你真的了解Web Component吗?
为什么使用框架?
对框架的理解
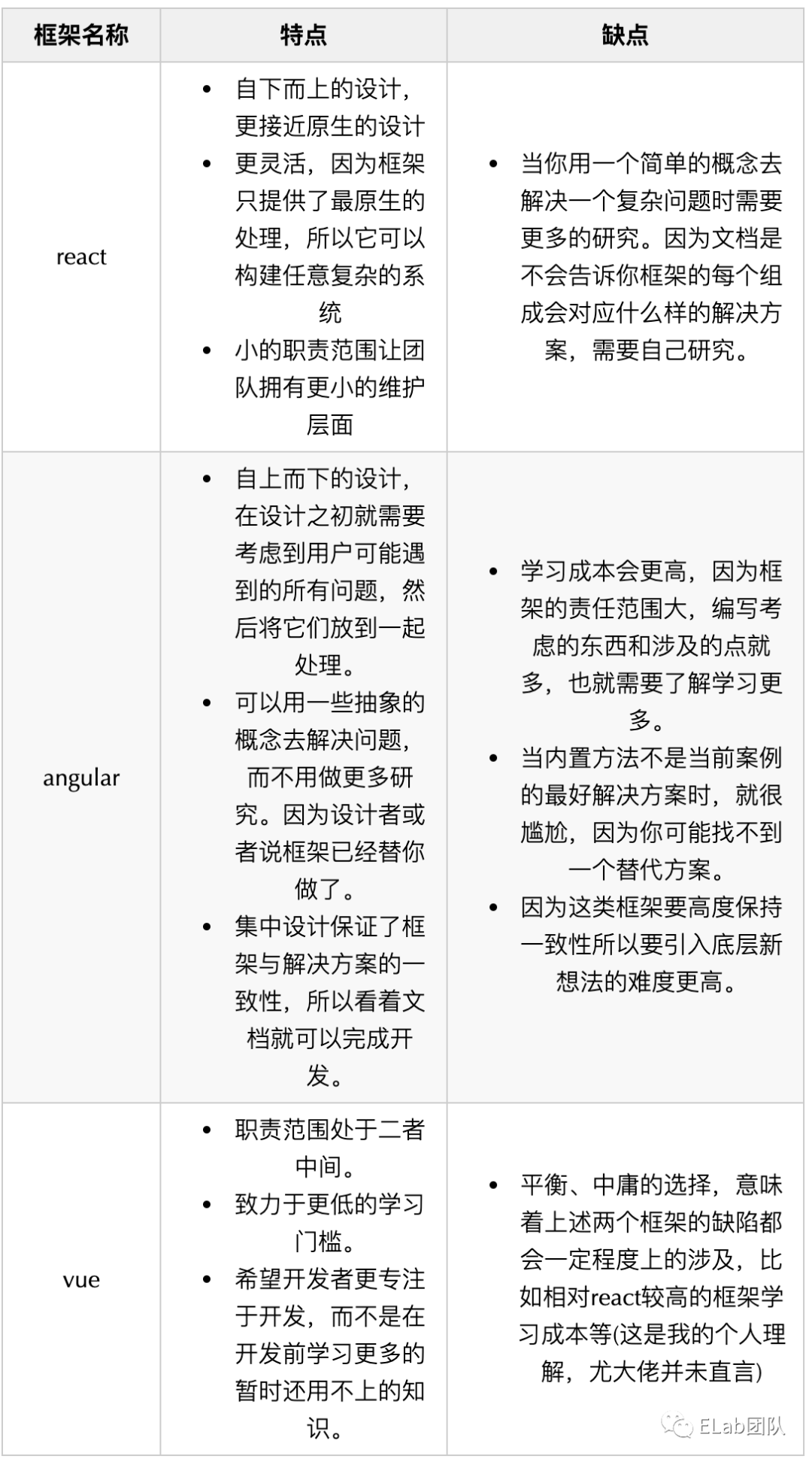
作为现代前端开发者,拥抱框架是生存的不二法则,有些人一入场便投身框架的海洋,有些人则有幸见证过变革,从原生,到jq,到各种框架大行其道的今天。而当前,国内占领市场份额最多的要数vue、react和angular,他们都有着各自的特点,这也是它们一路走来的立足之本。
那么作为使用者的我们,在使用框架高效处理业务的同时,对框架本身也是需要一定程度的理解,以此来辅助我们更好的学习、了解和应用框架。下面有一个表格,内容提炼自尤雨溪本人对三大框架的对比看法,也许可以一定程度提升我们对框架的认知。
职责范围的意义:
- 大的职责范围让开发者习惯把问题抛给框架,
- 小的职责范围让开发者习惯把问题抛给社区。
框架的优势
基于上述框架间的差异化,我们可以看出框架各自不同的设计、发展和其衍生出的生态其实都是源自于最初各自对于职责范围界定的不同而来。但尽管差异不小,它们依然存在着共性,而共性,正是源于框架本身存在的意义和目标。
回头审视,你会发现所有的框架其实都有共同的特点和目标,就是基于原生,然后更高的效率,更棒的性能,更好的差异抹平。
但我们需要正确理解这句话,这并不意味着框架的指标就优于原生,而是说,因为有了框架,我们不用再手写不依赖业务场景的数据-视图的绑定,不用再手动抹平平台或浏览器之间的差异,不用再陷入操作dom的同时还要兼顾性能苦恼。可以说框架提高了开发者开发和实现功能的各项下限,让快速开发和基础性能之间更好的平衡。我们以react和vue为例,这两大框架所带来的优势包括但不限于:
- 数据绑定(单/双向)
- 组件化开发(各种钩子/生命周期/作用域隔离)
- 虚拟dom(diff算法)以及路由等。
- ......
