蚂蚁金服在线笔试:设计和实现一个LRU(最近最少使用)缓存机制
这道中等算法题,一开始没写出来
这是
胖头鱼面试蚂蚁金服时的一道在线笔试题,当时看到题目我就懵逼了,潜意识里感觉它很难,题目又长,内心打起了退堂鼓。结果自然是没有写出来...
做算法题的一些小经验
遇到不会的题时,千万不能慌,一定要稳住心神,从题目中找出更多有效的信息,并尝试多画图,多动笔(如果是现场面试,记得带只笔,多画画有时候思路就出来了)
画图是解题非常有效的方式之一
画图是解题非常有效的方式之一
画图是解题非常有效的方式之一
看看题目
leetCode(https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lru-cache/)
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。实现 LRUCache 类:
- LRUCache(int capacity) 以
正整数作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存 - int get(int key)
如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1。 - void put(int key, int value)
如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
题目要求的1和2相对简单,主要是条件3,当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值。容量和条件1相呼应,关键是怎么理解最久未使用呢?
读和写都在使用数据,最久未使用就是容量达到上线时,最久没读也没写的那个key。还是太生涩了,来画个图试试。
画图理解
假设我是一个卖玩具的商人,我在街上租了一个只能放下三个玩具(没办法太穷了)的摊位,所以大部分的玩具都没摆出来而是放在仓库里。
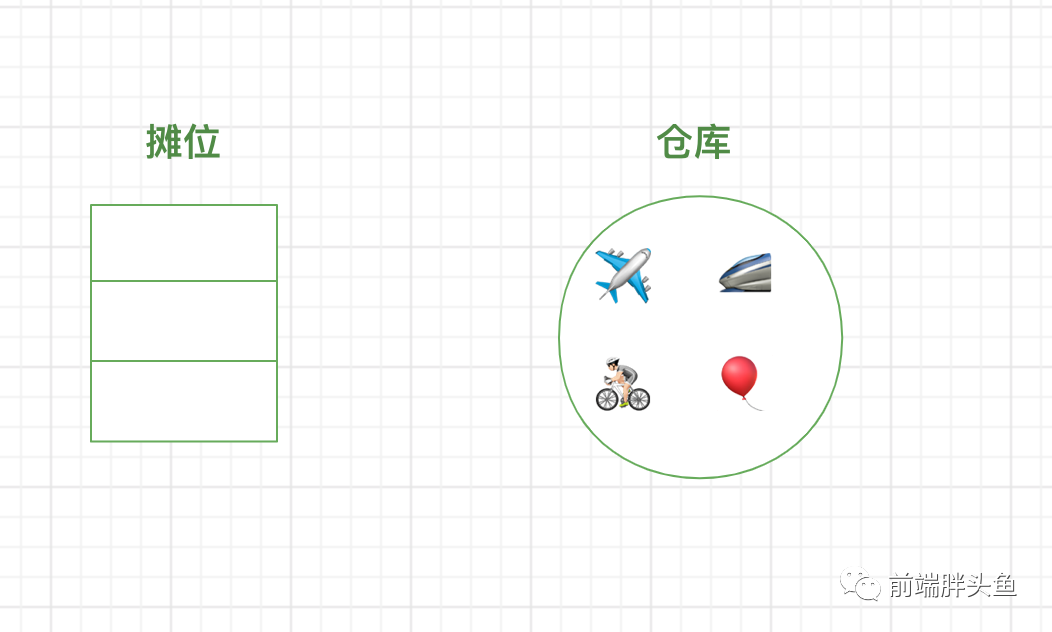
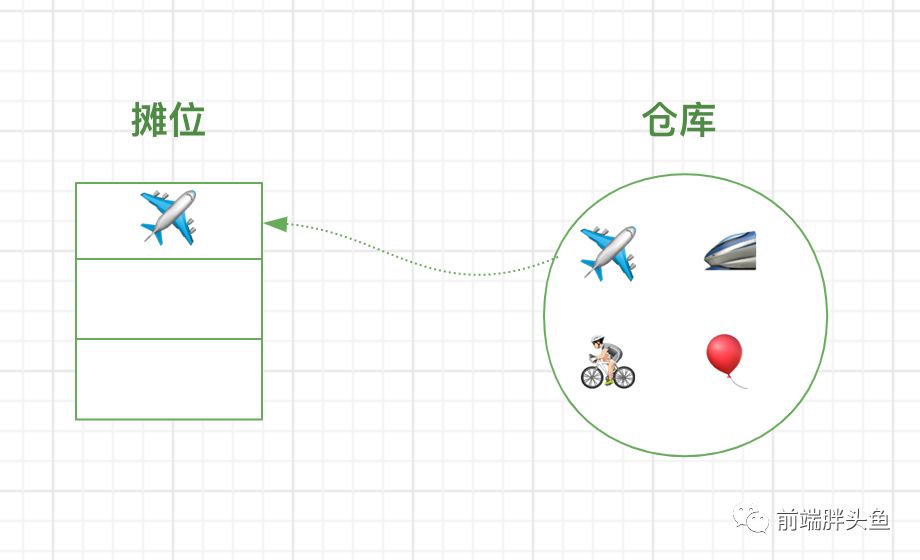
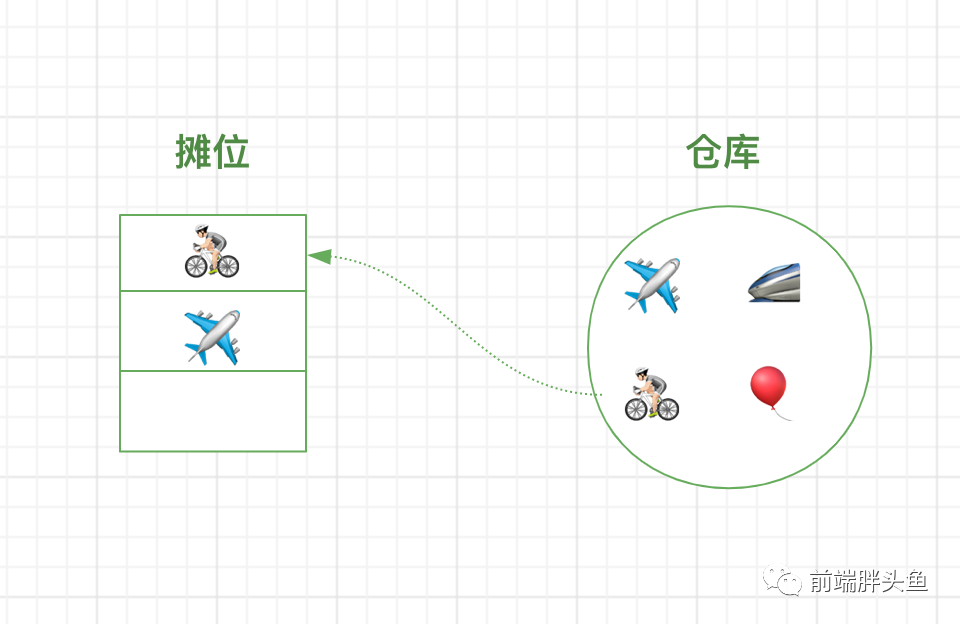
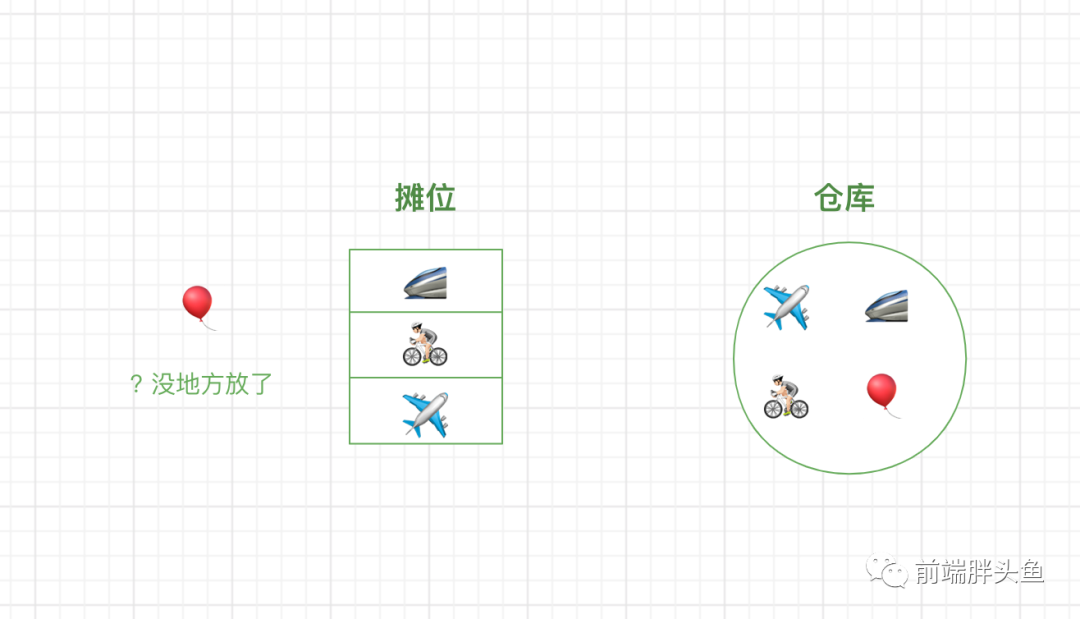
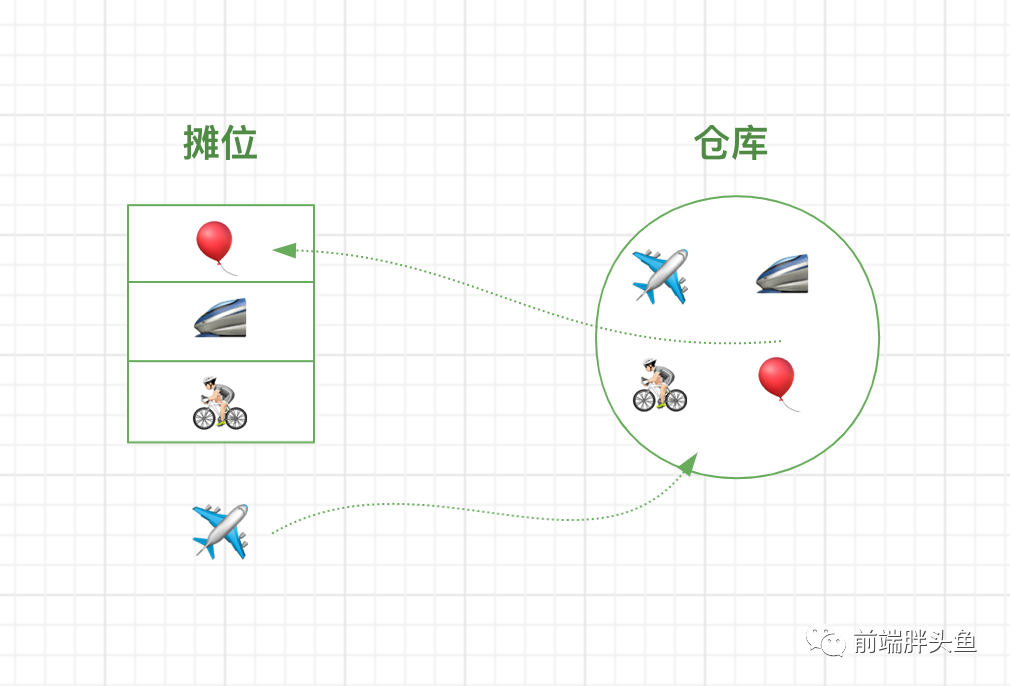
图文映射起来
重新回到题目,咱们看图就很好理解了
- 三个格子就是条件一: LRUCache(int capacity) 以
正整数作为容量capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存 - 不断调整玩具位置,从仓库中取玩具放到摊位和从摊位放回仓库,可以理解为条件二和三
开始撸起来...
