介绍一个新一代的请求库-Undici
前言
在浏览器中,如果想发起一个请求,我们以前会使用到 xhr,不过这种底层 api,往往调用方式比较简陋。为了提高开发效率, jQuery 的 $.ajax 可能是最好的选择,好在后来出现了更加现代化的 fetch api 。
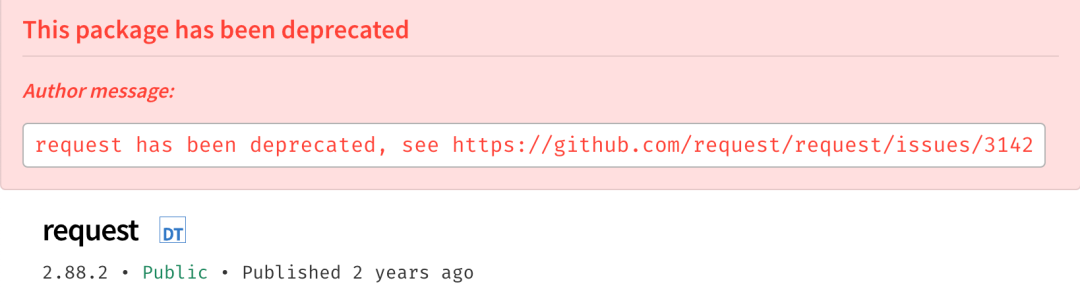
但是考虑到 fetch 的兼容性,而且它也不支持一些全局性的配置,以及请求中断,在实际的使用过程中,我们可能会用到 axios 请求库,来进行一些请求。到了 Node.js 中,几乎都会通过 request 这个库,来进行请求。遗憾的是,request 在两年前就停止维护了,在 Node.js 中需要找到一个能够替代的库还挺不容易的。
| 包名 | 包大小 | API风格 | 简介 |
|---|---|---|---|
| node-fetch[2] | 0.4kb | promise / stream | A light-weight module that brings window.fetch to Node.js |
| got[3] | 48.4kb | promise / stream | Simplified HTTP requests |
| axios[4] | 11.9kb | promise / stream | Promise based HTTP client for the browser and node.js |
| superagent[5] | 18kb | chaining / promise | Small progressive client-side HTTP request library, and Node.js module with the same API, sporting many high-level HTTP client features |
| urllib[6] | 816kb | callback / promise | Help in opening URLs (mostly HTTP) in a complex world — basic and digest authentication, redirections, cookies and more. |
浏览器中使用比较多的 axios,在 Node.js 中并不好用,特别是要进行文件上传的时候,会有很多意想不到的问题。
最近我在网上的时候,发现 Node.js 官方是有一个请求库的:undici,名字取得还挺复杂的。所以,今天的文章就来介绍一下 undici。顺便提一句,undici 是意大利语 11 的意思,好像双十一也快到了,利好茅台。
Undici means eleven in Italian. 1.1 -> 11 -> Eleven -> Undici. It is also a Stranger Things reference.
上手
我们可以直接通过 npm 来安装 undici:
npm install undici -S
undici 对外暴露一个对象,该对象下面提供了几个 API:
undici.fetch:发起一个请求,和浏览器中的fetch方法一致;undici.request:发起一个请求,和request库有点类似,该方法支持 Promise;undici.stream:处理文件流,可以用来进行文件的下载;
undici.fetch
注意:该方法需要 node 版本 >= v16.5.0
undici.fetch 请求服务之前,需要先通过 koa 启动一个简单登录服务。
const Koa = require('koa')
const bodyParser = require('koa-bodyparser')
const app = new Koa()
app.use(bodyParser())
app.use(ctx => {
const { url, method, body } = ctx.request
if (url === '/login') {