但这些优势不是凭空而来,就像vue的双向绑定,从使用object.defineProperty转为使用proxy,这种类似的实现或者说转变,核心之处都需要js语法以及浏览器的原生支持。因为web应用最终都是要运行在宿主--浏览器上的,所以制定规范的各大浏览器厂商以及提供原生api支持的浏览器环境才是王道,而框架不是。我们之所以需要引入各类的框架、工具库去实现各种优秀的设计与思想,比如组件化,本质上是因为原生未直接提供对应的方式或是api,所以才需要框架去构建棋盘之上的又一层规则体系,来实现开发者的诉求。
而框架这种在浏览器原生规则之上又一层较高程度的封装,在带来便利高效的同时,不可避免的带来两个缺陷:
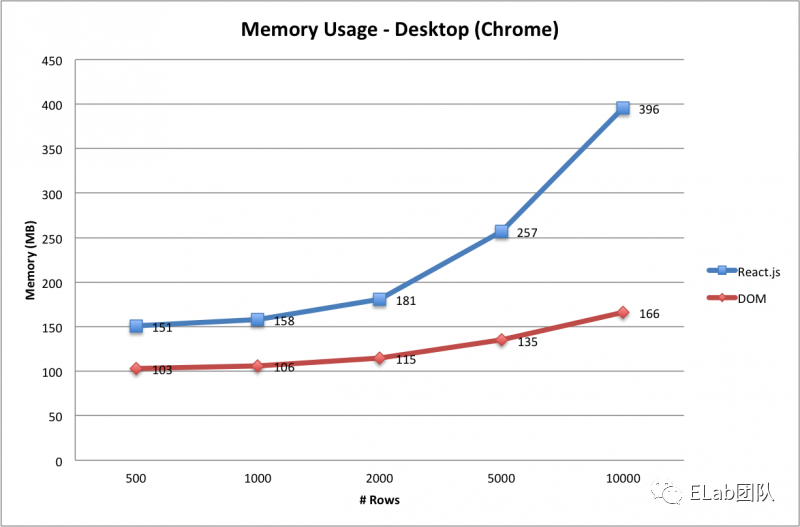
- 性能的下降,这也是为什么上面说有时原生的直接操作指标要优于框架。下面是一些关于处理dom的react vs js的对比:
(图1:桌面chrome; 图2:平板chrome; 图3:移动端chrome;)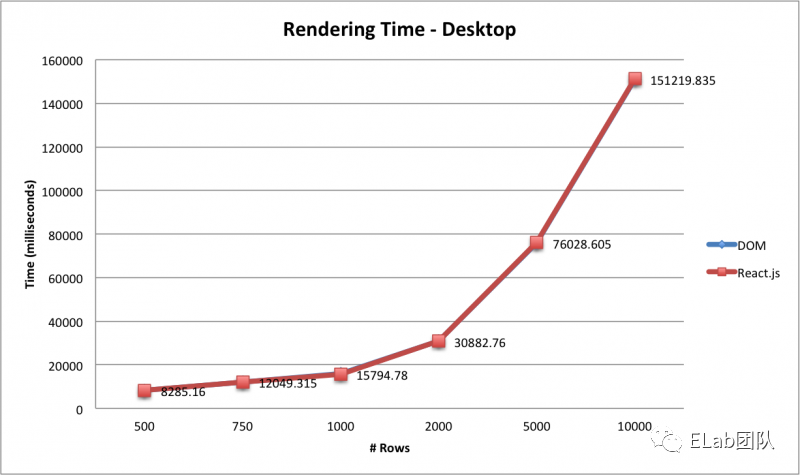
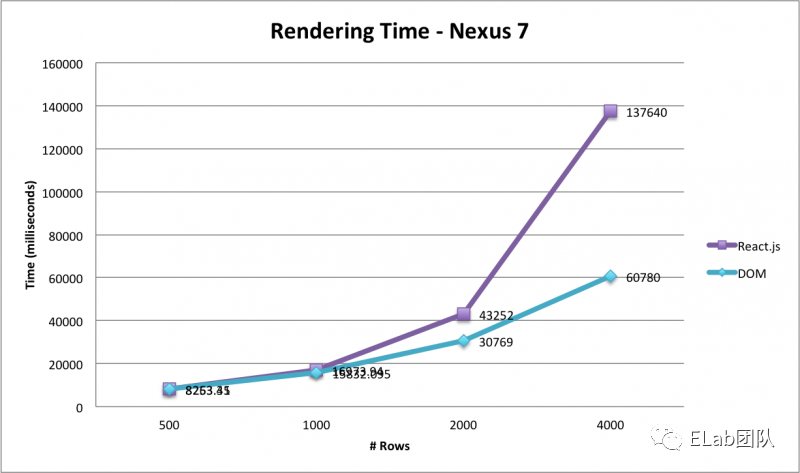

- 框架环境的隔离,例如vue的组件库没办法很好的衔接在react的项目中(也许你会说vuera或微前端,但事实上ROI和性能并不好,开发和维护的成本较高)。
那么如果原生可以提供某些api,是不是就可以一定程度上替代框架的某些功能,在拥有便利高效的同时,跨平台、跨框架的使用,还能较大限度的保持原生的性能?
这就是接下来要聊到的是web component和其所能带来的可能甚至是变革。
认识web component
web component


回看上文中,我们对框架优势的分析罗列,可以发现解决这些开发痛点的方案早已存在,也就是与之对应的框架优势中的组件化。那么根据上面的分析,既然原生支持了,是不是意味着可以颠覆框架?这种想法是有些冲动的,单纯依靠原生的api去颠覆框架是不现实的,能颠覆框架的也必须是框架,因为每一个框架都意味着对应的生态(路由管理、状态管理、dom性能优化管理等)。如果有一天,当前框架中的大部分优秀的设计与思想被原生环境所吸收并支持,那么在此基础上衍生的框架,才能真正具备替代当前三大框架的能力,成为前端唯一一类框架。
而现在,我们虽然还是无法舍弃框架拥抱原生,但是我们可以将其中的一部分进行替代,使之拥有框架提供的优势,又能避免因框架而导致的缺陷。
原生组件化能否替代框架组件化?
我们先来看看组件化的特点:
- 高内聚,低耦合
- 标记鲜明易维护
- 块状接口易扩展
再看看依据组件化的规范,框架组件化提供给我们最直观的体验:
- 高效复用
- 作用域及样式隔离
- 自定义开发
- 钩子函数(生命周期)
- ......
