使用 LLVM 实现一个简单编译器
1. 目标
这个系列来自 LLVM 的[Kaleidoscope 教程] ,增加了我对代码的注释以及一些理解,修改了部分代码。现在开始我们要使用 LLVM 实现一个编译器,完成对如下代码的编译运行。
# 斐波那契数列函数定义
def fib(x)
if x < 3 then
1
else
fib(x - 1) + fib(x - 2)
fib(40)
# 函数声明
extern sin(arg)
extern cos(arg)
extern atan2(arg1 arg2)
# 声明后的函数可调用
atan2(sin(.4), cos(42))这个语言称为 Kaleidoscope, 从代码可以看出,Kaleidoscope 支持函数、条件分支、数值计算等语言特性。为了方便,Kaleidoscope 唯一支持的数据类型为 float64, 所以示例中的所有数值都是 float64。
2. Lex
编译的第一个步骤称为 Lex, 词法分析,其功能是将文本输入转为多个 tokens, 比如对于如下代码:
atan2(sin(.4), cos(42))
就应该转为:
tokens = ["atan2", "(", "sin", "(", .4, ")", ",", "cos", "(", 42, ")", ")"]
接下来我们使用 C++来写这个 Lexer, 由于这是教程代码,所以并没有使用工程项目应有的设计:
// 如果不是以下5种情况,Lexer返回[0-255]的ASCII值,否则返回以下枚举值
enum Token {
TOKEN_EOF = -1, // 文件结束标识符
TOKEN_DEF = -2, // 关键字def
TOKEN_EXTERN = -3, // 关键字extern
TOKEN_IDENTIFIER = -4, // 名字
TOKEN_NUMBER = -5 // 数值
};
std::string g_identifier_str; // Filled in if TOKEN_IDENTIFIER
double g_number_val; // Filled in if TOKEN_NUMBER
// 从标准输入解析一个Token并返回
int GetToken() {
static int last_char = ' ';
// 忽略空白字符
while (isspace(last_char)) {
last_char = getchar();
}
// 识别字符串
if (isalpha(last_char)) {
g_identifier_str = last_char;
while (isalnum((last_char = getchar()))) {
g_identifier_str += last_char;
}
if (g_identifier_str == "def") {
return TOKEN_DEF;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "extern") {
return TOKEN_EXTERN;
} else {
return TOKEN_IDENTIFIER;
}
}
// 识别数值
if (isdigit(last_char) || last_char == '.') {
std::string num_str;
do {
num_str += last_char;
last_char = getchar();
} while (isdigit(last_char) || last_char == '.');
g_number_val = strtod(num_str.c_str(), nullptr);
return TOKEN_NUMBER;
}
// 忽略注释
if (last_char == '#') {
do {
last_char = getchar();
} while (last_char != EOF && last_char != '\n' && last_char != '\r');
if (last_char != EOF) {
return GetToken();
}
}
// 识别文件结束
if (last_char == EOF) {
return TOKEN_EOF;
}
// 直接返回ASCII
int this_char = last_char;
last_char = getchar();
return this_char;
}使用 Lexer 对之前的代码处理结果为(使用空格分隔 tokens):
def fib ( x ) if x < 3 then 1 else fib ( x - 1 ) + fib ( x - 2 ) fib ( 40 ) extern sin ( arg )
extern cos ( arg ) extern atan2 ( arg1 arg2 ) atan2 ( sin ( 0.4 ) , cos ( 42 ) )Lexer 的输入是代码文本,输出是有序的一个个 Token。
3. Parser
编译的第二个步骤称为 Parse, 其功能是将 Lexer 输出的 tokens 转为 AST (Abstract Syntax Tree)。我们首先定义表达式的 AST Node:
// 所有 `表达式` 节点的基类
class ExprAST {
public:
virtual ~ExprAST() {}
};
// 字面值表达式
class NumberExprAST : public ExprAST {
public:
NumberExprAST(double val) : val_(val) {}
private:
double val_;
};
// 变量表达式
class VariableExprAST : public ExprAST {
public:
VariableExprAST(const std::string& name) : name_(name) {}
private:
std::string name_;
};
// 二元操作表达式
class BinaryExprAST : public ExprAST {
public:
BinaryExprAST(char op, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> lhs,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> rhs)
: op_(op), lhs_(std::move(lhs)), rhs_(std::move(rhs)) {}
private:
char op_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> lhs_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> rhs_;
};
// 函数调用表达式
class CallExprAST : public ExprAST {
public:
CallExprAST(const std::string& callee,
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> args)
: callee_(callee), args_(std::move(args)) {}
private:
std::string callee_;
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> args_;
};为了便于理解,关于条件表达式的内容放在后面,这里暂不考虑。接着我们定义函数声明和函数的 AST Node:
// 函数接口
class PrototypeAST {
public:
PrototypeAST(const std::string& name, std::vector<std::string> args)
: name_(name), args_(std::move(args)) {}
const std::string& name() const { return name_; }
private:
std::string name_;
std::vector<std::string> args_;
};
// 函数
class FunctionAST {
public:
FunctionAST(std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> proto,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> body)
: proto_(std::move(proto)), body_(std::move(body)) {}
private:
std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> proto_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> body_;
};接下来我们要进行 Parse, 在正式 Parse 前,定义如下函数方便后续处理:
int g_current_token; // 当前待处理的Token
int GetNextToken() {
return g_current_token = GetToken();
}首先我们处理最简单的字面值:
// numberexpr ::= number
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseNumberExpr() {
auto result = std::make_unique<NumberExprAST>(g_number_val);
GetNextToken();
return std::move(result);
}这段程序非常简单,当前 Token 为 TOKEN_NUMBER 时被调用,使用 g_number_val,创建一个 NumberExprAST, 因为当前 Token 处理完毕,让 Lexer 前进一个 Token, 最后返回。接着我们处理圆括号操作符、变量、函数调用:
// parenexpr ::= ( expression )
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseParenExpr() {
GetNextToken(); // eat (
auto expr = ParseExpression();
GetNextToken(); // eat )
return expr;
}
/// identifierexpr
/// ::= identifier
/// ::= identifier ( expression, expression, ..., expression )
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseIdentifierExpr() {
std::string id = g_identifier_str;
GetNextToken();
if (g_current_token != '(') {
return std::make_unique<VariableExprAST>(id);
} else {
GetNextToken(); // eat (
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>> args;
while (g_current_token != ')') {
args.push_back(ParseExpression());
if (g_current_token == ')') {
break;
} else {
GetNextToken(); // eat ,
}
}
GetNextToken(); // eat )
return std::make_unique<CallExprAST>(id, std::move(args));
}
}上面代码中的 ParseExpression 与 ParseParenExpr 等存在循环依赖,这里按照其名字理解意思即可,具体实现在后面。我们将 NumberExpr、ParenExpr、IdentifierExpr 视为 PrimaryExpr, 封装 ParsePrimary 方便后续调用:
/// primary
/// ::= identifierexpr
/// ::= numberexpr
/// ::= parenexpr
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParsePrimary() {
switch (g_current_token) {
case TOKEN_IDENTIFIER: return ParseIdentifierExpr();
case TOKEN_NUMBER: return ParseNumberExpr();
case '(': return ParseParenExpr();
default: return nullptr;
}
}接下来我们考虑如何处理二元操作符,为了方便,Kaleidoscope 只支持 4 种二元操作符,优先级为:
'<' < '+' = '-' < '*'
即'<'的优先级最低,而'*'的优先级最高,在代码中实现为:
// 定义优先级
const std::map<char, int> g_binop_precedence = {
{'<', 10}, {'+', 20}, {'-', 20}, {'*', 40}};
// 获得当前Token的优先级
int GetTokenPrecedence() {
auto it = g_binop_precedence.find(g_current_token);
if (it != g_binop_precedence.end()) {
return it->second;
} else {
return -1;
}
}对于带优先级的二元操作符的解析,我们会将其分成多个片段。比如一个表达式:
a + b + (c + d) * e * f + g
首先解析 a, 然后处理多个二元组:
[+, b], [+, (c+d)], [*, e], [*, f], [+, g]
即,复杂表达式可以抽象为一个 PrimaryExpr 跟着多个[binop, PrimaryExpr]二元组,注意由于圆括号属于 PrimaryExpr, 所以这里不需要考虑怎么特殊处理(c+d),因为会被 ParsePrimary 自动处理。
// parse
// lhs [binop primary] [binop primary] ...
