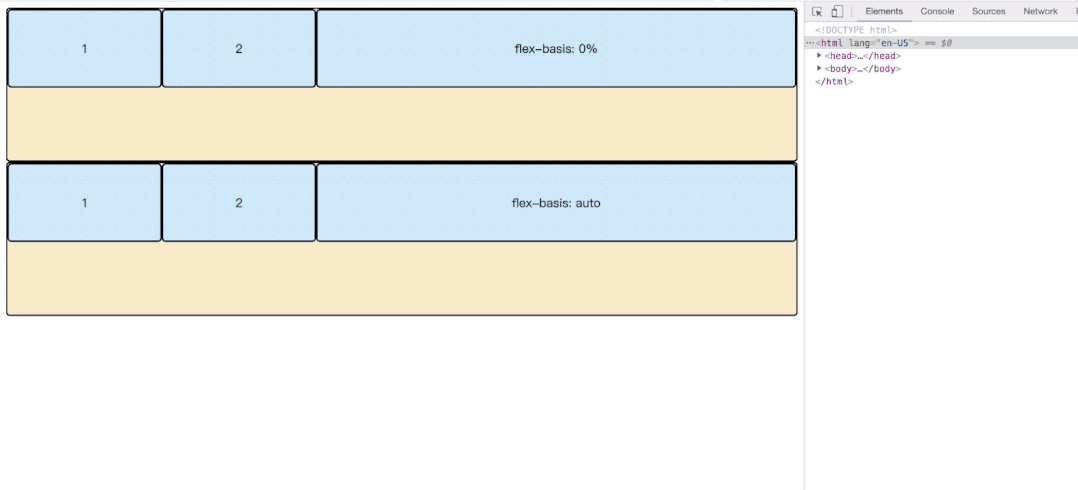
根据上面我们可以看到flex-basis有的是auto,有的是0%;这里是不一样的。我们看一下效果。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.child-flex {
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.child-flex2 {
width: 200px;
}
.child-flex3 {
width: 200px;
}
.child-flex2:nth-child(3) {
flex: 1 2;
}
.child-flex3:nth-child(3) {
flex: 1 2 auto;
}
.parent {
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex child-flex2">
1
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex2">
2
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex2">
flex-basis: 0%
</div>
</div>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex child-flex3">
1
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex3">
2
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex3">
flex-basis: auto
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>- flex: auto;当main宽度收缩至当前item width的宽度的时候,才会继续所有item一起缩小。
- flex: 0%; 这种相当于flex-basis无效,顺便造成width无效。main收缩的时候,会将当前item收缩至contentWidth大小的时候,才会继续其他item的缩小。
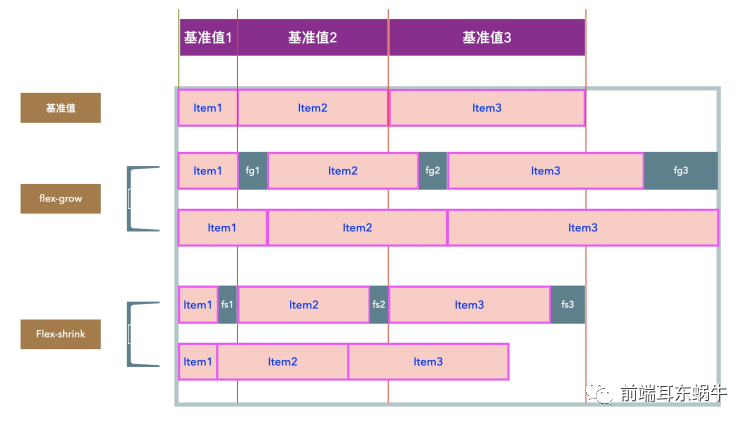
4.5.3 flex-grow,flex-shrink,flex-basis三个属性之间的关系
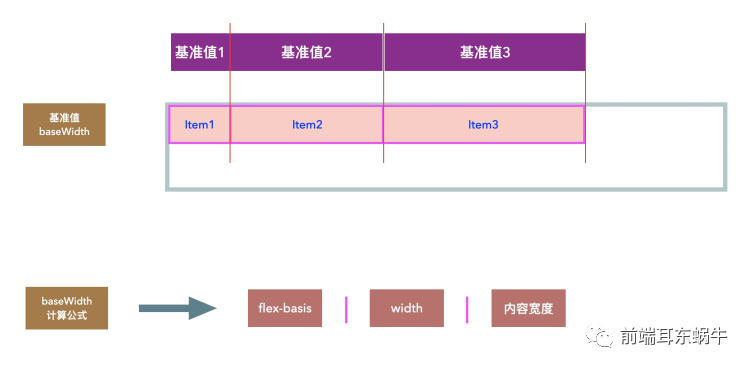
4.5.3.1 flex-grow,flex-shrink的基准值是什么?