最后我们来看看web component给我们提供了什么:
- Custom elements:自定义元素,通过使用对应的api,用户可以在不依赖框架的情况下,开发原生层面的自定义元素,最关键的是,它将包含独立的生命周期,以及提供了自定义属性的监听。这就意味着它也同样具备了较高的可操作性。
- Shadow DOM:影子dom(最大的特点是不暴露给全局),你可以通过对应的api,将shadow dom附加给你的自定义元素,并控制其相关功能。利用shadow dom的特性,起到隔离的作用,使特性保密,不用再担心所编写的脚本及样式与文档其他部分冲突。
- HTML模版:通过
<template/>、<slot/>去实现内容分发。或者你可以回忆一下vue的插槽(slot)和react的props.children。但事实上,真的是vue最先创立的slot吗?看下面~

那么至少从理论的角度上说,web component是完全有能力替代框架组件化的,这意味着开发者可以在不使用的框架的前提下进行组件化开发,而且开发出的组件可以无缝嵌入使用了框架的项目中。有趣的是在最新发布的vue3.2中,也初步引入了对于web component的使用:
兼容性
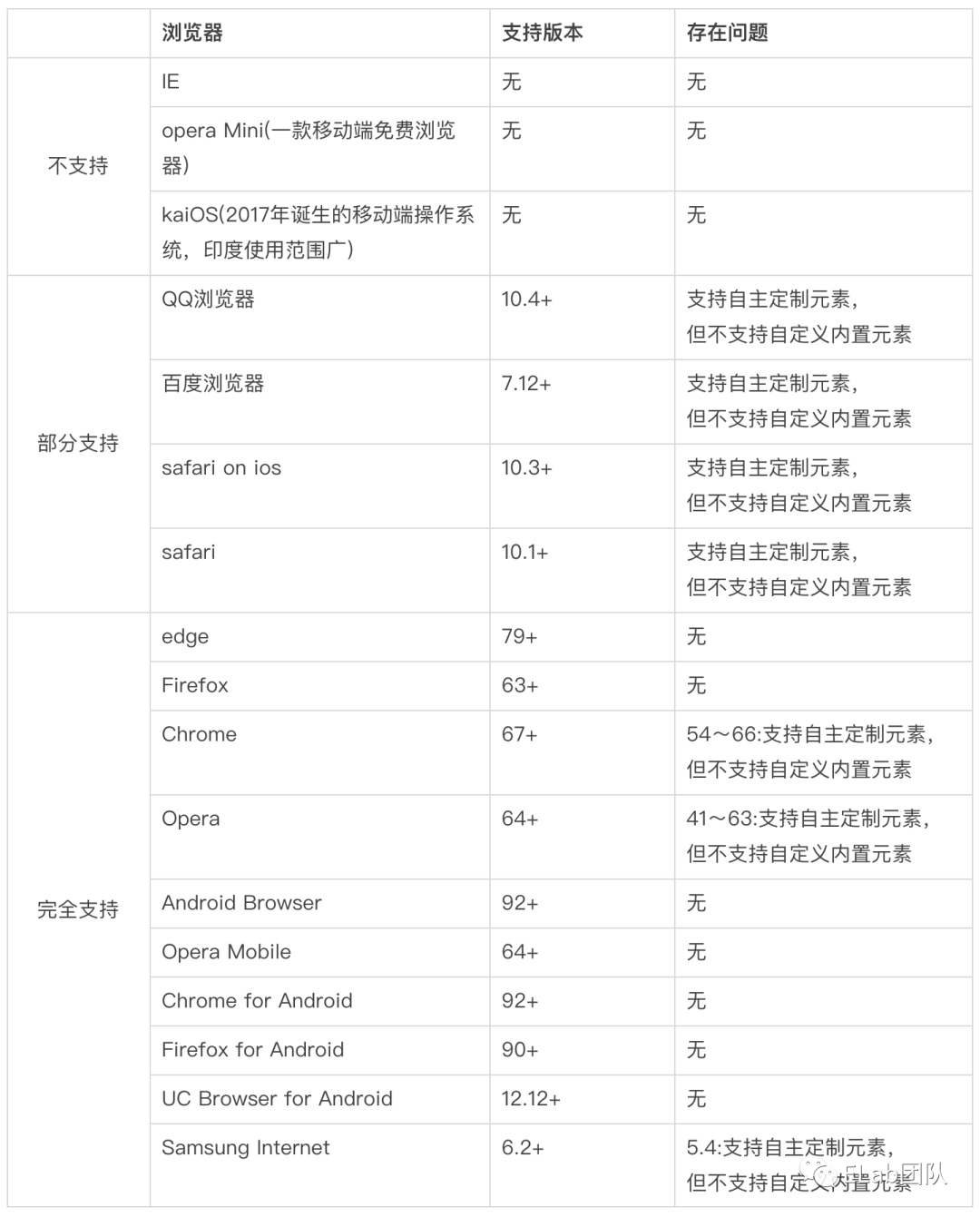
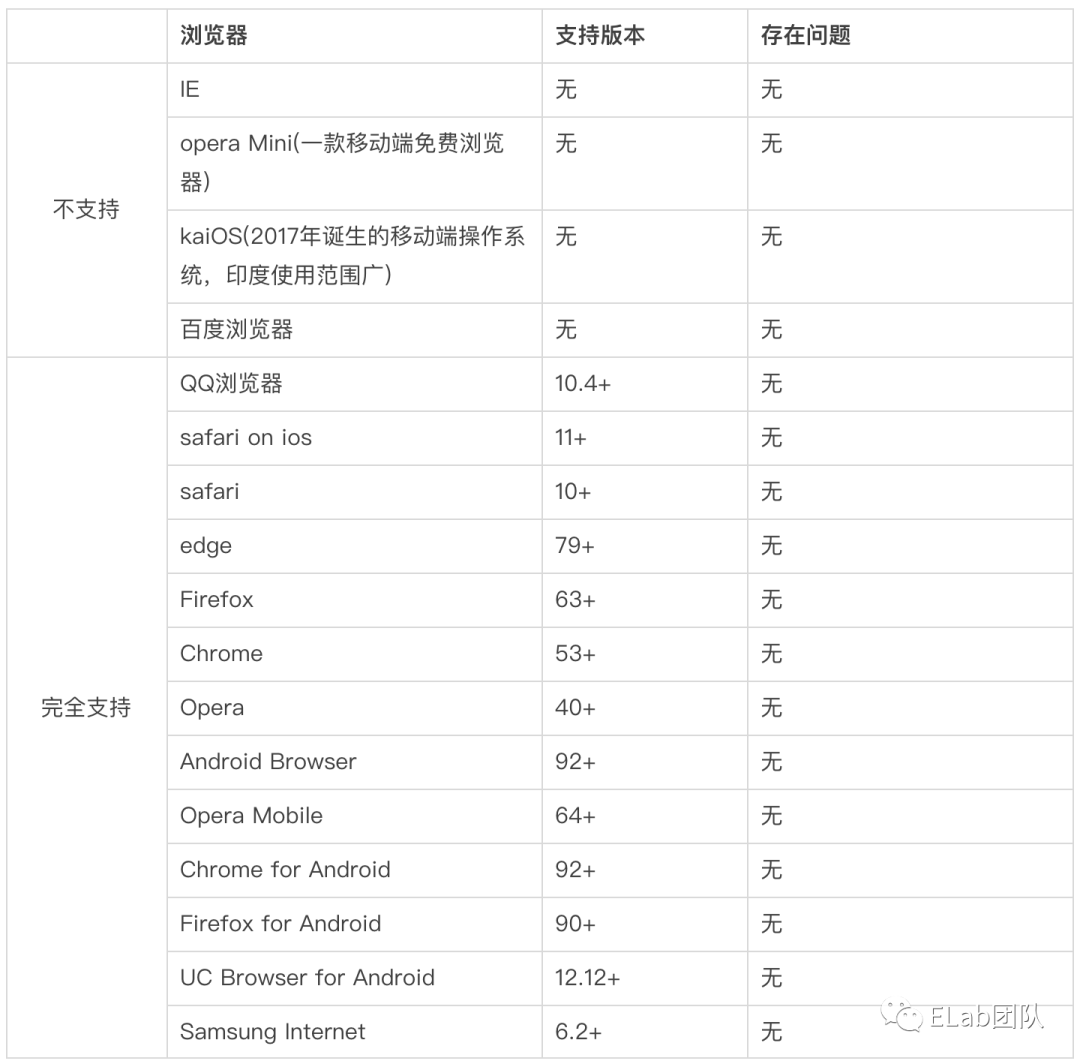
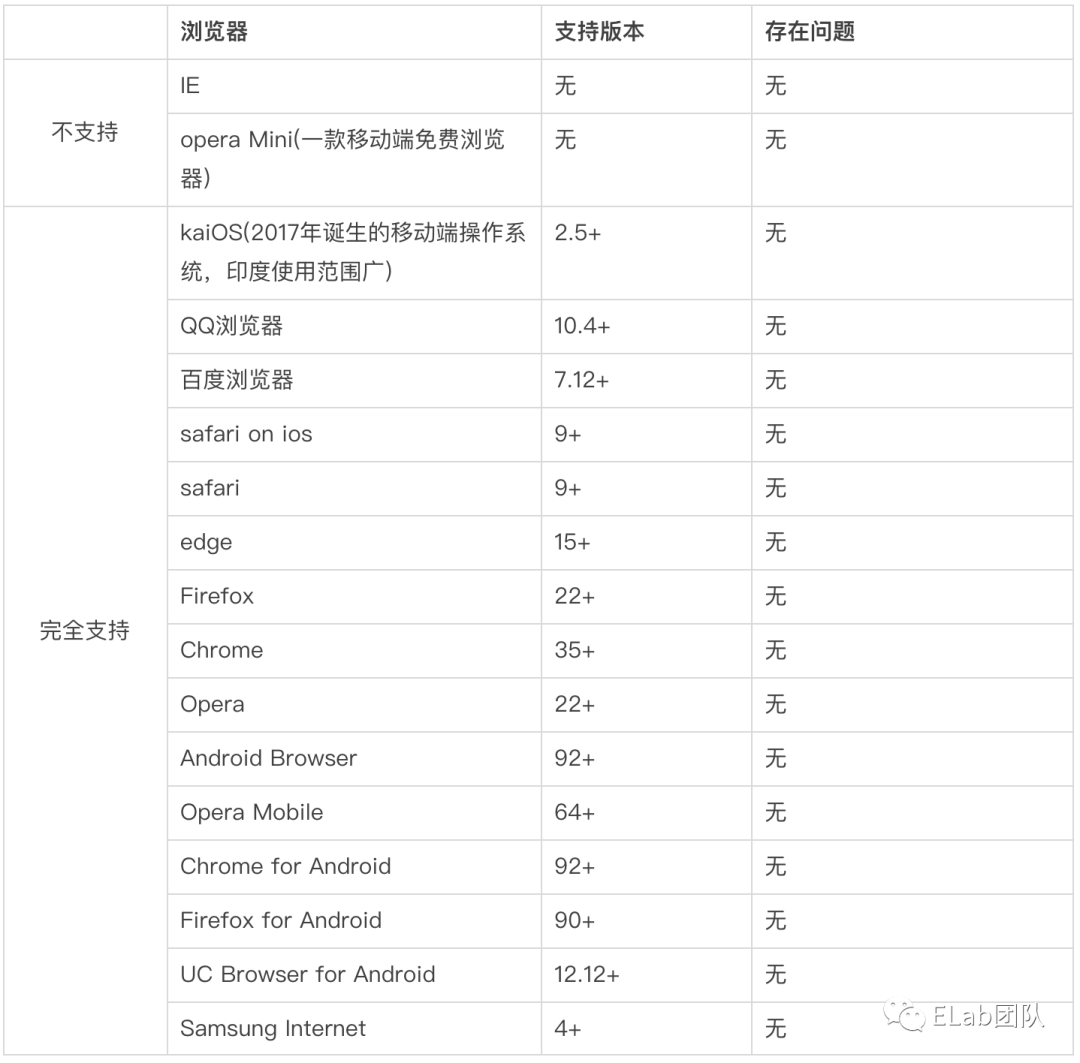
作为开发者,面对新的强大的api,在充满热情的同时,更需要关注其可用性和普及范围。我们可以通过can i use去查看它的兼容性:https://caniuse.com/?search=web%20component。从中我们可以看到:
1. Custom elements兼容性
2. Shadow DOM兼容性
3. HTML templates兼容性
自主定制元素和自定义内置元素
在Custom elements兼容性的描述中,我们看到两个概念,如下:
- 自主定制元素:独立元素;它们不继承自内置的 HTML 元素。
- 自定义内置元素:这些元素继承并扩展了内置的 HTML 元素。
那么这里怎么去理解自主定制元素和自定义内置元素?我们可以从具体的code实现上进行观察:
- 自主定制元素
js:
...
customElements.define('custom-elements', class);
...
html:
<body>
...