// 如遇到优先级小于min_precedence的操作符,则停止
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseBinOpRhs(int min_precedence,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> lhs) {
while (true) {
int current_precedence = GetTokenPrecedence();
if (current_precedence < min_precedence) {
// 如果当前token不是二元操作符,current_precedence为-1, 结束任务
// 如果遇到优先级更低的操作符,也结束任务
return lhs;
}
int binop = g_current_token;
GetNextToken(); // eat binop
auto rhs = ParsePrimary();
// 现在我们有两种可能的解析方式
// * (lhs binop rhs) binop unparsed
// * lhs binop (rhs binop unparsed)
int next_precedence = GetTokenPrecedence();
if (current_precedence < next_precedence) {
// 将高于current_precedence的右边的操作符处理掉返回
rhs = ParseBinOpRhs(current_precedence + 1, std::move(rhs));
}
lhs =
std::make_unique<BinaryExprAST>(binop, std::move(lhs), std::move(rhs));
// 继续循环
}
}
// expression
// ::= primary [binop primary] [binop primary] ...
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseExpression() {
auto lhs = ParsePrimary();
return ParseBinOpRhs(0, std::move(lhs));
}最复杂的部分完成后,按部就班把 function 写完:
// prototype
// ::= id ( id id ... id)
std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> ParsePrototype() {
std::string function_name = g_identifier_str;
GetNextToken();
std::vector<std::string> arg_names;
while (GetNextToken() == TOKEN_IDENTIFIER) {
arg_names.push_back(g_identifier_str);
}
GetNextToken(); // eat )
return std::make_unique<PrototypeAST>(function_name, std::move(arg_names));
}
// definition ::= def prototype expression
std::unique_ptr<FunctionAST> ParseDefinition() {
GetNextToken(); // eat def
auto proto = ParsePrototype();
auto expr = ParseExpression();
return std::make_unique<FunctionAST>(std::move(proto), std::move(expr));
}
// external ::= extern prototype
std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> ParseExtern() {
GetNextToken(); // eat extern
return ParsePrototype();
}最后,我们为顶层的代码实现匿名 function:
// toplevelexpr ::= expression
std::unique_ptr<FunctionAST> ParseTopLevelExpr() {
auto expr = ParseExpression();
auto proto = std::make_unique<PrototypeAST>("", std::vector<std::string>());
return std::make_unique<FunctionAST>(std::move(proto), std::move(expr));
}顶层代码的意思是放在全局而不放在 function 内定义的一些执行语句比如变量赋值,函数调用等。编写一个 main 函数:
int main() {
GetNextToken();
while (true) {
switch (g_current_token) {
case TOKEN_EOF: return 0;
case TOKEN_DEF: {
ParseDefinition();
std::cout << "parsed a function definition" << std::endl;
break;
}
case TOKEN_EXTERN: {
ParseExtern();
std::cout << "parsed a extern" << std::endl;
break;
}
default: {
ParseTopLevelExpr();
std::cout << "parsed a top level expr" << std::endl;
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}编译:
clang++ main.cpp `llvm-config --cxxflags --ldflags --libs`
输入如下代码进行测试:
def foo(x y)
x + foo(y, 4)
def foo(x y)
x + y
y
extern sin(a)得到输出:
parsed a function definition
parsed a function definition
parsed a top level expr
parsed a extern至此成功将 Lexer 输出的 tokens 转为 AST。
4. Code Generation to LLVM IR
终于开始 codegen 了,首先我们 include 一些 LLVM 头文件,定义一些全局变量:
#include "llvm/ADT/APFloat.h"
#include "llvm/ADT/STLExtras.h"
#include "llvm/IR/BasicBlock.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Constants.h"
#include "llvm/IR/DerivedTypes.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Function.h"
#include "llvm/IR/IRBuilder.h"
#include "llvm/IR/LLVMContext.h"
#include "llvm/IR/LegacyPassManager.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Module.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Type.h"
#include "llvm/IR/Verifier.h"
#include "llvm/Support/TargetSelect.h"
#include "llvm/Target/TargetMachine.h"
#include "llvm/Transforms/InstCombine/InstCombine.h"
#include "llvm/Transforms/Scalar.h"
#include "llvm/Transforms/Scalar/GVN.h"
// 记录了LLVM的核心数据结构,比如类型和常量表,不过我们不太需要关心它的内部
llvm::LLVMContext g_llvm_context;
// 用于创建LLVM指令
llvm::IRBuilder<> g_ir_builder(g_llvm_context);
// 用于管理函数和全局变量,可以粗浅地理解为类c++的编译单元(单个cpp文件)
llvm::Module g_module("my cool jit", g_llvm_context);
// 用于记录函数的变量参数
std::map<std::string, llvm::Value*> g_named_values;然后给每个 AST Class 增加一个 CodeGen 接口:
// 所有 `表达式` 节点的基类
class ExprAST {
public:
virtual ~ExprAST() {}
virtual llvm::Value* CodeGen() = 0;
};
// 字面值表达式
class NumberExprAST : public ExprAST {
public:
NumberExprAST(double val) : val_(val) {}
llvm::Value* CodeGen() override;
private:
double val_;
};首先实现 NumberExprAST 的 CodeGen:
llvm::Value* NumberExprAST::CodeGen() {
return llvm::ConstantFP::get(g_llvm_context, llvm::APFloat(val_));
}由于 Kaleidoscope 只有一种数据类型 FP64, 所以直接调用 ConstantFP 传入即可,APFloat 是 llvm 内部的数据结构,用于存储 Arbitrary Precision Float. 在 LLVM IR 中,所有常量是唯一且共享的,所以这里使用的 get 而不是 new/create。
然后实现 VariableExprAST 的 CodeGen:
llvm::Value* VariableExprAST::CodeGen() {
return g_named_values.at(name_);
}由于 Kaleidoscope 的 VariableExpr 只存在于函数内对函数参数的引用,我们假定函数参数已经被注册到 g_name_values 中,所以 VariableExpr 直接查表返回即可。
接着实现 BinaryExprAST, 分别 codegen lhs, rhs 然后创建指令处理 lhs, rhs 即可:
llvm::Value* BinaryExprAST::CodeGen() {
llvm::Value* lhs = lhs_->CodeGen();
llvm::Value* rhs = rhs_->CodeGen();
switch (op_) {
case '<': {
llvm::Value* tmp = g_ir_builder.CreateFCmpULT(lhs, rhs, "cmptmp");
// 把 0/1 转为 0.0/1.0
return g_ir_builder.CreateUIToFP(
tmp, llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context), "booltmp");
}
case '+': return g_ir_builder.CreateFAdd(lhs, rhs, "addtmp");
case '-': return g_ir_builder.CreateFSub(lhs, rhs, "subtmp");
case '*': return g_ir_builder.CreateFMul(lhs, rhs, "multmp");
default: return nullptr;
}
}实现 CallExprAST:
llvm::Value* CallExprAST::CodeGen() {
// g_module中存储了全局变量/函数等
llvm::Function* callee = g_module.getFunction(callee_);
std::vector<llvm::Value*> args;
for (std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>& arg_expr : args_) {
args.push_back(arg_expr->CodeGen());
}
return g_ir_builder.CreateCall(callee, args, "calltmp");
}实现 ProtoTypeAST:
llvm::Value* PrototypeAST::CodeGen() {
// 创建kaleidoscope的函数类型 double (doube, double, ..., double)
std::vector<llvm::Type*> doubles(args_.size(),
llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context));
// 函数类型是唯一的,所以使用get而不是new/create
llvm::FunctionType* function_type = llvm::FunctionType::get(
llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context), doubles, false);
// 创建函数, ExternalLinkage意味着函数可能不在当前module中定义,在当前module
// 即g_module中注册名字为name_, 后面可以使用这个名字在g_module中查询
llvm::Function* func = llvm::Function::Create(
function_type, llvm::Function::ExternalLinkage, name_, &g_module);
// 增加IR可读性,设置function的argument name
int index = 0;
for (auto& arg : func->args()) {
arg.setName(args_[index++]);
}
return func;
}实现 FunctionAST:
llvm::Value* FunctionAST::CodeGen() {
// 检查函数声明是否已完成codegen(比如之前的extern声明), 如果没有则执行codegen
llvm::Function* func = g_module.getFunction(proto_->name());
if (func == nullptr) {
func = proto_->CodeGen();
}
// 创建一个Block并且设置为指令插入位置。
// llvm block用于定义control flow graph, 由于我们暂不实现control flow, 创建
// 一个单独的block即可
llvm::BasicBlock* block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "entry", func);
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(block);
// 将函数参数注册到g_named_values中,让VariableExprAST可以codegen
g_named_values.clear();
for (llvm::Value& arg : func->args()) {
g_named_values[arg.getName()] = &arg;
}
// codegen body然后return
llvm::Value* ret_val = body_->CodeGen();
g_ir_builder.CreateRet(ret_val);
llvm::verifyFunction(*func);
return func;
}至此,所有 codegen 都已完成,修改 main:
int main() {
GetNextToken();
while (true) {
switch (g_current_token) {
case TOKEN_EOF: return 0;
case TOKEN_DEF: {
auto ast = ParseDefinition();
std::cout << "parsed a function definition" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cerr << std::endl;
break;
}
case TOKEN_EXTERN: {
auto ast = ParseExtern();
std::cout << "parsed a extern" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cerr << std::endl;
break;
}
default: {
auto ast = ParseTopLevelExpr();
std::cout << "parsed a top level expr" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cerr << std::endl;
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}输入测试:
4 + 5
def foo(a b)
a*a + 2*a*b + b*b
foo(2, 3)
def bar(a)
foo(a, 4) + bar(31337)
extern cos(x)
cos(1.234)得到输出:
parsed a top level expr
define double @0() {
entry:
ret double 9.000000e+00
}
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %a, double %b) {
entry:
%multmp = fmul double %a, %a
%multmp1 = fmul double 2.000000e+00, %a
%multmp2 = fmul double %multmp1, %b
%addtmp = fadd double %multmp, %multmp2
%multmp3 = fmul double %b, %b
%addtmp4 = fadd double %addtmp, %multmp3
ret double %addtmp4
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @1() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 2.000000e+00, double 3.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
parsed a function definition
define double @bar(double %a) {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double %a, double 4.000000e+00)
%calltmp1 = call double @bar(double 3.133700e+04)
%addtmp = fadd double %calltmp, %calltmp1
ret double %addtmp
}
parsed a extern
declare double @cos(double)
parsed a top level expr
define double @2() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @cos(double 1.234000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}至此,我们已成功将 Parser 输出的 AST 转为 LLVM IR。
5. Optimizer
我们使用上一节的程序处理如下代码:
def test(x)
1 + 2 + x可以得到:
parsed a function definition
define double @test(double %x) {
entry:
%addtmp = fadd double 3.000000e+00, %x
ret double %addtmp
}可以看到,生成的指令直接是 1+2 的结果,而没有 1 + 2 的指令,这种自动把常量计算完毕而不是生成加法指令的优化称为 Constant Folding。
在大部分时候仅有这个优化仍然不够,比如如下代码:
def test(x)
(1 + 2 + x) * (x + (1 + 2))可以得到编译结果:
parsed a function definition
define double @test(double %x) {
entry:
%addtmp = fadd double 3.000000e+00, %x
%addtmp1 = fadd double %x, 3.000000e+00
%multmp = fmul double %addtmp, %addtmp1
ret double %multmp
}生成了两个加法指令,但最优做法只需要一个加法即可,因为乘法的两边 lhs 和 rhs 是相等的。
这需要其他的优化技术,llvm 以"passes"的形式提供,llvm 中的 passes 可以选择是否启用,可以设置 passes 的顺序。
这里我们对每个函数单独做优化,定义 g_fpm, 增加几个 passes:
llvm::legacy::FunctionPassManager g_fpm(&g_module);
int main() {
g_fpm.add(llvm::createInstructionCombiningPass());
g_fpm.add(llvm::createReassociatePass());
g_fpm.add(llvm::createGVNPass());
g_fpm.add(llvm::createCFGSimplificationPass());
g_fpm.doInitialization();
...
}在 FunctionAST 的 CodeGen 中增加一句:
llvm::Value* ret_val = body_->CodeGen();
g_ir_builder.CreateRet(ret_val);
llvm::verifyFunction(*func);
g_fpm.run(*func); // 增加这句
return func;即启动了对每个 function 的优化,接下来测试之前的代码:
parsed a function definition
define double @test(double %x) {
entry:
%addtmp = fadd double %x, 3.000000e+00
%multmp = fmul double %addtmp, %addtmp
ret double %multmp
}可以看到,和我们期望的一样,加法指令减少到一个。
6. Adding a JIT Compiler
由于 JIT 模式中我们需要反复创建新的 module, 所以我们将全局变量 g_module 改为 unique_ptr。
// 用于管理函数和全局变量,可以粗浅地理解为类c++的编译单元(单个cpp文件)
std::unique_ptr<llvm::Module> g_module =
std::make_unique<llvm::Module>("my cool jit", g_llvm_context);为了专注于 JIT,我们可以把优化的 passes 删掉。
修改 ParseTopLevelExpr,给 PrototypeAST 命名为__anon_expr, 让我们后面可以通过这个名字找到它。
// toplevelexpr ::= expression
std::unique_ptr<FunctionAST> ParseTopLevelExpr() {
auto expr = ParseExpression();
auto proto =
std::make_unique<PrototypeAST>("__anon_expr", std::vector<std::string>());
return std::make_unique<FunctionAST>(std::move(proto), std::move(expr));
}然后我们从 llvm-project 中拷贝一份代码 llvm/examples/Kaleidoscope/include/KaleidoscopeJIT.h 到本地再 include, 其定义了 KaleidoscopeJIT 类,关于这个类,在后面会做解读,这里先不管。
定义全局变量 g_jit, 并使用 InitializeNativeTarget*函数初始化环境。
#include "KaleidoscopeJIT.h"
std::unique_ptr<llvm::orc::KaleidoscopeJIT> g_jit;
int main() {
llvm::InitializeNativeTarget();
llvm::InitializeNativeTargetAsmPrinter();
llvm::InitializeNativeTargetAsmParser();
g_jit.reset(new llvm::orc::KaleidoscopeJIT);
g_module->setDataLayout(g_jit->getTargetMachine().createDataLayout());
...
}修改 main 处理 top level expr 的代码为:
auto ast = ParseTopLevelExpr();
std::cout << "parsed a top level expr" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cout << std::endl;
auto h = g_jit->addModule(std::move(g_module));
// 重新创建g_module在下次使用
g_module =
std::make_unique<llvm::Module>("my cool jit", g_llvm_context);
g_module->setDataLayout(g_jit->getTargetMachine().createDataLayout());
// 通过名字找到编译的函数符号
auto symbol = g_jit->findSymbol("__anon_expr");
// 强转为C函数指针
double (*fp)() = (double (*)())(symbol.getAddress().get());
// 执行输出
std::cout << fp() << std::endl;
g_jit->removeModule(h);
break;输入:
4 + 5
def foo(a b)
a*a + 2*a*b + b*b
foo(2, 3)得到输出:
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
ret double 9.000000e+00
}
9
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %a, double %b) {
entry:
%multmp = fmul double %a, %a
%multmp1 = fmul double 2.000000e+00, %a
%multmp2 = fmul double %multmp1, %b
%addtmp = fadd double %multmp, %multmp2
%multmp3 = fmul double %b, %b
%addtmp4 = fadd double %addtmp, %multmp3
ret double %addtmp4
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 2.000000e+00, double 3.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
25可以看到代码已经顺利执行,但现在的实现仍然是有问题的,比如上面的输入,foo 函数的定义和调用是被归在同一个 module 中,当第一次调用完成后,由于我们 removeModule, 第二次调用 foo 会失败。
在解决这个问题之前,我们先把 main 函数内对不同 TOKEN 的处理拆成多个函数,如下:
void ReCreateModule() {
g_module = std::make_unique<llvm::Module>("my cool jit", g_llvm_context);
g_module->setDataLayout(g_jit->getTargetMachine().createDataLayout());
}
void ParseDefinitionToken() {
auto ast = ParseDefinition();
std::cout << "parsed a function definition" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cerr << std::endl;
}
void ParseExternToken() {
auto ast = ParseExtern();
std::cout << "parsed a extern" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cerr << std::endl;
}
void ParseTopLevel() {
auto ast = ParseTopLevelExpr();
std::cout << "parsed a top level expr" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cout << std::endl;
auto h = g_jit->addModule(std::move(g_module));
// 重新创建g_module在下次使用
ReCreateModule();
// 通过名字找到编译的函数符号
auto symbol = g_jit->findSymbol("__anon_expr");
// 强转为C函数指针
double (*fp)() = (double (*)())(symbol.getAddress().get());
// 执行输出
std::cout << fp() << std::endl;
g_jit->removeModule(h);
}
int main() {
llvm::InitializeNativeTarget();
llvm::InitializeNativeTargetAsmPrinter();
llvm::InitializeNativeTargetAsmParser();
g_jit.reset(new llvm::orc::KaleidoscopeJIT);
g_module->setDataLayout(g_jit->getTargetMachine().createDataLayout());
GetNextToken();
while (true) {
switch (g_current_token) {
case TOKEN_EOF: return 0;
case TOKEN_DEF: ParseDefinitionToken(); break;
case TOKEN_EXTERN: ParseExternToken(); break;
default: ParseTopLevel(); break;
}
}
return 0;
}为了解决第二次调用 foo 失败的问题,我们需要让 function 和 top level expr 处于不同的 Module, 而处于不同 Module 的话,CallExprAST 的 CodeGen 在当前 module 会找不到 function, 所以需要自动在 CallExprAST 做 CodeGen 时在当前 Module 声明这个函数,即自动地增加 extern, 也就是在当前 Module 自动做对应 PrototypeAST 的 CodeGen.
