Node.js 动态表格大文件下载实践
前言
最近优化了几个新人写出的动态表格文件下载接口的性能瓶颈,感觉非常有必要总结一篇文章作为文档来抛砖引玉,以促进大家学习一起写出更专业的代码。
HTTP 文件下载
讲具体问题之前需要先了解一些 HTTP 基础,下面简单介绍一下用 Node.js&Koa 怎么实现文件下载。
参考:
rfc2616 19.5.1 Content-Disposition
rfc1806
Node.js Stream
简单下载
最简单的情况就是服务器上文件系统已经存在了某个文件,客户端请求下载直接把文件读了吐回去即可:
import Koa from 'koa';
import Router from 'koa-router';
import * as fs from 'fs/promises';
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
router.get('/download/simple', async (ctx) => {
const file = await fs.readFile(`${__dirname}/1.txt`, 'utf-8');
ctx.set({
'Content-Disposition': `attachment; filename=1.txt`,
});
ctx.body = file;
});
app.use(router.routes());
app.listen(80);
设置 Content-Disposition 头部为 attachment 是关键,告诉浏览器应该下载这个文件。
流式下载
简单下载在碰到大文件的情景就不够用了,因为 Node 无法将大文件一次性读取到进程内存里。这时候用流来解决:
router.get('/download/stream', async (ctx) => {
const file = fs.createReadStream(`${__dirname}/1.txt`);
ctx.set({
'Content-Disposition': `attachment; filename=1.txt`,
});
ctx.body = file;
});此例子不设置 Content-Disposition 头部也是会下载的,因为 Content-Type 被设置为了 application/octet-stream,浏览器认为其是一个二进制流文件所以默认下载处理了。
进度显示
当下载的文件特别大时,上个例子 Content-Length 正确设置时浏览器下载条里就能正常显示进度了,为了方便我们使用程序模拟一下:
router.get('/download/progress', async (ctx) => {
const { enable } = ctx.query;
const buffer = await fsp.readFile(`${__dirname}/1.txt`);
const stream = new PassThrough();
const l = buffer.length;
const count = 4;
const size = Math.floor(l / count);
const writeQuarter = (i = 0) => {
const start = i * size;
const end = i === count - 1 ? l : (i + 1) * size;
stream.write(buffer.slice(start, end));
if (end === l) {
stream.end();
} else {
setTimeout(() => writeQuarter(i + 1), 3000);
}
};
if (!!enable) {
ctx.set({
'Content-Length': `${l}`,
});
}
ctx.set({
'Content-Type': 'plain/txt',
'Content-Disposition': `attachment; filename=1.txt`,
Connection: 'keep-alive',
});
ctx.body = stream;
writeQuarter();
});这里利用了 PassThrough 流来替代 fs.createReadStream,故 Koa 不再知道文件大小和类型,并将文件分为 4 份,每份间隔 3 秒发送来模拟大文件下载。
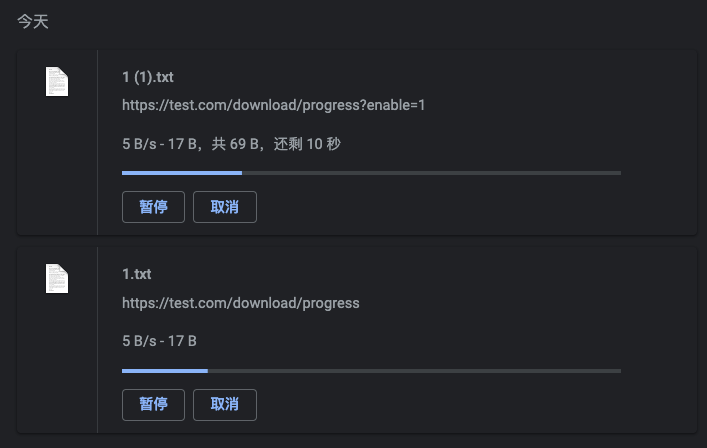