这里的基准主要是为了拆分出一个计算的公式。这里的基准值说的是item在进行flex-grow,flex-shrink作用前的每个item当前所占的位置宽度。
这里主要影响的有几个因素:flex-basis,width,内容宽度 计算公式如下:
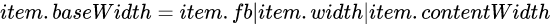
4.5.3.2 flex-grow计算
在基于基准值的情况下,item按照各自设置flex-grow数值比例分配容器剩余空间。 每个item具体放大的数值:
item总长度:
4.5.3.3 flex-shrink计算
在基于基准值的情况下,item按照各自设置flex-shrink数值比例缩小自身空间。 每个item缩小的具体的数值:
item总长度:
4.5.3.4 根据公式进行计算
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.child-flex {
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.child-flex1 {
flex: 0 1 auto;
}
.child-flex1:nth-child(2) {
width: 100px;
}
.child-flex1:nth-child(3) {
flex: 0 2 400px;
}
.parent {
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex child-flex1">
1
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex1">
2
</div>
<div class="child-flex child-flex1">
3
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>根据上面的例子进行测试即可:我们看一下:
| flex属性 | width属性 | contentwidt | baseWidth | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| flex-grow | flex-shrink | flex-basis | ||||
| item1 | 1 | 1 | auto | 无 | 根据上图:6.422 | 6.422 |
| item2 | 1 | 1 | auto | 100px | 不需要 | 100 |
| item3 | 2 | 2 | 400 | 无 | 不需要 | 400 |
然后现在我们将总宽度移动到:1000px。
| 1000px下当前内容宽度 | baseWidth | 增大数值 | flex-grow 比例 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| item1 | 126.812 | 6.422 | 120.39 | 1 |
| item2 | 220.391 | 100 | 120.391 | 1 |
| item3 | 640.797 | 400 | 240.797 | 2 |
这里存在小数点误差,这个数值是在google浏览器查看到的。但是基本是是满足比例的。
4.6 align-self
align-self属性允许单个项目有与其他项目不一样的对齐方式,可覆盖align-items属性。默认值为auto,表示继承父元素的align-items属性,如果没有父元素,则等同于stretch。
.item {
align-self: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;
}该属性可能取6个值,除了auto,其他都与align-items属性完全一致。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.child-flex {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(203,234,253);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.child-flex:nth-child(3) {
align-self: center;
}
.parent {
width: 800px;
height: 600px;
background-color: rgb(250,234,202);
display: flex;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-space-around parent">
<div class="child-flex">
1
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
2
</div>
<div class="child-flex">
3
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>5 . 总结flex的用法
明确主轴侧轴的概念
- flex-direction
5.1 伸缩容器属性
5.1.1 容器内单行下,
- 多个项目的排列方式:justify-content 【主轴排列方式】
- 单个项目的排列方式:align-content【侧轴排列方式】
5.1.2 容器多行排列:
- 多行模式:flex-wrap
- 以单行为维度,多行之间的排列方式:align-content
5.2 伸缩item属性
- 单行单项目的顺序放置:order
- 单行单项目的扩大和缩小配置,flex-grow,flex-shrink
- 处理单行单个项目的参与扩大和缩小的起点位置,这样说的可能有点绕,或者记忆成参与计算baseWidth值。
- 容器单行下,单个item的侧轴排列方式 align-self
6 . 设为Flex布局以后,子元素的float、clear和vertical-align属性将失效
- 第一个在原先的布局方式中,float的存在是为了可以自由的控制div的位置。但是现在flex可以实现float的效果。
- 第二个clear属性没有作用,是因为flex是弹性布局,不会出现溢出的问题。
- 第三个vertical-align的属性可以依靠align-items实现。
7 . 参照
https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2015/07/flex-grammar.html