<custom-elements></custom-elements>
...
</body> - 自定义内置元素
js:
...
customElements.define('custom-elements', class, { extends: 'p' });
...
html:
<body>
...
<p is="custom-elements"></p>
...
</body>可以看到从声明上是没有太大区别的,都是通过 customElements.define 去定义声明,并且需要一个 class 去构建内部的生命周期与属性监听。区别之处在于自定义内置元素需要在后面的配置项中设置要继承的内置HTML 元素(指原生的元素)。
而最大的区别是在于使用上,自主定制元素其实就是一个完整的自定义组件,可以让我们在不依赖任何框架的前提下实现组件化。而自定义内置组件,可以理解为是对所继承的原生元素的改造(如上述code呈现,声明定义自定义组件时,指定继承的原生元素,后续使用该原生元素时,通过is属性引用声明的自定义组件,就可以改造该原生元素,使其拥有生命周期、自定义组件和作用域隔离的功能)。
web component api的使用
自定义组件的声明和使用
所依赖的主要接口是CustomElementRegistry,该接口提供了,用作支持自定义组件的使用和声明:
- window.customElements.define。
该方法用来声明自定义组件,接受3个参数,无返回值:
- name:将要全局注册的自定义组件名字(必须是中划线的形式)。
- constructor:一个类,如果声明的是自主定制元素,则必须继承自HTMLElement;如果声明的是自定义内置元素,则必须继承它将要扩展的原生元素所属的类(如要扩展div,那就必须继承HTMLDivElement)。并且类的构造函数中,必须执行super。
- options:一个可选的配置对象,只有在声明自定义内置元素时使用,且当前只有一个配置项extends,值为将要扩展的原生元素的标签名。
声明示例:
//自主定制元素
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
...
}
}
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
//自定义内置元素,如果要扩展div的话
class CustomEleBuiltIn extends HTMLDivElement {
constructor() {
super();
...