首先,增加一个全局变量存储从函数名到函数接口的映射,并增加一个查询函数。
std::map<std::string, std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST>> name2proto_ast;
llvm::Function* GetFunction(const std::string& name) {
llvm::Function* callee = g_module->getFunction(name);
if (callee != nullptr) { // 当前module存在函数定义
return callee;
} else {
// 声明函数
return name2proto_ast.at(name)->CodeGen();
}
}更改 CallExprAST 的 CodeGen, 让其使用上面定义的 GetFuntion:
llvm::Value* CallExprAST::CodeGen() {
llvm::Function* callee = GetFunction(callee_);
std::vector<llvm::Value*> args;
for (std::unique_ptr<ExprAST>& arg_expr : args_) {
args.push_back(arg_expr->CodeGen());
}
return g_ir_builder.CreateCall(callee, args, "calltmp");
}更改 FunctionAST 的 CodeGen, 让其将结果写入 name2proto_ast:
llvm::Value* FunctionAST::CodeGen() {
PrototypeAST& proto = *proto_;
name2proto_ast[proto.name()] = std::move(proto_); // transfer ownership
llvm::Function* func = GetFunction(proto.name());
// 创建一个Block并且设置为指令插入位置。
// llvm block用于定义control flow graph, 由于我们暂不实现control flow, 创建
// 一个单独的block即可
llvm::BasicBlock* block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "entry", func);
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(block);
// 将函数参数注册到g_named_values中,让VariableExprAST可以codegen
g_named_values.clear();
for (llvm::Value& arg : func->args()) {
g_named_values[arg.getName()] = &arg;
}
// codegen body然后return
llvm::Value* ret_val = body_->CodeGen();
g_ir_builder.CreateRet(ret_val);
llvm::verifyFunction(*func);
return func;
}修改 ParseExternToken 将结果写入 name2proto_ast:
void ParseExternToken() {
auto ast = ParseExtern();
std::cout << "parsed a extern" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cerr << std::endl;
name2proto_ast[ast->name()] = std::move(ast);
}修改 ParseDefinitionToken 让其使用独立 Module:
void ParseDefinitionToken() {
auto ast = ParseDefinition();
std::cout << "parsed a function definition" << std::endl;
ast->CodeGen()->print(llvm::errs());
std::cerr << std::endl;
g_jit->addModule(std::move(g_module));
ReCreateModule();
}修改完毕,输入测试:
def foo(x)
x + 1
foo(2)
def foo(x)
x + 2
foo(2)
extern sin(x)
extern cos(x)
sin(1.0)
def foo(x)
sin(x) * sin(x) + cos(x) * cos(x)
foo(4)
foo(3)得到输出:
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %x) {
entry:
%addtmp = fadd double %x, 1.000000e+00
ret double %addtmp
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 2.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
3
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %x) {
entry:
%addtmp = fadd double %x, 2.000000e+00
ret double %addtmp
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 2.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
4
parsed a extern
declare double @sin(double)
parsed a extern
declare double @cos(double)
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @sin(double 1.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
0.841471
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %x) {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @sin(double %x)
%calltmp1 = call double @sin(double %x)
%multmp = fmul double %calltmp, %calltmp1
%calltmp2 = call double @cos(double %x)
%calltmp3 = call double @cos(double %x)
%multmp4 = fmul double %calltmp2, %calltmp3
%addtmp = fadd double %multmp, %multmp4
ret double %addtmp
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 4.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
1
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 3.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
1成功运行,执行正确!代码可以正确解析 sin, cos 的原因在 KaleidoscopeJIT.h 中,截取其寻找符号的代码。
JITSymbol findMangledSymbol(const std::string &Name) {
#ifdef _WIN32
// The symbol lookup of ObjectLinkingLayer uses the SymbolRef::SF_Exported
// flag to decide whether a symbol will be visible or not, when we call
// IRCompileLayer::findSymbolIn with ExportedSymbolsOnly set to true.
//
// But for Windows COFF objects, this flag is currently never set.
// For a potential solution see: https://reviews.llvm.org/rL258665
// For now, we allow non-exported symbols on Windows as a workaround.
const bool ExportedSymbolsOnly = false;
#else
const bool ExportedSymbolsOnly = true;
#endif
// Search modules in reverse order: from last added to first added.
// This is the opposite of the usual search order for dlsym, but makes more
// sense in a REPL where we want to bind to the newest available definition.
for (auto H : make_range(ModuleKeys.rbegin(), ModuleKeys.rend()))
if (auto Sym = CompileLayer.findSymbolIn(H, Name, ExportedSymbolsOnly))
return Sym;
// If we can't find the symbol in the JIT, try looking in the host process.
if (auto SymAddr = RTDyldMemoryManager::getSymbolAddressInProcess(Name))
return JITSymbol(SymAddr, JITSymbolFlags::Exported);
#ifdef _WIN32
// For Windows retry without "_" at beginning, as RTDyldMemoryManager uses
// GetProcAddress and standard libraries like msvcrt.dll use names
// with and without "_" (for example "_itoa" but "sin").
