你最少用几行代码实现深拷贝?
前言
深度克隆(深拷贝)一直都是初、中级前端面试中经常被问到的题目,网上介绍的实现方式也都各有千秋,大体可以概括为三种方式:
JSON.stringify+JSON.parse, 这个很好理解;- 全量判断类型,根据类型做不同的处理
- 2的变型,简化类型判断过程
前两种比较常见也比较基础,所以我们今天主要讨论的是第三种。
阅读全文你将学习到:
- 更简洁的深度克隆方式
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()api- 类型判断的通用方法
问题分析
深拷贝 自然是 相对 浅拷贝 而言的。我们都知道 引用数据类型 变量存储的是数据的引用,就是一个指向内存空间的指针, 所以如果我们像赋值简单数据类型那样的方式赋值的话,其实只能复制一个指针引用,并没有实现真正的数据克隆。
通过这个例子很容易就能理解:
const obj1 = {
name: 'superman'
}
const obj2 = obj1;
obj1.name = '前端切图仔';
console.log(obj2.name); // 前端切图仔
复制代码所以深度克隆就是为了解决引用数据类型不能被通过赋值的方式 复制 的问题。
引用数据类型
我们不妨来罗列一下引用数据类型都有哪些:
- ES6之前:Object, Array, Date, RegExp, Error,
- ES6之后:Map, Set, WeakMap, WeakSet,
所以,我们要深度克隆,就需要对数据进行遍历并根据类型采取相应的克隆方式。当然因为数据会存在多层嵌套的情况,采用递归是不错的选择。
简单粗暴版本
function deepClone(obj) {
let res = {};
// 类型判断的通用方法
function getType(obj) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj).replaceAll(new RegExp(/\[|\]|object /g), "");
}
const type = getType(obj);
const reference = ["Set", "WeakSet", "Map", "WeakMap", "RegExp", "Date", "Error"];
if (type === "Object") {
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
} else if (type === "Array") {
console.log('array obj', obj);
obj.forEach((e, i) => {
res[i] = deepClone(e);
});
}
else if (type === "Date") {
res = new Date(obj);
} else if (type === "RegExp") {
res = new RegExp(obj);
} else if (type === "Map") {
res = new Map(obj);
} else if (type === "Set") {
res = new Set(obj);
} else if (type === "WeakMap") {
res = new WeakMap(obj);
} else if (type === "WeakSet") {
res = new WeakSet(obj);
}else if (type === "Error") {
res = new Error(obj);
}
else {
res = obj;
}
return res;
}
复制代码其实这就是我们最前面提到的第二种方式,很傻对不对,明眼人一眼就能看出来有很多冗余代码可以合并。
我们先进行最基本的优化:
合并冗余代码
将一眼就能看出来冗余的代码合并下。
function deepClone(obj) {
let res = null;
// 类型判断的通用方法
function getType(obj) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj).replaceAll(new RegExp(/\[|\]|object /g), "");
}
const type = getType(obj);
const reference = ["Set", "WeakSet", "Map", "WeakMap", "RegExp", "Date", "Error"];
if (type === "Object") {
res = {};
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
} else if (type === "Array") {
console.log('array obj', obj);
res = [];
obj.forEach((e, i) => {
res[i] = deepClone(e);
});
}
// 优化此部分冗余判断
// else if (type === "Date") {
// res = new Date(obj);
// } else if (type === "RegExp") {
// res = new RegExp(obj);
// } else if (type === "Map") {
// res = new Map(obj);
// } else if (type === "Set") {
// res = new Set(obj);
// } else if (type === "WeakMap") {
// res = new WeakMap(obj);
// } else if (type === "WeakSet") {
// res = new WeakSet(obj);
// }else if (type === "Error") {
// res = new Error(obj);
//}
else if (reference.includes(type)) {
res = new obj.constructor(obj);
} else {
res = obj;
}
return res;
}
复制代码为了验证代码的正确性,我们用下面这个数据验证下:
const map = new Map();
map.set("key", "value");
map.set("ConardLi", "coder");
const set = new Set();
set.add("ConardLi");
set.add("coder");
const target = {
field1: 1,
field2: undefined,
field3: {
child: "child",
},
field4: [2, 4, 8],
empty: null,
map,
set,
bool: new Boolean(true),
num: new Number(2),
str: new String(2),
symbol: Object(Symbol(1)),
date: new Date(),
reg: /\d+/,
error: new Error(),
func1: () => {
let t = 0;
console.log("coder", t++);
},
func2: function (a, b) {
return a + b;
},
};
//测试代码
const test1 = deepClone(target);
target.field4.push(9);
console.log('test1: ', test1);
复制代码执行结果:
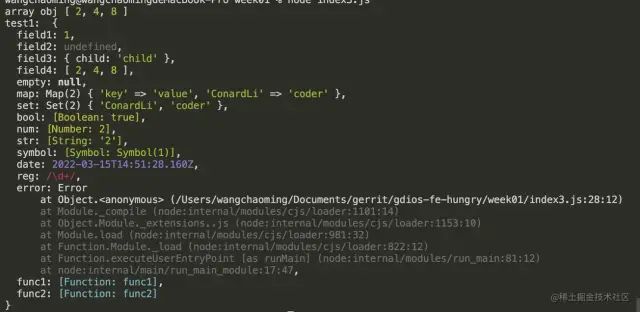
还有进一步优化的空间吗?