}
}
customElements.define('custom-ele-build-in', CustomEleBuiltIn, { extends: 'div' }); 使用的方式也是多样的。可以通过document.createElement的方式使用,也可以直接书写在html中。使用示例:
//自主定制元素
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
customEle.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
customEle.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
document.querySelector('#app').appendChild(customEle);
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
//或
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
const customEle = new CustomEle();
customEle.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
customEle.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
document.querySelector('#app').appendChild(customEle);
//或
<custom-ele img="https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png" text="我是一段悬停说明">
//自定义内置元素,如果要扩展div的话
customElements.define('custom-ele-build-in', CustomEleBuiltIn, { extends: 'div' });
const div = document.createElement('div', { is: 'custom-ele-build-in' });
div.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
div.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
document.querySelector('#app').appNode.appendChild(div);
//或
<div is="custom-ele-build-in" img="https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png" text="我是一段悬停说明" /> 这里的几 种使用方式其实还是有差异的,在初始化的时候,直接引用的方式可以在构造阶段就拿到挂载的各个属性;但是采用create的方式时,构造阶段无法第一时间获取属性,当然,利用生命周期的钩子函数,也是解决该问题的。
- window.customElements.get。
该方法用来获取自定义组件的构造函数,接受一个参数,即声明过的自定义组件的name,返回构造函数。
const getCustomConstructorBefore = customElements.get('custom-ele');
console.log('getCustomConstructor-before', getCustomConstructorBefore);//undefined
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
const getCustomConstructorAfter = customElements.get('custom-ele');
console.log('getCustomConstructor-after', getCustomConstructorAfter);//CustomEle - window.customElements.upgrade。
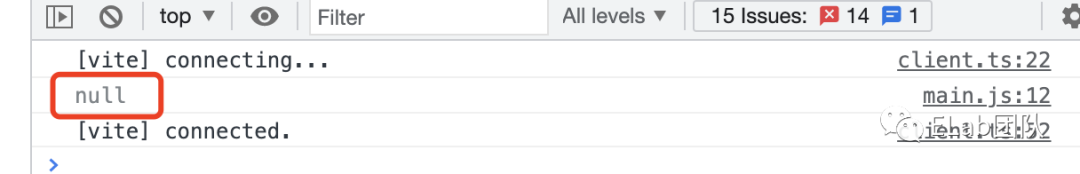
该方法是用来更新挂载主文档之前的包含shadow dom的自定义组件的,接受一个参数,即包含了shadow dom的自定义组件节点,无返回值。(自定义组件在被append到主文档的时候,会触发自动更新)。
//先创建了自定义元素
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
customEle.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
customEle.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
//后声明自定义元素
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
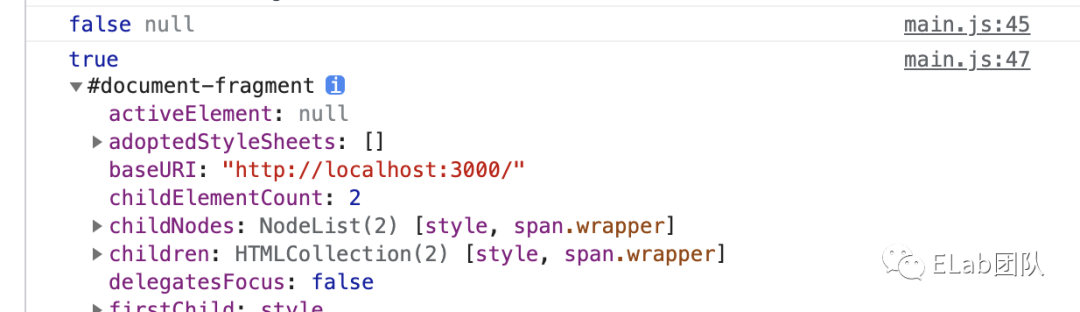
//结果为false,null
console.log(customEle instanceof CustomEle, customEle.shadowRoot);
//进行更新节点
customElements.upgrade(customEle);//或document.querySelector('#app').appendChild(customEle);
//true,#document-fragment
console.log(customEle instanceof CustomEle, customEle.shadowRoot); - window.customElements.whenDefined。
该方法是用来检测并提供自定义组件被定义声明完毕的时机得,接受一个参数,即自定义元素的name,返回值是一个promise(只检测自定义组件是否被defined,不检测是否被挂载于主文档)。若提供的name无效,则触发promise的catch。
//创建了自定义元素dom
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
customEle.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
customEle.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
//用来判断关闭定时器得标识
let isStop = false;
//获取自定义组件定义完毕的时机
customElements.whenDefined('custom-ele').then(() => {
console.log('定义完毕');
isStop = true;
});
//一个用于观察得计时器
const timer = setInterval(() => {
if (isStop) {
clearInterval(timer);
return;
}
console.log(Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000));
}, 1000);
//延迟3秒进行自定义组件的定义及声明
setTimeout(() => {
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
}, 3000) 自定义组件的生命周期
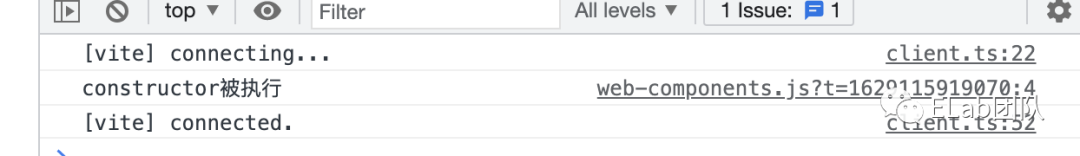
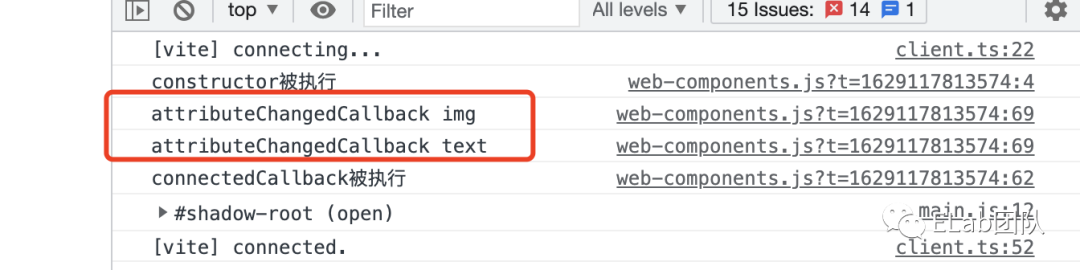
- constructor
自定义组件的第一个生命周期,用来初始化自定义组件本身。触发的时机在自定义组件被document.createElement的时候(前提是组件已经被customElements.define过,如果组件是先create,后defined,那么constructor的执行时机在append到主文档里时)。
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
console.log('constructor被执行');
......
}
}
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
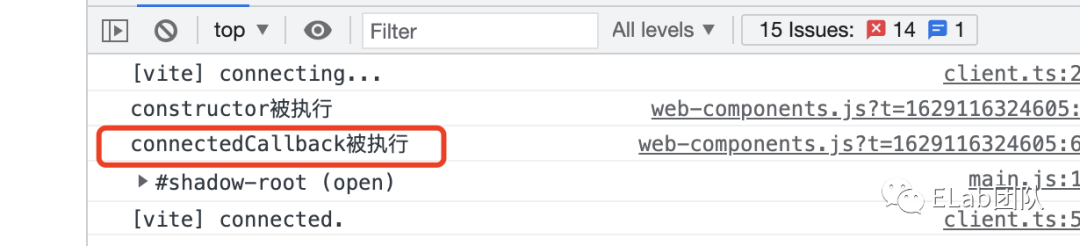
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele'); - connectedCallback
在组件被成功添加到主文档时触发的生命周期,在constructor之后。
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
console.log('constructor被执行');
......
}
connectedCallback () {
console.log('connectedCallback被执行');
}
}
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
document.querySelector('#app').appendChild(customEle); - attributeChangedCallback
自定义组件最关键的一个生命周期。触发时机在组件属性被增加、删除或修改的时候。如果你是在组件被append之前设置了属性,那么就会在connectedCallback之前触发;反之,则在connectedCallback之后触发。需要配合静态方法observedAttributes来使用,只有注册在observedAttributes中的属性才会被监听。
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
console.log('constructor被执行');
......