数组&&对象实现方式
var LRUCache = function (capacity) {
// 用数组记录读和写的顺序
this.keys = []
// 用对象来保存key value值
this.cache = {}
// 容量
this.capacity = capacity
}
LRUCache.prototype.get = function (key) {
// 如果存在
if (typeof this.cache[key] !== 'undefined') {
// 先删除原来的位置
remove(this.keys, key)
// 再移动到最后一个,以保持最新访问
this.keys.push(key)
// 返回值
return this.cache[key]
}
return -1
}
LRUCache.prototype.put = function (key, value) {
if (typeof this.cache[key] !== 'undefined') {
// 存在的时候先更新值
this.cache[key] = value
// 再更新位置到最后一个
remove(this.keys, key)
this.keys.push(key)
} else {
// 不存在的时候加入
this.keys.push(key)
this.cache[key] = value
// 容量如果超过了最大值,则删除最久未使用的(也就是数组中的第一个key)
if (this.keys.length > this.capacity) {
removeCache(this.cache, this.keys, this.keys[0])
}
}
}
// 移出数组中的key
function remove(arr, key) {
if (arr.length) {
const index = arr.indexOf(key)
if (index > -1) {
return arr.splice(index, 1)
}
}
}
// 移除缓存中 key
function removeCache(cache, keys, key) {
cache[key] = null
remove(keys, key)
}
const lRUCache = new LRUCache(2)
console.log(lRUCache.put(1, 1)) // 缓存是 {1=1}
console.log(lRUCache.put(2, 2)) // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
console.log(lRUCache.get(1)) // 返回 1
console.log(lRUCache.put(3, 3)) // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
console.log(lRUCache.get(2)) // 返回 -1 (未找到)
console.log(lRUCache.put(4, 4)) // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
console.log(lRUCache.get(1) ) // 返回 -1 (未找到)
console.log(lRUCache.get(3)) // 返回 3
console.log(lRUCache.get(4) ) // 返回 4
Map实现方式
第一种实现方式,我们借助了数组来存储每次key被访问(get、set)的顺序,这样实现比较麻烦一些,有没有其他方案,让我们更加便捷一些,不需要额外维护数组呢?借助
Map设置值时可以保持顺序性,处理LRU算法将会及其方便
/**
* @param {number} capacity
*/
var LRUCache = function (capacity) {
this.cache = new Map()
this.capacity = capacity
};
/**
* @param {number} key
* @return {number}
*/
LRUCache.prototype.get = function (key) {
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
const value = this.cache.get(key)
// 更新位置
this.cache.delete(key)
this.cache.set(key, value)
return value
}
return -1
};
/**
* @param {number} key
* @param {number} value
* @return {void}
*/
LRUCache.prototype.put = function (key, value) {
// 已经存在的情况下,更新其位置到”最新“即可
// 先删除,后插入
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
this.cache.delete(key)
} else {
// 插入数据前先判断,size是否符合capacity
// 已经>=capacity,需要把最开始插入的数据删除掉
// keys()方法得到一个可遍历对象,执行next()拿到一个形如{ value: 'xxx', done: false }的对象
if (this.cache.size >= this.capacity) {
this.cache.delete(this.cache.keys().next().value)
}
}
this.cache.set(key, value)
};
const lRUCache = new LRUCache(2)
console.log(lRUCache.put(1, 1)) // 缓存是 {1=1}
console.log(lRUCache.put(2, 2)) // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
console.log(lRUCache.get(1)) // 返回 1
console.log(lRUCache.put(3, 3)) // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
console.log(lRUCache.get(2)) // 返回 -1 (未找到)
console.log(lRUCache.put(4, 4)) // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
console.log(lRUCache.get(1) ) // 返回 -1 (未找到)
console.log(lRUCache.get(3)) // 返回 3
console.log(lRUCache.get(4) ) // 返回 4
最后
也许你我素未谋面,但很可能相见恨晚。希望这里能成为你的栖息之地,我愿和你一起收获喜悦,奔赴成长。
