简洁易懂的Java8 Collectors.toMap方法使用
先来看一下函数的签名:
public static <T, K, U>
Collector<T, ?, Map<K,U>> toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T, ? extends U> valueMapper,
BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction)这个函数的作用一句话以概之,如果要将List<E>中的元素E转换成Map<K,V>,那么toMap方法的三个参数分别就是自定义K,V的映射函数,以及当K有重复时多个V怎么来处理。
看一下官网的API使用说明:
For example, if you have a stream of Person, and you want to produce a "phone book" mapping name to address, but it is possible that two persons have the same name, you can do as follows to gracefully deals with these collisions, and produce a Map mapping names to a concatenated list of addresses
接下来看代码实现,先定义Person类:
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@Builder
public class Person {
private String name;
private String address;
}测试类:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(Person.builder().name("Luke").address("Road1").build());
list.add(Person.builder().name("Tyler").address("road2").build());
list.add(Person.builder().name("Luke").address("Road3").build());
Map<String, String> phoneBook = list.stream().collect(
Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, Person::getAddress, (s, a) -> s + ", " + a));
System.out.println(phoneBook);
}
}输出:
{Luke=Road1, Road3, Tyler=road2}
toMap方法详解
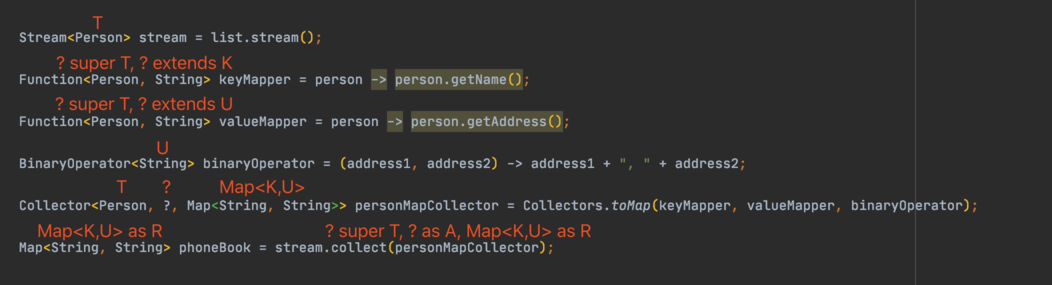
如上面的例子见到的,一般是Stream<T>.collect(Collectors.toMap(...))这样来调用。而collect方法的签名是:
<R,A> R collect(Collector<? super T,A,R> collector)
再来回顾一下toMap方法的签名:
public static <T, K, U>
Collector<T, ?, Map<K,U>> toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T, ? extends U> valueMapper,
BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction)那么上面测试类的代码可以富写成:
这样对应起来就不用被各种泛型参数看的绕晕了。
注:方法引用
Person::getName只是lambda表达式person -> person.getName()的另一种写法。