}
connectedCallback () {
console.log('connectedCallback被执行');
}
static get observedAttributes () { return [ 'img', 'text' ]; }
attributeChangedCallback (name, oldValue, newValue) {
console.log('attributeChangedCallback', name)
if (name === 'img') {
this.shadowRoot.querySelector('img').src = this.getAttribute('img');
}
if (name === 'text') {
this.shadowRoot.querySelector('.info').textContent = this.getAttribute('text');
}
}
}
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
customEle.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
customEle.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
document.querySelector('#app').appendChild(customEle); - adoptedCallback
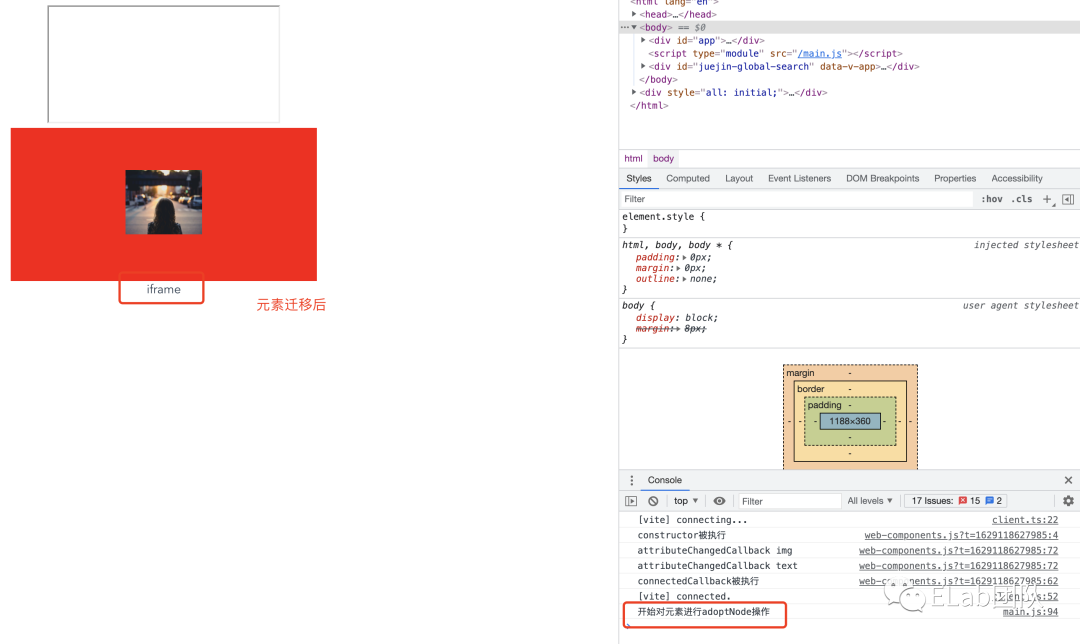
当元素被移动到新的文档时,被调用。即元素是另一个文档的元素,而adoptedCallback是新文档下的自定义组件的回调。
//声明自定义组件的类
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
......
}
adoptedCallback () {
console.log('adoptedCallback被执行');
}
}
//创造场景,增加iframe,即旧文档
appNode.innerHTML = '<iframe></iframe>';
const p = document.createElement('p');
p.innerHTML = 'iframe';
appNode.querySelector('iframe').contentWindow.document.body.appendChild(p);
//新文档中创建自定义组件
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
customEle.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
customEle.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
appNode.appendChild(customEle);
//将元素从旧文档迁移到新文档
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('开始对元素进行adoptNode操作')
const node = appNode.querySelector('iframe').contentWindow.document.body.firstElementChild;
appNode.appendChild(document.adoptNode(node))
}, 2000); 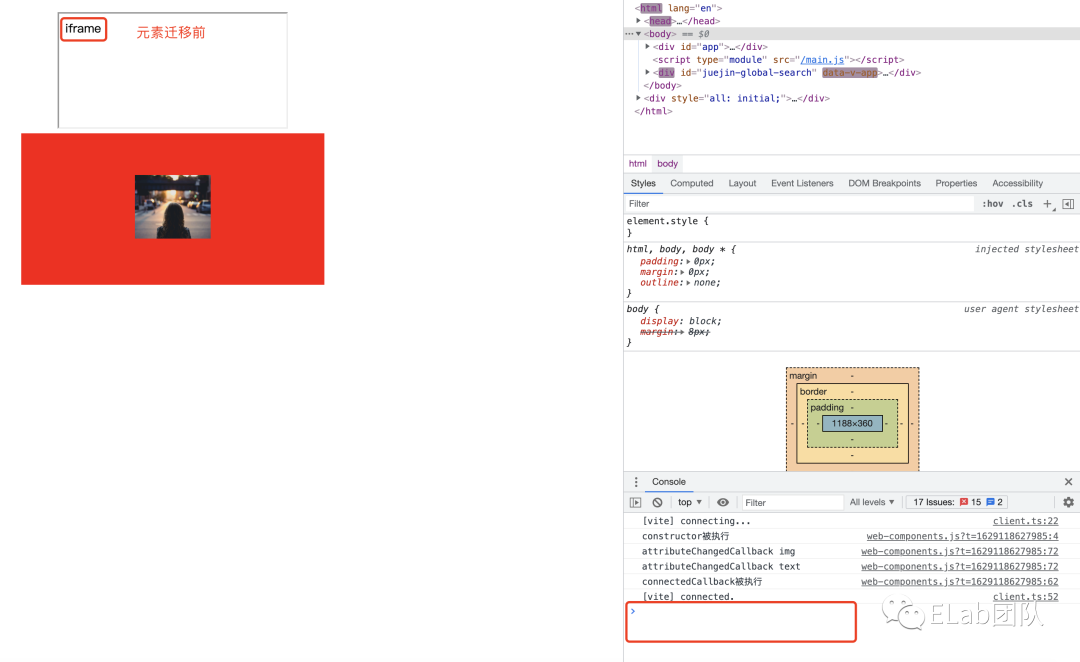
- disconnectedCallback
自定义组件的最后一个生命周期,触发的时机在组件被成功从主文档移除时。
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
......