当参数 enable 为真时,设置了 Content-Length 则会显示进度 (剩余时间),否则不显示:
断点续传
下载文件特别大时,常常也会因为网络不稳定导致下载中途断开而失败,这时候可以考虑支持断点续传:
function getStartPos(range = '') {
var startPos = 0;
if (typeof range === 'string') {
var matches = /^bytes=([0-9]+)-$/.exec(range);
if (matches) {
startPos = Number(matches[1]);
}
}
return startPos;
}
router.get('/download/partial', async (ctx) => {
const range = ctx.get('range');
const start = getStartPos(range);
const stat = await fsp.stat(`${__dirname}/1.txt`);
const stream = fs.createReadStream(`${__dirname}/1.txt`, {
start,
highWaterMark: Math.ceil((stat.size - start) / 4),
});
stream.on('data', (chunk) => {
console.log(`Readed ${chunk.length} bytes of data.`);
stream.pause();
setTimeout(() => {
stream.resume();
}, 3000);
});
console.log(`Start Pos: ${start}.`);
if (start === 0) {
ctx.status = 200;
ctx.set({
'Accept-Ranges': 'bytes',
'Content-Length': `${stat.size}`,
});
} else {
ctx.status = 206;
ctx.set({
'Content-Range': `bytes ${start}-${stat.size - 1}/${stat.size}`,
});
}
ctx.set({
'Content-Type': 'application/octet-stream',
'Content-Disposition': `attachment; filename=1.txt`,
Connection: 'keep-alive',
});
ctx.body = stream;
});
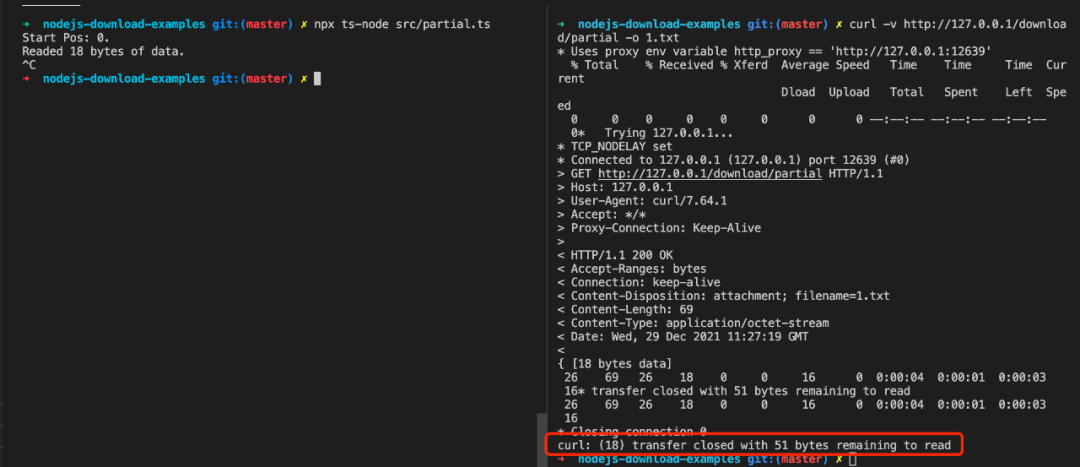
让我们来试验一下(Chrome 默认下载工具不支持断点续传):
curl -v http://127.0.0.1/download/partial -o 1.txt
此时我们趁传输间隙,将服务进程停止,这时可以看到 1.txt 文件仅仅只传了 18 bytes:
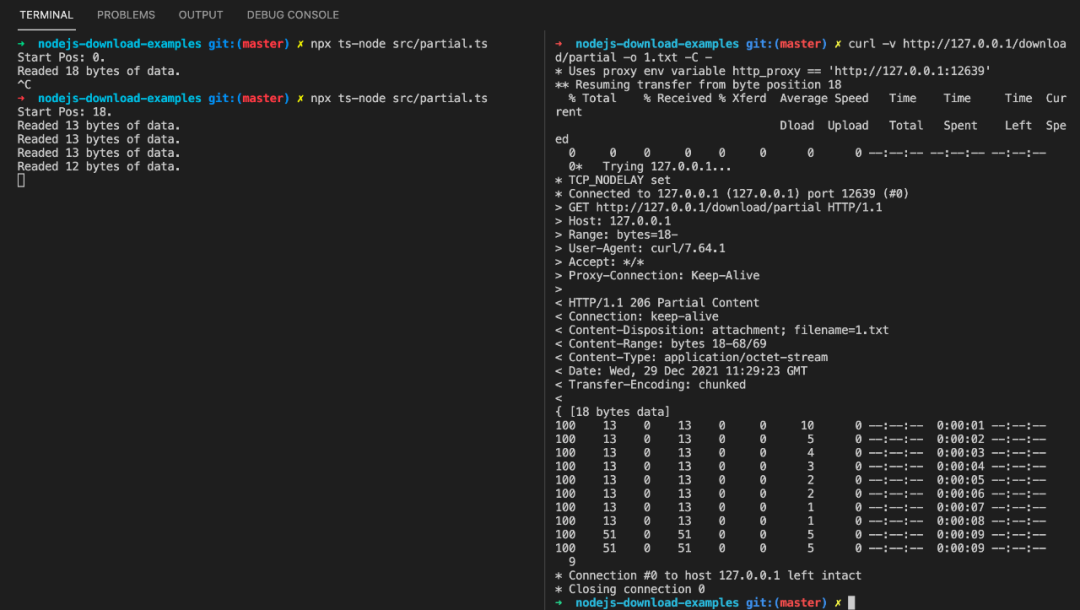
我们将服务恢复,恢复下载:
curl -v http://127.0.0.1/download/partial -o 1.txt -C -
可以看到剩下的部分也分 4 次传完了。
动态表格
在了解完上述关于文件下载实现的基础后,我们来看一个实际问题:根据请求参数条件读取数据库的某张表的全部记录并导出为表格。
参考:
exceljs
瓶颈
// Controller.js
const sequelize = new Sequelize(name, user, password, {
dialect: 'mysql',
host,
port,
});
const model = sequelize.import('/path/to/model');
const { rows } = await model.findAndCountAll({
where: conditions,
attributes: ['f_user_id'],
group: 'f_user_id',
});
const list = awaitPromise.all(
rows.map((item) => {
const { f_user_id } = item;
const userRows = await model.findAll({
where: { ...conditions, f_user_id },
// ordering, eager loading, ...