if (Name.length() > 2 && Name[0] == '_')
if (auto SymAddr =
RTDyldMemoryManager::getSymbolAddressInProcess(Name.substr(1)))
return JITSymbol(SymAddr, JITSymbolFlags::Exported);
#endif
return null可以看到,在之前定义的 Module 找不到后会在 host process 中寻找这个符号。
7. SSA
继续给我们的 Kaleidoscope 添加功能之前,需要先介绍 SSA, Static Single Assignment,考虑下面代码:
y := 1
y := 2
x := y我们可以发现第一个赋值是不必须的,而且第三行使用的 y 来自第二行的赋值,改成 SSA 格式为
y_1 = 1
y_2 = 2
x_1 = y_2改完可以方便编译器进行优化,比如把第一个赋值删去,于是我们可以给出 SSA 的定义:
- 每个变量仅且必须被赋值一次,原本代码中的多次变量赋值会被赋予版本号然后视为不同变量;
- 每个变量在被使用之前必须被定义。
考虑如下 Control Flow Graph:

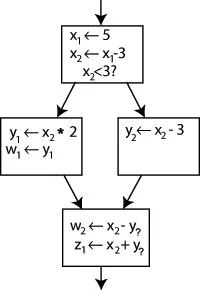
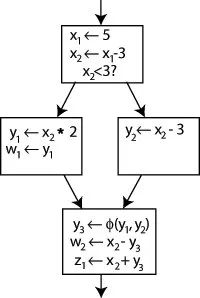
8. Control Flow
我们现在实现的 Kaleidoscope 还不够完善,缺少 if else 控制流,比如不支持如下代码:
def fib(x)
if x < 3 then
1
else
fib(x - 1) + fib(x - 2)首先让我们的 Lexer 能识别 if then else 三个关键字,增加 TOKEN 类型:
TOKEN_IF = -6, // if
TOKEN_THEN = -7, // then
TOKEN_ELSE = -8, // else增加识别规则:
// 识别字符串
if (isalpha(last_char)) {
g_identifier_str = last_char;
while (isalnum((last_char = getchar()))) {
g_identifier_str += last_char;
}
if (g_identifier_str == "def") {
return TOKEN_DEF;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "extern") {
return TOKEN_EXTERN;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "if") {
return TOKEN_IF;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "then") {
return TOKEN_THEN;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "else") {
return TOKEN_ELSE;
} else {
return TOKEN_IDENTIFIER;
}
}增加 IfExprAST:
// if then else
class IfExprAST : public ExprAST {
public:
IfExprAST(std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> cond, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> then_expr,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> else_expr)
: cond_(std::move(cond)),
then_expr_(std::move(then_expr)),
else_expr_(std::move(else_expr)) {}
llvm::Value* CodeGen() override;
private:
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> cond_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> then_expr_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> else_expr_;
};增加对 IfExprAST 的解析:
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseIfExpr() {
GetNextToken(); // eat if
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> cond = ParseExpression();
GetNextToken(); // eat then
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> then_expr = ParseExpression();
GetNextToken(); // eat else
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> else_expr = ParseExpression();
return std::make_unique<IfExprAST>(std::move(cond), std::move(then_expr),
std::move(else_expr));
}增加到 ParsePrimary 中:
// primary
// ::= identifierexpr
// ::= numberexpr
// ::= parenexpr
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParsePrimary() {
switch (g_current_token) {
case TOKEN_IDENTIFIER: return ParseIdentifierExpr();
case TOKEN_NUMBER: return ParseNumberExpr();
case '(': return ParseParenExpr();
case TOKEN_IF: return ParseIfExpr();
default: return nullptr;
}
}完成了 lex 和 parse,接下来是最有意思的 codegen:
llvm::Value* IfExprAST::CodeGen() {
llvm::Value* cond_value = cond_->CodeGen();
// 创建fcmp one指令, cond_value = (cond_value != 0.0)
// 转为1bit (bool)类型
cond_value = g_ir_builder.CreateFCmpONE(
cond_value, llvm::ConstantFP::get(g_llvm_context, llvm::APFloat(0.0)),
"ifcond");
// 在每个function内我们会创建一个block, 这里一定在这个block内,根据block得到
// 对应的上层function
llvm::Function* func = g_ir_builder.GetInsertBlock()->getParent();
// 为then else以及最后的final创建block
llvm::BasicBlock* then_block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "then", func);
llvm::BasicBlock* else_block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "else");
llvm::BasicBlock* final_block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "ifcont");
// 创建跳转指令,根据cond_value选择then_block/else_block
g_ir_builder.CreateCondBr(cond_value, then_block, else_block);
// codegen then_block, 增加跳转final_block指令
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(then_block);
llvm::Value* then_value = then_expr_->CodeGen();
g_ir_builder.CreateBr(final_block);
// then语句内可能会有嵌套的if/then/else, 在嵌套的codegen时,会改变当前的
// InsertBlock, 我们需要有最终结果的那个block作为这里的then_block
then_block = g_ir_builder.GetInsertBlock();
// 在这里才加入是为了让这个block位于上面的then里嵌套block的后面
func->getBasicBlockList().push_back(else_block);
// 与then类似
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(else_block);
llvm::Value* else_value = else_expr_->CodeGen();
g_ir_builder.CreateBr(final_block);
else_block = g_ir_builder.GetInsertBlock();
// codegen final
func->getBasicBlockList().push_back(final_block);
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(final_block);
llvm::PHINode* pn = g_ir_builder.CreatePHI(
llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context), 2, "iftmp");
pn->addIncoming(then_value, then_block);
pn->addIncoming(else_value, else_block);
return pn;
}这里使用了上一节 SSA 中提到的 phi function,输入:
def foo(x)
if x < 3 then
1
else
foo(x - 1) + foo(x - 2)
foo(1)
foo(2)
foo(3)
foo(4)得到输出:
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %x) {
entry:
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %x, 3.000000e+00
%booltmp = uitofp i1 %cmptmp to double
%ifcond = fcmp one double %booltmp, 0.000000e+00
br i1 %ifcond, label %then, label %else
then: ; preds = %entry
br label %ifcont
else: ; preds = %entry
%subtmp = fsub double %x, 1.000000e+00
%calltmp = call double @foo(double %subtmp)
%subtmp1 = fsub double %x, 2.000000e+00
%calltmp2 = call double @foo(double %subtmp1)
%addtmp = fadd double %calltmp, %calltmp2
br label %ifcont
ifcont: ; preds = %else, %then
%iftmp = phi double [ 1.000000e+00, %then ], [ %addtmp, %else ]
ret double %iftmp
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 1.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
1
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 2.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
1
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 3.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
2
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @foo(double 4.000000e+00)
ret double %calltmp
}
3成功完成了斐波那契数列的计算,接下来我们需要增加循环的支持,在此之前我们实现一个 printd 函数:
extern "C" double printd(double x) {
printf("%lf\n", x);
return 0.0;
}编译:
clang++ -g main.cpp \`llvm-config --cxxflags --ldflags --libs\` -Wl,-no-as-needed -rdynamic
输入:
extern printd(x)
printd(12)得到输出:
parsed a extern
declare double @printd(double)
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%calltmp = call double @printd(double 1.200000e+01)
ret double %calltmp
}
12.000000
0可以看到,我们成功给 Kaleiscope 添加了 printd 函数,接下来看我们需要实现的循环语法, 使用 C++代码作为注释:
def printstar(n):
for i = 1, i < n, 1.0 in # for (double i = 1.0; i < n; i += 1.0)
printd(n)同样,我们增加 for 和 in 的 TOKEN:
enum Token {
TOKEN_EOF = -1, // 文件结束标识符
TOKEN_DEF = -2, // 关键字def
TOKEN_EXTERN = -3, // 关键字extern
TOKEN_IDENTIFIER = -4, // 名字
TOKEN_NUMBER = -5, // 数值
TOKEN_IF = -6, // if
TOKEN_THEN = -7, // then
TOKEN_ELSE = -8, // else
TOKEN_FOR = -9, // for
TOKEN_IN = -10 // in
};增加 TOKEN 的识别:
// 识别字符串
if (isalpha(last_char)) {
g_identifier_str = last_char;
while (isalnum((last_char = getchar()))) {
g_identifier_str += last_char;
}
if (g_identifier_str == "def") {
return TOKEN_DEF;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "extern") {
return TOKEN_EXTERN;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "if") {
return TOKEN_IF;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "then") {
return TOKEN_THEN;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "else") {
return TOKEN_ELSE;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "for") {
return TOKEN_FOR;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "in") {
return TOKEN_IN;
} else {
return TOKEN_IDENTIFIER;
}