}
disconnectedCallback () {
console.log('disconnectedCallback被执行');
}
}
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
document.querySelector('#app').appendChild(customEle);
setTimeout(() => {
appNode.removeChild(customEle);
}, 2000) 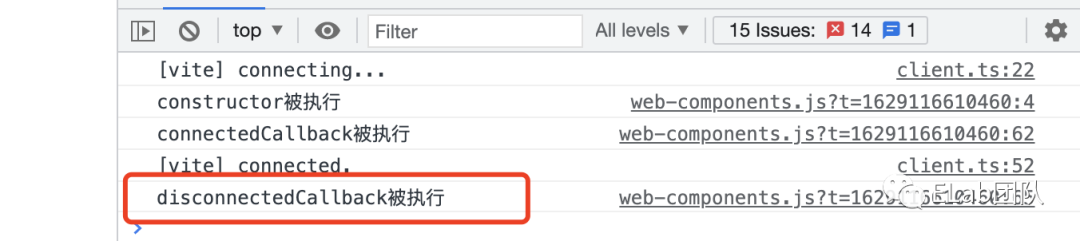
Shadow DOM的使用
其作用是将标记结构、样式和行为隐藏起来,并与页面上的其他代码相隔离。Shadow DOM 都不是一个新事物,在过去的很长一段时间里,浏览器用它来封装一些元素的内部结构,回忆一下video标签内部被隐藏起来的控制按钮们。
- 为元素附加Shadow DOM:ele.attachShadow
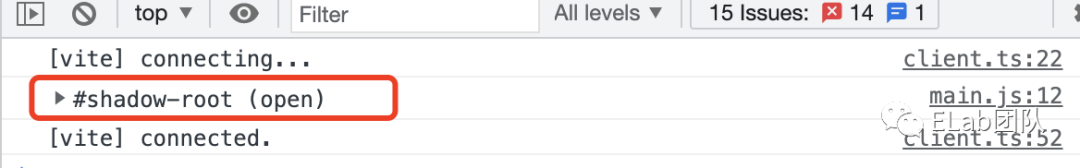
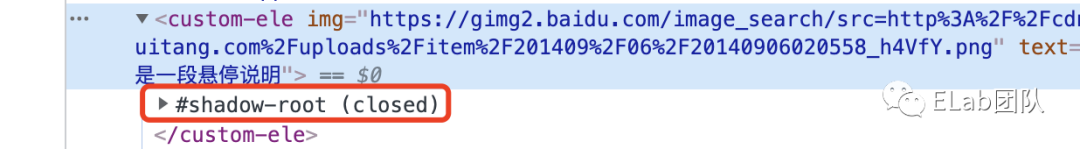
attachShadow接受一个对象参数,只需关注一个配置属性mode,如果设置为open,表示可以从外部获取Shadow DOM内部的元素;如果设置为closed,则表示隐藏Shadow DOM内部,例如
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
const shadow = this.attachShadow({ mode: 'open' });
......
}
}
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
document.querySelector('#app').appendChild(customEle);
console.log(customEle.shadowRoot) 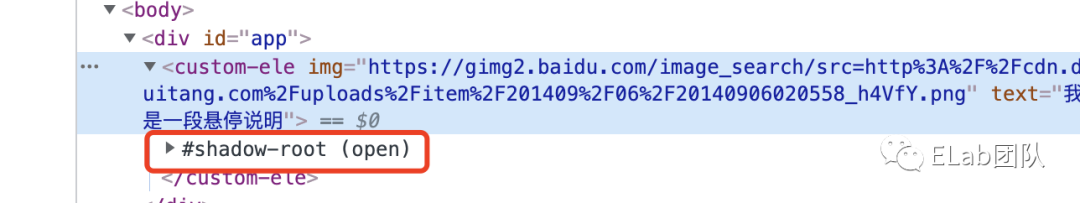
-
操作元素的Shadow DOM并添加样式
当为一个元素附加了Shadow DOM后,就可以使用同操作正常dom一样的方法去操作了。示例如下:
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
const shadow = this.attachShadow({ mode: 'open' });
const wrapper = document.createElement('span');
wrapper.setAttribute('class', 'wrapper');
const icon = document.createElement('span');
icon.setAttribute('class', 'icon');
const info = document.createElement('span');
info.setAttribute('class', 'info');
const text = this.getAttribute('text');
info.textContent = text;
const img = document.createElement('img');
img.src = this.getAttribute('img');
icon.appendChild(img);
const style = document.createElement('style');
// console.log('CustomEle', style.isConnected);
style.textContent = `
.wrapper {
position: relative;
}
.info {
font-size: 0.8rem;
width: 200px;
display: inline-block;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 10px;
background: white;
border-radius: 10px;
opacity: 0;
transition: 0.6s all;
position: absolute;
bottom: 20px;
left: 10px;
z-index: 3;
}
img {
width: 1.2rem;
}
.icon:hover + .info, .icon:focus + .info {
opacity: 1;
}
`;
shadow.appendChild(style);
// console.log('CustomEle', style.isConnected);
shadow.appendChild(wrapper);
wrapper.appendChild(icon);
wrapper.appendChild(info);
}
}
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
customEle.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
customEle.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
document.querySelector('#app').appendChild(customEle); 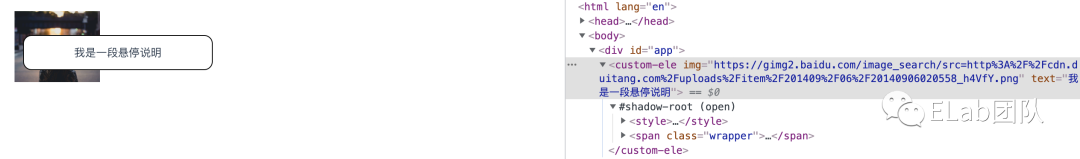
const style = document.createElement('style');
// console.log('CustomEle', style.isConnected);
style.textContent = `
.wrapper {
position: relative;
}
.info {
font-size: 0.8rem;
width: 200px;
display: inline-block;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 10px;
background: white;
border-radius: 10px;
opacity: 0;
transition: 0.6s all;
position: absolute;
bottom: 20px;
left: 10px;
z-index: 3;
}
img {
width: 1.2rem;
}
.icon:hover + .info, .icon:focus + .info {
opacity: 1;
}
`;
shadow.appendChild(style); 替换为:
const linkElem = document.createElement('link');
linkElem.setAttribute('rel', 'stylesheet');
linkElem.setAttribute('href', 'style.css');//样式的地址
shadow.appendChild(linkElem); 需要注意的是:由于link元素不会打断 shadow root 的绘制, 因此在加载样式表时可能会出现未添加样式内容(FOUC),导致闪烁。
模版
- template
使用包裹的内容不会在页面上显示,但是却可以被js引用到。这就意味着有些内容我们不用重复构建多遍,使用构建一遍,然后多次引用处理就好了。
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
console.log('constructor被执行');
const shadow = this.attachShadow({ mode: 'open' });
let template = document.getElementById('my-paragraph');
if (template) {
let templateContent = template.content;
shadow.appendChild(templateContent.cloneNode(true));
}
......
}
}
appNode.innerHTML = '<template id="my-paragraph"><style>p {color: white;background-color: #666;padding: 5px;}</style><p>My paragraph</p></template>';
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
customEle.setAttribute('img', 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fcdn.duitang.com%2Fuploads%2Fitem%2F201409%2F06%2F20140906020558_h4VfY.png');
customEle.setAttribute('text', '我是一段悬停说明');
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
appNode.appendChild(customEle); - slot
- 在template的基础上,更加灵活的内容分发,可以配合template使用(在template中定义占位符,然后将template的内容clone到shadow DOM中)。也可以直接在shadow DOM中添加占位符。
然后在自定义组件的innerhtml中使用即可。
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
console.log('constructor被执行');
const shadow = this.attachShadow({ mode: 'open' });
let template = document.getElementById('my-paragraph');
if (template) {
let templateContent = template.content;
shadow.appendChild(templateContent.cloneNode(true));
}
const slot2 = document.createElement('slot');
slot2.setAttribute('name', 'newText2');
shadow.appendChild(slot2);
......