答案当然是肯定的。
// 判断类型的方法移到外部,避免递归过程中多次执行
const judgeType = origin => {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(origin).replaceAll(new RegExp(/\[|\]|object /g), "");
};
const reference = ["Set", "WeakSet", "Map", "WeakMap", "RegExp", "Date", "Error"];
function deepClone(obj) {
// 定义新的对象,最后返回
//通过 obj 的原型创建对象
const cloneObj = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj), Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj));
// 遍历对象,克隆属性
for (let key of Reflect.ownKeys(obj)) {
const val = obj[key];
const type = judgeType(val);
if (reference.includes(type)) {
newObj[key] = new val.constructor(val);
} else if (typeof val === "object" && val !== null) {
// 递归克隆
newObj[key] = deepClone(val);
} else {
// 基本数据类型和function
newObj[key] = val;
}
}
return newObj;
}
复制代码执行结果如下:
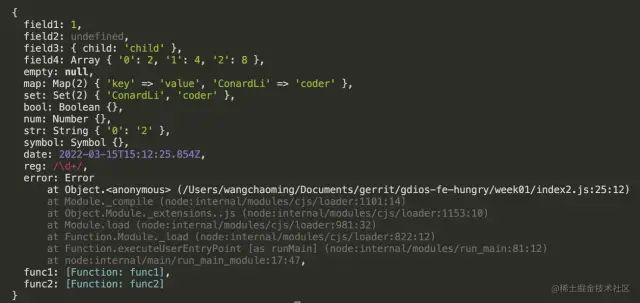
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()方法用来获取一个对象的所有自身属性的描述符。- 返回所指定对象的所有自身属性的描述符,如果没有任何自身属性,则返回空对象。
具体解释和内容见MDN[1]
这样做的好处就是能够提前定义好最后返回的数据类型。
这个实现参考了网上一位大佬的实现方式,个人觉得理解成本有点高,而且对数组类型的处理也不是特别优雅, 返回类数组。
我在我上面代码的基础上进行了改造,改造后的代码如下:
function deepClone(obj) {
let res = null;
const reference = [Date, RegExp, Set, WeakSet, Map, WeakMap, Error];
if (reference.includes(obj?.constructor)) {
res = new obj.constructor(obj);
} else if (Array.isArray(obj)) {
res = [];
obj.forEach((e, i) => {
res[i] = deepClone(e);
});
} else if (typeof obj === "object" && obj !== null) {
res = {};
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
} else {
res = obj;
}
return res;
}
复制代码虽然代码量上没有什么优势,但是整体的理解成本和你清晰度上我觉得会更好一点。那么你觉得呢?
最后,还有循环引用问题,避免出现无线循环的问题。
我们用hash来存储已经加载过的对象,如果已经存在的对象,就直接返回。
function deepClone(obj, hash = new WeakMap()) {
if (hash.has(obj)) {
return obj;
}
let res = null;
const reference = [Date, RegExp, Set, WeakSet, Map, WeakMap, Error];
if (reference.includes(obj?.constructor)) {
res = new obj.constructor(obj);
} else if (Array.isArray(obj)) {
res = [];
obj.forEach((e, i) => {
res[i] = deepClone(e);
});
} else if (typeof obj === "object" && obj !== null) {
res = {};
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
hash.set(obj, res);
} else {
res = obj;
}
return res;
}
复制代码
总结
对于深拷贝的实现,可能存在很多不同的实现方式,关键在于理解其原理,并能够记住一种最容易理解和实现的方式,面对类似的问题才能做到 临危不乱,泰然自若。上面的实现你觉得哪个更好呢?欢迎大佬们在评论区交流~