if (method === 'POST') {
if (body.account === 'shenfq' && body.password === '123456') {
ctx.body = JSON.stringify({
name: 'shenfq',
mobile: '130xxxxxx'
})
return
}
}
}
ctx.status = 404
ctx.body = JSON.stringify({})
})
app.listen(3100)上面代码很简单,只支持接受一个 POST 方法到 /login 路由。下面使用 undici.fetch 发起一个 POST 请求。
const { fetch } = require('undici')
const bootstrap = async () => {
const api = 'http://localhost:3100/login'
const rsp = await fetch(api, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
account: 'shenfq',
password: '123456'
})
})
if (rsp.status !== 200) {
console.log(rsp.status, '请求失败')
return
}
const json = await rsp.json()
console.log(rsp.status, json)
}
bootstrap()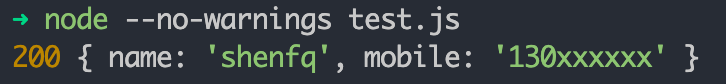
GET,就会返回 404。
const rsp = await fetch(api, {
method: 'GET'
})undici.request
undici.request 的调用方式与 undici.fetch 类似,传参形式也差不多。
const { request } = require('undici')
const bootstrap = async () => {
const api = 'http://localhost:3100/login'
const { body, statusCode } = await request(api, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
account: 'shenfq',
password: '123456'
})
})
const json = await body.json()
console.log(statusCode, json)
}
bootstrap()
request 方法返回的 http 响应结果在 body 属性中,而且该属性也支持同 fetch 类似的 .json()/.text() 等方法。
中断请求
安装 abort-controller 库,然后实例化 abort-controller,将中断信号传入 request 配置中。
npm i abort-controller
const undici = require('undici')
const AbortController = require('abort-controller')
// 实例化 abort-controller
const abortController = new AbortController()
undici.request('http://127.0.0.1:3100', {
method: 'GET',
// 传入中断信号量
signal: abortController.signal,
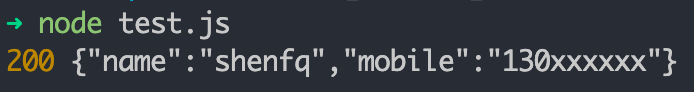
}).then(({ statusCode, body }) => {
body.on('data', (data) => {
console.log(statusCode, data.toString())
})
})
undici.request('http://127.0.0.1:3100', {