}增加 ForExprAST:
// for in
class ForExprAST : public ExprAST {
public:
ForExprAST(const std::string& var_name, std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> start_expr,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> end_expr,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> step_expr,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> body_expr)
: var_name_(var_name),
start_expr_(std::move(start_expr)),
end_expr_(std::move(end_expr)),
step_expr_(std::move(step_expr)),
body_expr_(std::move(body_expr)) {}
llvm::Value* CodeGen() override;
private:
std::string var_name_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> start_expr_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> end_expr_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> step_expr_;
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> body_expr_;
};添加到 Primary 的解析中:
// forexpr ::= for var_name = start_expr, end_expr, step_expr in body_expr
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParseForExpr() {
GetNextToken(); // eat for
std::string var_name = g_identifier_str;
GetNextToken(); // eat var_name
GetNextToken(); // eat =
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> start_expr = ParseExpression();
GetNextToken(); // eat ,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> end_expr = ParseExpression();
GetNextToken(); // eat ,
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> step_expr = ParseExpression();
GetNextToken(); // eat in
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> body_expr = ParseExpression();
return std::make_unique<ForExprAST>(var_name, std::move(start_expr),
std::move(end_expr), std::move(step_expr),
std::move(body_expr));
}
// primary
// ::= identifierexpr
// ::= numberexpr
// ::= parenexpr
std::unique_ptr<ExprAST> ParsePrimary() {
switch (g_current_token) {
case TOKEN_IDENTIFIER: return ParseIdentifierExpr();
case TOKEN_NUMBER: return ParseNumberExpr();
case '(': return ParseParenExpr();
case TOKEN_IF: return ParseIfExpr();
case TOKEN_FOR: return ParseForExpr();
default: return nullptr;
}
}开始 codegen:
llvm::Value* ForExprAST::CodeGen() {
// codegen start
llvm::Value* start_val = start_expr_->CodeGen();
// 获取当前function
llvm::Function* func = g_ir_builder.GetInsertBlock()->getParent();
// 保存当前的block
llvm::BasicBlock* pre_block = g_ir_builder.GetInsertBlock();
// 新增一个loop block到当前function
llvm::BasicBlock* loop_block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "loop", func);
// 为当前block增加到loop_block的跳转指令
g_ir_builder.CreateBr(loop_block);
// 开始在loop_block内增加指令
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(loop_block);
llvm::PHINode* var = g_ir_builder.CreatePHI(
llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context), 2, var_name_.c_str());
// 如果来自pre_block的跳转,则取start_val的值
var->addIncoming(start_val, pre_block);
// 现在我们新增了一个变量var,因为可能会被后面的代码引用,所以要注册到
// g_named_values中,其可能会和函数参数重名,但我们这里为了方便不管
// 这个特殊情况,直接注册到g_named_values中,
g_named_values[var_name_] = var;
// 在loop_block中增加body的指令
body_expr_->CodeGen();
// codegen step_expr
llvm::Value* step_value = step_expr_->CodeGen();
// next_var = var + step_value
llvm::Value* next_value = g_ir_builder.CreateFAdd(var, step_value, "nextvar");
// codegen end_expr
llvm::Value* end_value = end_expr_->CodeGen();
// end_value = (end_value != 0.0)
end_value = g_ir_builder.CreateFCmpONE(
end_value, llvm::ConstantFP::get(g_llvm_context, llvm::APFloat(0.0)),
"loopcond");
// 和if/then/else一样,这里的block可能会发生变化,保存当前的block
llvm::BasicBlock* loop_end_block = g_ir_builder.GetInsertBlock();
// 创建循环结束后的block
llvm::BasicBlock* after_block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "afterloop", func);
// 根据end_value选择是再来一次loop_block还是进入after_block
g_ir_builder.CreateCondBr(end_value, loop_block, after_block);
// 给after_block增加指令
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(after_block);
// 如果是再次循环,取新的值
var->addIncoming(next_value, loop_end_block);
// 循环结束,避免被再次引用
g_named_values.erase(var_name_);
// return 0
return llvm::Constant::getNullValue(llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context));
}输入:
extern printd(x)
def foo(x)
if x < 3 then
1
else
foo(x - 1) + foo(x - 2)
for i = 1, i < 10, 1.0 in
printd(foo(i))输出:
parsed a extern
declare double @printd(double)
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %x) {
entry:
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %x, 3.000000e+00
%booltmp = uitofp i1 %cmptmp to double
%ifcond = fcmp one double %booltmp, 0.000000e+00
br i1 %ifcond, label %then, label %else
then: ; preds = %entry
br label %ifcont
else: ; preds = %entry
%subtmp = fsub double %x, 1.000000e+00
%calltmp = call double @foo(double %subtmp)
%subtmp1 = fsub double %x, 2.000000e+00
%calltmp2 = call double @foo(double %subtmp1)
%addtmp = fadd double %calltmp, %calltmp2
br label %ifcont
ifcont: ; preds = %else, %then
%iftmp = phi double [ 1.000000e+00, %then ], [ %addtmp, %else ]
ret double %iftmp
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
br label %loop
loop: ; preds = %loop, %entry
%i = phi double [ 1.000000e+00, %entry ], [ %nextvar, %loop ]
%calltmp = call double @foo(double %i)
%calltmp1 = call double @printd(double %calltmp)
%nextvar = fadd double %i, 1.000000e+00
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %i, 1.000000e+01
%booltmp = uitofp i1 %cmptmp to double
%loopcond = fcmp one double %booltmp, 0.000000e+00
br i1 %loopcond, label %loop, label %afterloop
afterloop: ; preds = %loop
ret double 0.000000e+00
}
1.000000
1.000000
2.000000
3.000000
5.000000
8.000000
13.000000
21.000000
34.000000
55.000000
0成功遍历了斐波那契数列。
9. User-Defined Operators
在 C++中,用户可以重载操作符而不能增加操作符。在这里,我们将给 Kaleidoscope 增加一个功能,让用户可以增加二元操作符。
# 新增二元操作符 `>`, 优先级等于内置的 `<`
def binary> 10 (LHS RHS)
RHS < LHS
# 新增二元操作符 `|`, 优先级为5
def binary| 5 (LHS RHS)
if LHS then
1
else if RHS then
1
else
0
# 新增二元操作符 `=`,优先级为9,这个操作符类似C++的 `==`
def binary= 9 (LHS RHS)
!(LHS < RHS | LHS > RHS)增加 TOKEN 的类型:
enum Token {
...
TOKEN_BINARY = -11, // binary
};增加 TOKEN 的识别:
// 从标准输入解析一个Token并返回
int GetToken() {
...
// 识别字符串
if (isalpha(last_char)) {
...
if (g_identifier_str == "def") {
return TOKEN_DEF;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "extern") {
return TOKEN_EXTERN;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "if") {
return TOKEN_IF;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "then") {
return TOKEN_THEN;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "else") {
return TOKEN_ELSE;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "for") {
return TOKEN_FOR;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "in") {
return TOKEN_IN;
} else if (g_identifier_str == "binary") {
return TOKEN_BINARY;
} else {
return TOKEN_IDENTIFIER;
}
}
...
}我们把新增的二元操作符视为一个函数,所以不需要新增 AST,但是需要修改 PrototypeAST。
// 函数接口
class PrototypeAST {
public:
PrototypeAST(const std::string& name, std::vector<std::string> args,
bool is_operator = false, int op_precedence = 0)
: name_(name),
args_(std::move(args)),
is_operator_(is_operator),
op_precedence_(op_precedence) {}
llvm::Function* CodeGen();
const std::string& name() const { return name_; }
int op_precedence() const { return op_precedence_; }
bool IsUnaryOp() const { return is_operator_ && args_.size() == 1; }
bool IsBinaryOp() const { return is_operator_ && args_.size() == 2; }
// like `|` in `binary|`
char GetOpName() { return name_[name_.size() - 1]; }
private:
std::string name_;
std::vector<std::string> args_;
bool is_operator_;
int op_precedence_;
};修改 parse 部分:
// prototype
// ::= id ( id id ... id)
// ::= binary binop precedence (id id)
std::unique_ptr<PrototypeAST> ParsePrototype() {
std::string function_name;