});
// formating userRows -> userData
return userData;
})
);
const headers = ['ID', /*...*/];
const sheetData = [headers, ...list];
ctx.attachment(`${sheetName}.xlsx`);
ctx.body = await exportXlsx(sheetName, sheetData);// xlsx
const ExcelJS = require('exceljs');
const fs = require('fs');
module.exports = {
exportXlsx: async (name = 'sheet', data) => {
const tempFilePath = `./xlsx/${Date.now()}.xlsx`;
const workbook = new ExcelJS.stream.xlsx.WorkbookWriter({
filename: tempFilePath
}); // 创建一个流式写入器
const sheet = workbook.addWorksheet('My Sheet'); // 添加工作表
const { length } = data;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
sheet.addRow(data[i]);
}
sheet.commit(); // 提交工作表
await workbook.commit(); // 交工作簿,即写入文件
return fs.createReadStream(tempFilePath);
},
};多数人业务初期做需求时,考虑到数据量还不是很多,排期紧任务重,都像上面这样实现:
- 不考虑数据量,当数据库表记录数超过 2w 时,内存就已经承受不住导致 Node 进程退出了
- 没有考虑内存限制,找个成熟的
exceljs库,但却没有用其提供的流 API - 数据查询逻辑实现完全不考虑性能,拿到 ORM 库就是调用查询,完全不考虑 SQL 查询并发数
优化
分段处理
最简单的策略就是将几 w 条数据库数据按每组 1w 条分组,分批次处理,有很多优秀的开源库以供使用比如 async 。
简单代码示意:
// xlsx
const ExcelJS = require('exceljs');
const fs = require('fs');
module.exports = {
exportXlsx: async (name = 'sheet', data) => {
const tempFilePath = `./xlsx/${Date.now()}.xlsx`;
const workbook = new ExcelJS.stream.xlsx.WorkbookWriter({
filename: tempFilePath
}); // 创建一个流式写入器
const sheet = workbook.addWorksheet('My Sheet'); // 添加工作表
const { length } = data;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
sheet.addRow(data[i]);
}
sheet.commit(); // 提交工作表
await workbook.commit(); // 交工作簿,即写入文件
return fs.createReadStream(tempFilePath);
},
};减少 SQL 查询数
源码中出现先 group by 查询出去重的 f_user_id 后,再来并发查询某一用户的所有记录。
这里应该用 SQL 中的 IN 先查完再匹配处理:
model.findAll({
where: {
...conditions,
f_user_id: rows.map(x =>`${x.f_user_id}`)
}
})流处理
在上面的 xlsx.js 文件中,是先输出一个文件再使用 fs.createReadStream 流输出
exceljs 库提供了 API 来实现流写:
const workbook = new Excel.stream.xlsx.WorkbookWriter(options);
const sheet = workbook.addWorksheet('My Sheet');
// .,,
ctx.body = workbook.stream;更多
当然除了上述提到的优化手段,还有离线生成、缓存等等诸多优化手段可用,这里不再展开。
总结
文件导出是最常见的需求之一,把功能实现好是专业素质最好的体现。
此文篇幅有限,原理性的细节如 Exceljs 的依赖里对 xlsx 规范的 zip 流处理等等大家可以自行去了解一番。