}
}
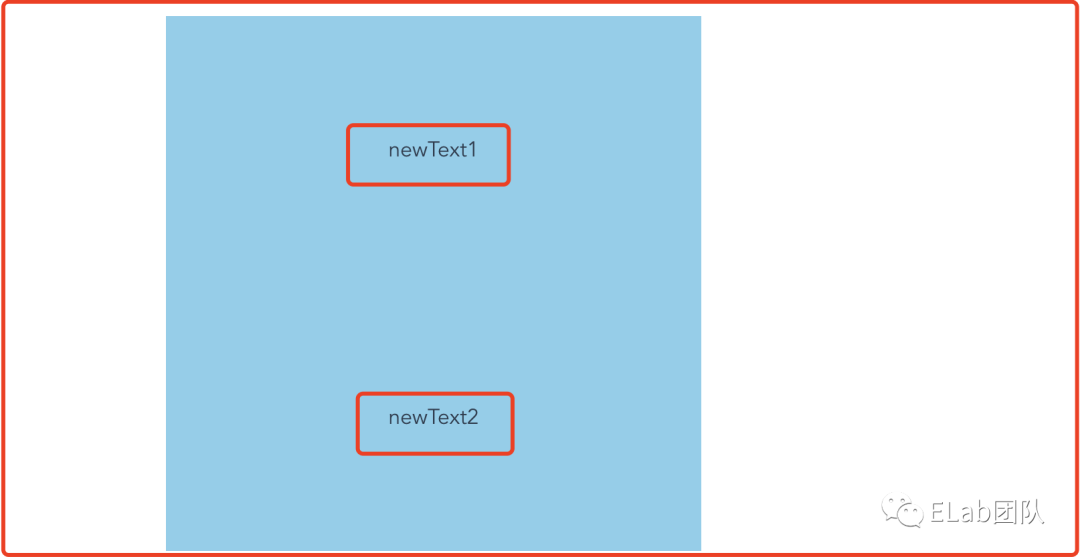
appNode.innerHTML = '<template id="my-paragraph"><style>p {color: white;background-color: #666;padding: 5px;}</style><slot name="newText1"></slot></template><custom-ele><p slot="newText1">newText1</p></custom-ele>';
const customEle = document.createElement('custom-ele');
customEle.innerHTML = '<p slot="newText2">newText2</p>';
customElements.define('custom-ele', CustomEle);
appNode.appendChild(customEle); - slotchange:用于监听shadow DOM中的slot插入或移除的事件。
class CustomEle extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
let template = document.getElementById('my-paragraph');
if (template) {
let templateContent = template.content;
shadow.appendChild(templateContent.cloneNode(true));
}
const slots = shadow.querySelectorAll('slot');
slots.forEach(slot => {
slot.addEventListener('slotchange', function (e) {
console.log('slotchange', slot.name, e);
});
});
......
}
}
appNode.innerHTML = '<template id="my-paragraph">' +
'<style>p {color: white;background-color: #666;padding: 5px;}</style>' +
'<slot name="newText1"></slot>' +
'<slot name="spanText"></slot>' +
'</template>' +
'<h3>' +
'<custom-ele class="newText1Box">' +
'<p slot="newText1">newText1</p>' +
'<span slot="spanText">spanText</span>' +
'</custom-ele>' +
'</h3>';
setTimeout(() => {
document.querySelector('.newText1Box').removeChild(document.querySelector('.newText1Box p'));
//或
document.querySelector('.newText1Box p').removeAttribute('slot');
}, 2000)
在添加slot时(直接插入包含slot属性的元素或给已插入的元素增加slot属性)或删除slot时(直接remove包含slot属性的元素或给已插入的元素removeAttribute slot属性),都会触发slotchange事件。 相关的其他api
- element.attachShadow(opt):用来给指定元素挂载shadow DOM。
opt的配置项:
-
mode:如果为open,表示可以在外部通过element.shadowRoot获取shadow DOM节点。并且方法会返回shadow DOM对象。如果为closed,表示不允许外部访问shadow DOM节点,并且方法返回null。
-
delegatesFocus:表示是否减轻自定义元素的聚焦性能问题。当shadow DOM中不可聚焦的部分被点击时, 让第一个可聚焦的部分成为焦点, 并且shadow host将提供所有可用的 :focus 样式.
-
css伪类:
-
:defined:表示所有内置元素及已经通过customElements.define注册的元素。
-
:host:只能在shadow DOM的样式表内书写。表示当前所在的自定义组件的所有实例及shadow DOM下所有的元素。
-
:host([选择器]):只能在shadow DOM的样式表内书写。是:host的增强,表示:host()所在的自定义组件的所有实例中选择器符合括号中名称的实例及其包含的shadow DOM下属所有元素。
-
:host-context([选择器]):只能在shadow DOM的样式表内书写。是:host的增强,表示:host()-context所在的自定义组件的所有实例的父元素中选择器符合括号中名称的实例及其包含的shadow DOM下属所有元素。
-
:slotted([选择器]):只能在shadow DOM的样式表内书写。表示: slotted()所在的自定义组件的所有实例中选择器符合括号中名称的slot元素,若选择器为*,则表示命中所有slot。
-
节点相关拓展
-
getRootNode:使用方式为ele. getRootNode(opt),opt中包含一个属性composed,为true时,检索到的根元素为document;为false时,如果ele是属于shadow DOM,那么检索到shadow DOM,否则检索到document。
-
isConnected:是元素的一个只读属性接口。返回元素是否与dom树连接的boolean值。即是否被append到主文档中。
-
event扩展
-
composed属性:用来指示该事件是否可以从 Shadow DOM 传递到一般的 DOM(测试后发现不论是普通DOM还是shadow DOM均为true)。
-
path属性:返回事件的路径。如果shadow root是使用mode为closed创建的,则不包括shadow树中的节点(测试后发现尽管shadowdom设置了mode为closed,依然能获取完整的path)。
-
关于slot
-
ele.assignedSlot:用来获取ele元素上代表插入slot的元素。但如果ele.attachShadow中的mode是closed为closed时,返回null。
-
ele.slot:用来获取元素上slot的name值。
-
......
相关的库及网站
- webcomponents.org — site featuring web components examples, tutorials, and other information.
- Hybrids — Open source web components library, which favors plain objects and pure functions over class and this syntax. It provides a simple and functional API for creating custom elements.
- Polymer — Google's web components framework — a set of polyfills, enhancements, and examples. Currently the easiest way to use web components cross-browser.
- Snuggsi.es — Easy Web Components in ~1kB Including polyfill — All you need is a browser and basic understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript classes to be productive.
- Slim.js — Open source web components library — a high-performant library for rapid and easy component authoring; extensible and pluggable and cross-framework compatible.
- Smart.js — Web Components library with simple API for creating cross-browser custom elements.
- Stencil — Toolchain for building reusable, scalable design systems in web components.
参考
- https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/Web_Components
- https://medium.com/jspoint/the-anatomy-of-web-components-d6afedb81b37
- https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2019/08/web_components.html
- https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/custom-elements.html#custom-elements
- https://developers.google.cn/web/fundamentals/web-components
- https://objectpartners.com/2015/11/19/comparing-react-js-performance-vs-native-dom/
- https://bugs.webkit.org/show_bug.cgi?id=182671