bool is_operator = false;
int precedence = 0;
switch (g_current_token) {
case TOKEN_IDENTIFIER: {
function_name = g_identifier_str;
is_operator = false;
GetNextToken(); // eat id
break;
}
case TOKEN_BINARY: {
GetNextToken(); // eat binary
function_name = "binary";
function_name += (char)(g_current_token);
is_operator = true;
GetNextToken(); // eat binop
precedence = g_number_val;
GetNextToken(); // eat precedence
break;
}
}
std::vector<std::string> arg_names;
while (GetNextToken() == TOKEN_IDENTIFIER) {
arg_names.push_back(g_identifier_str);
}
GetNextToken(); // eat )
return std::make_unique<PrototypeAST>(function_name, arg_names, is_operator,
precedence);
}修改 BinaryExprAST 的 CodeGen 处理自定义 Operator, 增加函数调用指令:
llvm::Value* BinaryExprAST::CodeGen() {
llvm::Value* lhs = lhs_->CodeGen();
llvm::Value* rhs = rhs_->CodeGen();
switch (op_) {
case '<': {
llvm::Value* tmp = g_ir_builder.CreateFCmpULT(lhs, rhs, "cmptmp");
// 把 0/1 转为 0.0/1.0
return g_ir_builder.CreateUIToFP(
tmp, llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context), "booltmp");
}
case '+': return g_ir_builder.CreateFAdd(lhs, rhs, "addtmp");
case '-': return g_ir_builder.CreateFSub(lhs, rhs, "subtmp");
case '*': return g_ir_builder.CreateFMul(lhs, rhs, "multmp");
default: {
// user defined operator
llvm::Function* func = GetFunction(std::string("binary") + op_);
llvm::Value* operands[2] = {lhs, rhs};
return g_ir_builder.CreateCall(func, operands, "binop");
}
}
}在 FunctionAST 的 CodeGen 时,注册操作符优先级,从而让自定义操作符被识别为操作符。
llvm::Value* FunctionAST::CodeGen() {
PrototypeAST& proto = *proto_;
name2proto_ast[proto.name()] = std::move(proto_); // transfer ownership
llvm::Function* func = GetFunction(proto.name());
if (proto.IsBinaryOp()) {
g_binop_precedence[proto.GetOpName()] = proto.op_precedence();
}
// 创建一个Block并且设置为指令插入位置。
// llvm block用于定义control flow graph, 由于我们暂不实现control flow, 创建
// 一个单独的block即可
llvm::BasicBlock* block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "entry", func);
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(block);
// 将函数参数注册到g_named_values中,让VariableExprAST可以codegen
g_named_values.clear();
for (llvm::Value& arg : func->args()) {
g_named_values[arg.getName()] = &arg;
}
// codegen body然后return
llvm::Value* ret_val = body_->CodeGen();
g_ir_builder.CreateRet(ret_val);
llvm::verifyFunction(*func);
return func;
}输入:
# 新增二元操作符 `>`, 优先级等于内置的 `<`
def binary> 10 (LHS RHS)
RHS < LHS
1 > 2
2 > 1
# 新增二元操作符 `|`, 优先级为5
def binary| 5 (LHS RHS)
if LHS then
1
else if RHS then
1
else
0
1 | 0
0 | 1
0 | 0
1 | 1得到输出:
parsed a function definition
define double @"binary>"(double %LHS, double %RHS) {
entry:
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %RHS, %LHS
%booltmp = uitofp i1 %cmptmp to double
ret double %booltmp
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%binop = call double @"binary>"(double 1.000000e+00, double 2.000000e+00)
ret double %binop
}
0
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%binop = call double @"binary>"(double 2.000000e+00, double 1.000000e+00)
ret double %binop
}
1
parsed a function definition
define double @"binary|"(double %LHS, double %RHS) {
entry:
%ifcond = fcmp one double %LHS, 0.000000e+00
br i1 %ifcond, label %then, label %else
then: ; preds = %entry
br label %ifcont4
else: ; preds = %entry
%ifcond1 = fcmp one double %RHS, 0.000000e+00
br i1 %ifcond1, label %then2, label %else3
then2: ; preds = %else
br label %ifcont
else3: ; preds = %else
br label %ifcont
ifcont: ; preds = %else3, %then2
%iftmp = phi double [ 1.000000e+00, %then2 ], [ 0.000000e+00, %else3 ]
br label %ifcont4
ifcont4: ; preds = %ifcont, %then
%iftmp5 = phi double [ 1.000000e+00, %then ], [ %iftmp, %ifcont ]
ret double %iftmp5
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%binop = call double @"binary|"(double 1.000000e+00, double 0.000000e+00)
ret double %binop
}
1
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%binop = call double @"binary|"(double 0.000000e+00, double 1.000000e+00)
ret double %binop
}
1
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%binop = call double @"binary|"(double 0.000000e+00, double 0.000000e+00)
ret double %binop
}
0
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%binop = call double @"binary|"(double 1.000000e+00, double 1.000000e+00)
ret double %binop
}
110. Mutable Variables
本节我们将让 Kaleidoscope 支持可变变量,首先我们看如下 C 代码:
int G, H;
int test(_Bool Condition) {
int X;
if (Condition)
X = G;
else
X = H;
return X;
}由于变量 X 的值依赖于程序的执行路径,会加入一个 phi node 来选取分支结果。上面代码的 LLVM IR 如下:
@G = weak global i32 0 ; type of @G is i32*
@H = weak global i32 0 ; type of @H is i32*
define i32 @test(i1 %Condition) {
entry:
br i1 %Condition, label %cond_true, label %cond_false
cond_true:
%X.0 = load i32* @G
br label %cond_next
cond_false:
%X.1 = load i32* @H
br label %cond_next
cond_next:
%X.2 = phi i32 [ %X.1, %cond_false ], [ %X.0, %cond_true ]
ret i32 %X.2
}上面的 X 是符合 SSA 格式的,但是这里真正的难题是给可变变量赋值时怎么自动添加 phi node。我们先了解一些信息,LLVM 要求寄存器变量是 SSA 格式,但却不允许内存对象是 SSA 格式。比如上面的例子中,G 和 H 就没有版本号。在 LLVM 中,所有内存访问都是显示的 load/store 指令,并且不存在取内存地址的操作。注意上面的例子中,即使@G/@H 全局变量定义时用的 i32, 但其类型仍然是 i32*, 表示在全局数据区存放 i32 的空间地址。
现在假设我们想创建一个类似@G 但是在栈上的内存变量,基本指令如下:
define i32 @example() {entry:
%X = alloca i32 ; type of %X is i32*.
...
%tmp = load i32* %X ; load the stack value %X from the stack.
%tmp2 = add i32 %tmp, 1 ; increment it
store i32 %tmp2, i32* %X ; store it back
...于是我们可以把上面使用 phi node 的 LLVM IR 改写为使用栈上变量:
@G = weak global i32 0 ; type of @G is i32*
@H = weak global i32 0 ; type of @H is i32*
define i32 @test(i1 %Condition) {
entry:
%X = alloca i32 ; type of %X is i32*.
br i1 %Condition, label %cond_true, label %cond_false
cond_true:
%X.0 = load i32* @G
store i32 %X.0, i32* %X ; Update X
br label %cond_next
cond_false:
%X.1 = load i32* @H
store i32 %X.1, i32* %X ; Update X
br label %cond_next
cond_next:
%X.2 = load i32* %X ; Read X
ret i32 %X.2
}于是我们找到了一个处理任意可变变量而且不需要创建 phi node 的办法:
- 每个可变变量在栈上创建
- 变量读取变为 load from stack
- 变量更新变为 store to stack
- 使用栈上地址作为变量地址
但是这会带来一个新的问题,因为内存速度不如寄存器,大量使用栈会有性能问题。不过,LLVM 优化器有一个 pass 称为"mem2reg", 专门将 stack 的使用自动地尽可能转为使用 phi node, 下面为自动优化的结果:
@G = weak global i32 0
@H = weak global i32 0
define i32 @test(i1 %Condition) {
entry:
br i1 %Condition, label %cond_true, label %cond_false
cond_true:
%X.0 = load i32* @G
br label %cond_next
cond_false:
%X.1 = load i32* @H
br label %cond_next
cond_next:
%X.01 = phi i32 [ %X.1, %cond_false ], [ %X.0, %cond_true ]
ret i32 %X.01}mem2reg 实现了一个称为"iterated dominance frontier"的标准算法来自动创建 SSA 格式。对 mem2reg 的使用需要注意:
- mem2reg 只能优化栈上变量,不会优化全局变量和堆上变量;
- mem2reg 只优化 entry block 中的栈上变量创建, 因为在 entry block 中就意味着只创建一次;
- 如果对栈上变量有 load 和 store 之外的操作, mem2reg 也不会优化;
- mem2reg 只能优化基本类型的栈上变量,比如指针,数值和数组。其中数组的大小必须为 1. 对于结构体和数组等的优化需要另一个称为"sroa"的 pass。
因为我们后面需要启用 mem2reg,我们先把优化器加回来,修改全局定义:
std::unique_ptr<llvm::Module> g_module;
std::unique_ptr<llvm::legacy::FunctionPassManager> g_fpm;修改 ReCreateModule:
void ReCreateModule() {
g_module = std::make_unique<llvm::Module>("my cool jit", g_llvm_context);
g_module->setDataLayout(g_jit->getTargetMachine().createDataLayout());
g_fpm = std::make_unique<llvm::legacy::FunctionPassManager>(g_module.get());
g_fpm->add(llvm::createInstructionCombiningPass());
g_fpm->add(llvm::createReassociatePass());
g_fpm->add(llvm::createGVNPass());
g_fpm->add(llvm::createCFGSimplificationPass());
g_fpm->doInitialization();
}在 FunctionAST::CodeGen 中执行优化器:
g_ir_builder.CreateRet(ret_val);
llvm::verifyFunction(*func);
g_fpm->run(*func);修改 main:
int main() {
llvm::InitializeNativeTarget();
llvm::InitializeNativeTargetAsmPrinter();
llvm::InitializeNativeTargetAsmParser();
g_jit.reset(new llvm::orc::KaleidoscopeJIT);
ReCreateModule();
...