method: 'GET',
signal: abortController.signal,
}).then(({ statusCode, body }) => {
console.log('请求成功')
body.on('data', (data) => {
console.log(statusCode, data.toString())
})
}).catch(error => {
// 捕获由于中断触发的错误
console.log('error', error.name)
})
// 调用中断
abortController.abort()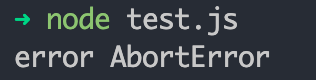
请求成功 的日志,进入了 catch 逻辑,成功的进行了请求的中断。
undici.steam
undici.steam 方法可以用来进行文件下载,或者接口代理。
文件下载
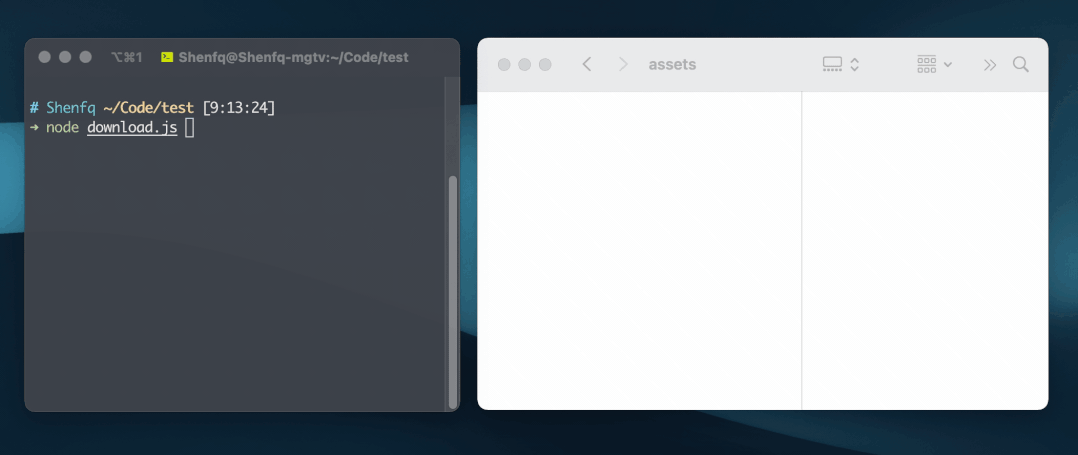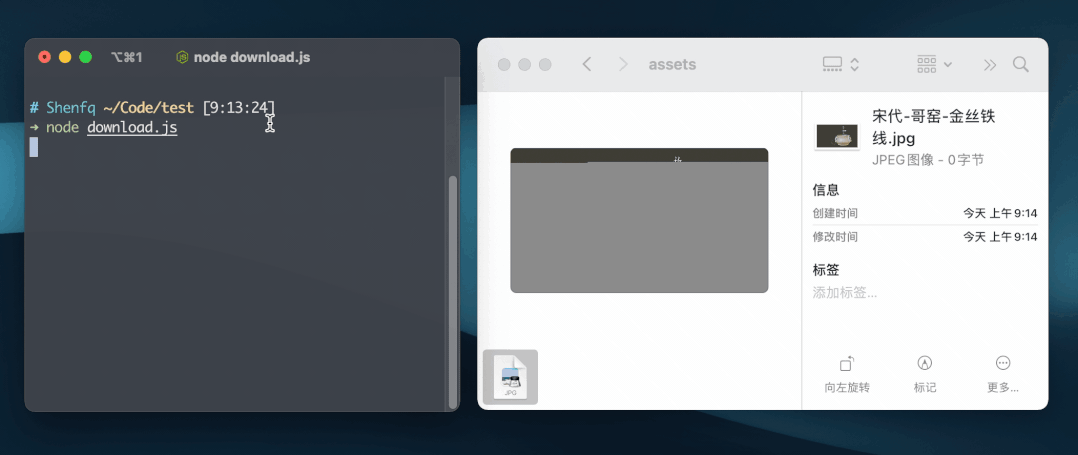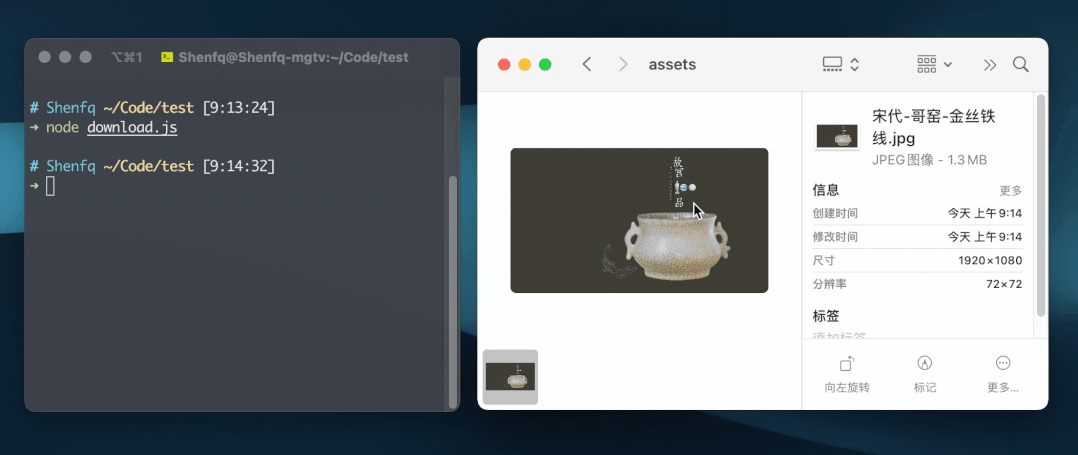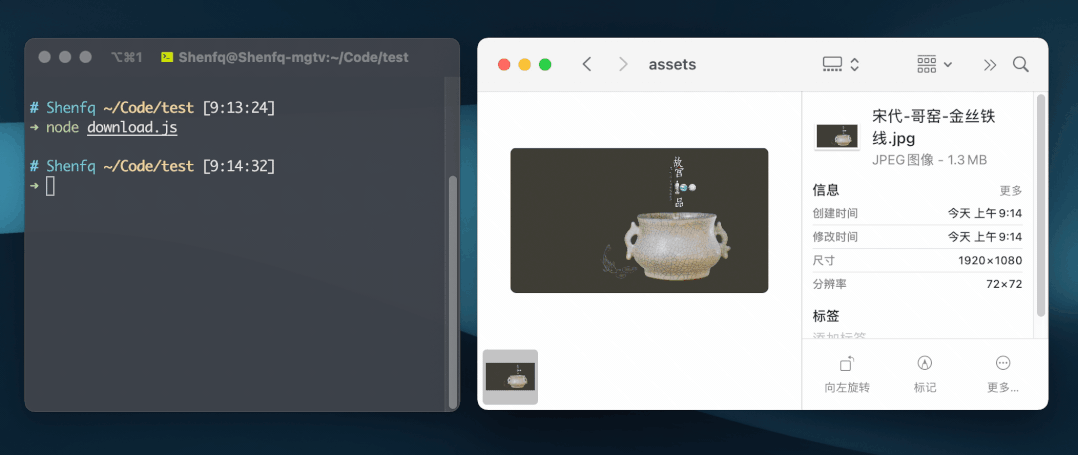
const fs = require('fs')
const { stream } = require('undici')
const out = fs.createWriteStream('./宋代-哥窑-金丝铁线.jpg')
const url = 'https://img.dpm.org.cn/Uploads/Picture/dc/cegift/cegift6389.jpg'
stream(url, { opaque: out }, ({ opaque }) => opaque)接口代理
const http = require('http')
const undici = require('undici')
// 将 3100 端口的请求,代理到 80 端口
const client = new undici.Client('http://localhost')
http.createServer((req, res) => {
const { url, method } = req
client.stream(
{ method, path: url,opaque: res },
({ opaque }) => opaque
)
}).listen(3100)
总结
本文只是介绍了 undici 几个 api 的使用方式,看起来 undici 上手难度还是比较低的。但是兼容性还不太行,比如,fetch 只支持 node@v16.5.0 以上的版本。
对于这种比较新的库,个人还是建议多观望一段时间,虽然 request 已经废弃了,我们还是使用一些经过较长时间考验过的库,比如,egg 框架中使用的 urllib[7],还有一个 node-fetch[8],上手难度也比较低,与浏览器中的 fetch api 使用方式一致。
参考资料
[1]issues: https://github.com/request/request/issues/3143
[2]node-fetch: https://www.npmjs.com/package/node-fetch
[3]got: https://www.npmjs.com/package/got
[4]axios: https://www.npmjs.com/package/axios
[5]superagent: https://www.npmjs.com/package/superagent
[6]urllib: https://www.npmjs.com/package/urllib
[7]urllib: https://www.npmjs.com/package/urllib
[8]node-fetch: https://www.npmjs.com/package/node-fetch
- END -