}我们有两种类型的变量,分别是函数参数以及 for 循环的变量,这里我们将这两种变量也修改为使用内存,再让 mem2reg 进行优化。因为所有的变量都会使用内存,修改 g_named_value 存储的类型为 AllocaInst*:
std::map<std::string, llvm::AllocaInst*> g_named_values;
编写一个函数 CreateEntryBlockAlloca,简化后续工作,其功能是往函数的 EntryBlock 的最开始的地方添加分配内存指令:
llvm::AllocaInst* CreateEntryBlockAlloca(llvm::Function* func,
const std::string& var_name) {
llvm::IRBuilder<> ir_builder(&(func->getEntryBlock()),
func->getEntryBlock().begin());
return ir_builder.CreateAlloca(llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context), 0,
var_name.c_str());
}修改 VariableExprAST::CodeGen, 由于我们所有变量都放在内存你上,所以增加 load 指令:
llvm::Value* VariableExprAST::CodeGen() {
llvm::AllocaInst* val = g_named_values.at(name_);
return g_ir_builder.CreateLoad(val, name_.c_str());
}接下来我们修改 for 循环里变量的 CodeGen:
llvm::Value* ForExprAST::CodeGen() {
// 获取当前function
llvm::Function* func = g_ir_builder.GetInsertBlock()->getParent();
// 将变量创建为栈上变量,不再是phi node
llvm::AllocaInst* var = CreateEntryBlockAlloca(func, var_name_);
// codegen start
llvm::Value* start_val = start_expr_->CodeGen();
// 将初始值赋给var
g_ir_builder.CreateStore(start_val, var);
// 新增一个loop block到当前function
llvm::BasicBlock* loop_block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "loop", func);
// 为当前block增加到loop_block的跳转指令
g_ir_builder.CreateBr(loop_block);
// 开始在loop_block内增加指令
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(loop_block);
// 现在我们新增了一个变量var,因为可能会被后面的代码引用,所以要注册到
// g_named_values中,其可能会和函数参数重名,但我们这里为了方便不管
// 这个特殊情况,直接注册到g_named_values中,
g_named_values[var_name_] = var;
// 在loop_block中增加body的指令
body_expr_->CodeGen();
// codegen step_expr
llvm::Value* step_value = step_expr_->CodeGen();
// var = var + step_value
llvm::Value* cur_value = g_ir_builder.CreateLoad(var);
llvm::Value* next_value =
g_ir_builder.CreateFAdd(cur_value, step_value, "nextvar");
g_ir_builder.CreateStore(next_value, var);
// codegen end_expr
llvm::Value* end_value = end_expr_->CodeGen();
// end_value = (end_value != 0.0)
end_value = g_ir_builder.CreateFCmpONE(
end_value, llvm::ConstantFP::get(g_llvm_context, llvm::APFloat(0.0)),
"loopcond");
// 和if/then/else一样,这里的block可能会发生变化,保存当前的block
llvm::BasicBlock* loop_end_block = g_ir_builder.GetInsertBlock();
// 创建循环结束后的block
llvm::BasicBlock* after_block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "afterloop", func);
// 根据end_value选择是再来一次loop_block还是进入after_block
g_ir_builder.CreateCondBr(end_value, loop_block, after_block);
// 给after_block增加指令
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(after_block);
// 循环结束,避免被再次引用
g_named_values.erase(var_name_);
// return 0
return llvm::Constant::getNullValue(llvm::Type::getDoubleTy(g_llvm_context));
}修改 FunctionAST::codegen()使得参数可变:
llvm::Value* FunctionAST::CodeGen() {
PrototypeAST& proto = *proto_;
name2proto_ast[proto.name()] = std::move(proto_); // transfer ownership
llvm::Function* func = GetFunction(proto.name());
if (proto.IsBinaryOp()) {
g_binop_precedence[proto.GetOpName()] = proto.op_precedence();
}
// 创建一个Block并且设置为指令插入位置。
// llvm block用于定义control flow graph, 由于我们暂不实现control flow, 创建
// 一个单独的block即可
llvm::BasicBlock* block =
llvm::BasicBlock::Create(g_llvm_context, "entry", func);
g_ir_builder.SetInsertPoint(block);
// 将函数参数注册到g_named_values中,让VariableExprAST可以codegen
g_named_values.clear();
for (llvm::Value& arg : func->args()) {
// 为每个参数创建一个栈上变量,并赋初值,修改g_named_values使得后面的引用
// 会引用这个栈上变量
llvm::AllocaInst* var = CreateEntryBlockAlloca(func, arg.getName());
g_ir_builder.CreateStore(&arg, var);
g_named_values[arg.getName()] = var;
}
// codegen body然后return
llvm::Value* ret_val = body_->CodeGen();
g_ir_builder.CreateRet(ret_val);
llvm::verifyFunction(*func);
g_fpm->run(*func);
return func;
}输入:
extern printd(x)
def foo(x)
if x < 3 then
1
else
foo(x - 1) + foo(x - 2)
for i = 1, i < 10, 1.0 in
printd(foo(i))输出:
parsed a extern [13/48988]
declare double @printd(double)
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %x) {
entry:
%x1 = alloca double, align 8
store double %x, double* %x1, align 8
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %x, 3.000000e+00
br i1 %cmptmp, label %ifcont, label %else
else: ; preds = %entry
%subtmp = fadd double %x, -1.000000e+00
%calltmp = call double @foo(double %subtmp)
%subtmp5 = fadd double %x, -2.000000e+00
%calltmp6 = call double @foo(double %subtmp5)
%addtmp = fadd double %calltmp, %calltmp6
br label %ifcont
ifcont: ; preds = %entry, %else
%iftmp = phi double [ %addtmp, %else ], [ 1.000000e+00, %entry ]
ret double %iftmp
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
%i = alloca double, align 8
store double 1.000000e+00, double* %i, align 8
br label %loop
loop: ; preds = %loop, %entry
%i1 = phi double [ %nextvar, %loop ], [ 1.000000e+00, %entry ]
%calltmp = call double @foo(double %i1)
%calltmp2 = call double @printd(double %calltmp)
%nextvar = fadd double %i1, 1.000000e+00
store double %nextvar, double* %i, align 8
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %nextvar, 1.000000e+01
br i1 %cmptmp, label %loop, label %afterloop
afterloop: ; preds = %loop
ret double 0.000000e+00
}
1.000000
1.000000
2.000000
3.000000
5.000000
8.000000
13.000000
21.000000
34.000000
0可以看到,新版本的 IR 中已经没有了 phi node, 接下来我们加入优化器:
g_fpm->add(llvm::createPromoteMemoryToRegisterPass());
g_fpm->add(llvm::createInstructionCombiningPass());
g_fpm->add(llvm::createReassociatePass());再次得到输出:
parsed a extern
declare double @printd(double)
parsed a function definition
define double @foo(double %x) {
entry:
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %x, 3.000000e+00
br i1 %cmptmp, label %ifcont, label %else
else: ; preds = %entry
%subtmp = fadd double %x, -1.000000e+00
%calltmp = call double @foo(double %subtmp)
%subtmp5 = fadd double %x, -2.000000e+00
%calltmp6 = call double @foo(double %subtmp5)
%addtmp = fadd double %calltmp, %calltmp6
br label %ifcont
ifcont: ; preds = %entry, %else
%iftmp = phi double [ %addtmp, %else ], [ 1.000000e+00, %entry ]
ret double %iftmp
}
parsed a top level expr
define double @__anon_expr() {
entry:
br label %loop
loop: ; preds = %loop, %entry
%i1 = phi double [ %nextvar, %loop ], [ 1.000000e+00, %entry ]
%calltmp = call double @foo(double %i1)
%calltmp2 = call double @printd(double %calltmp)
%nextvar = fadd double %i1, 1.000000e+00
%cmptmp = fcmp ult double %nextvar, 1.000000e+01
br i1 %cmptmp, label %loop, label %afterloop
afterloop: ; preds = %loop
ret double 0.000000e+00
}
1.000000
1.000000
2.000000
3.000000
5.000000
8.000000
13.000000
21.000000
34.000000
0可以看到,栈上变量自动地变为寄存器变量,且 phi node 自动地被添加。
11. 完整代码与参考资料
完整代码见:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336929719
参考:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Static_single_assignment_form
- https://llvm.org/docs/tutorial/MyFirstLanguageFrontend/index.html
欢迎大家多多交流,共同进步。