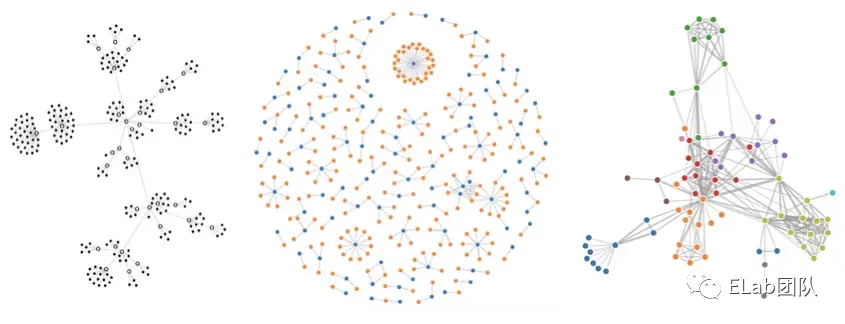
深入理解 D3.js 可视化库之力导向图原理与实现
简介
D3.js[1] 是一个基于 web 标准的 JS 可视化库,它借助 SVG、Canvas 和 HTML 进行数据可视化。在数据可视化中,我们很多时候会使用图来表达数据中所蕴含的信息,图方便让我们清晰的理清各个节点之间的联系,快速提取有用信息。而图布局算法可以使散乱的信息 (信息多以点线的关系承载) 通过一种清晰的方式呈现出来,符合相应的美学标准。
不同的图布局[2]也有不同的应用场景,例如树形布局 / Dagre布局,它是一个有向无环图,具有的拓扑性质,可以用作流程表达的场景。
思路
整体可以拆解为 2 个实体和 1 个作用因子:节点、线、力。d3-force的实现与传统的 FR 算法思路一样,可以分成三个部分组成,先计算节点间的互斥力,再计算连接点的吸引力,得出最终的作用力,得到每个节点的速度。使用模拟退火的衰减方案,达到稳定。
https://jsfiddle.net/smallstars/h8y6e031/51/
d3-force原理
节点处理
初始化导入节点
将节点导入 d3 中,需要对节点进行预处理,按照一定的半径和角度进行环绕。
// d3-force/simulation.js
var initialRadius = 10,
initialAngle = Math.PI * (3 - Math.sqrt(5));
function initializeNodes() {
for (var i = 0, n = nodes.length, node; i < n; ++i) {
node = nodes[i], node.index = i;
if (node.fx != null) node.x = node.fx;
if (node.fy != null) node.y = node.fy;
// 初始位置
if (isNaN(node.x) || isNaN(node.y)) {
var radius = initialRadius * Math.sqrt(0.5 + i), angle = i * initialAngle;
node.x = radius * Math.cos(angle);
node.y = radius * Math.sin(angle);
}
// vx, vy为 x, y 的速度
if (isNaN(node.vx) || isNaN(node.vy)) {
node.vx = node.vy = 0;
}
}
}建立节点四叉树
四叉树(quad-tree)
这里采取四叉树的结构原因是方便做碰撞检测, 四叉树是从根节点开始,每一个节点下面最多有四个子树的数据结构。通常我们把一部分二维空间细分为四象限,每一个节点存储相应的象限信息。
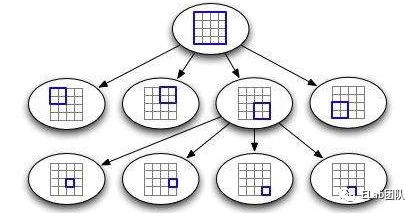
- 四叉树为空,节点添加为根节点。
- 当前查询节点为索引节点且添加处范围矩阵为空,直接添加。
- 当前查询节点为真实节点且添加节点坐标相等且无数组索引,建立数组索引,再次划分该矩阵,直到查询节点与添加节点处于不同矩阵。
- 当前查询节点为真实节点且添加节点坐标相等且有数组索引,直接下挂。
// d3-force/collide.js
for (var k = 0; k < iterations; ++k) {
// 调用 d3-quadtree 进行add
tree = quadtree(nodes, x, y).visitAfter(prepare);
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
node = nodes[i];
ri = radii[node.index], ri2 = ri * ri;
xi = node.x + node.vx;
yi = node.y + node.vy;
tree.visit(apply);
}
}
// d3-quadtree/add.js
function add(tree, x, y, d) {
if (isNaN(x) || isNaN(y)) return tree; // ignore invalid points
var parent,
node = tree._root,
leaf = {data: d},
// 象限坐标
x0 = tree._x0,
y0 = tree._y0,
x1 = tree._x1,
y1 = tree._y1,
xm,
ym,
xp,
yp,
right,
bottom,
i,
j;
// case1: If the tree is empty, initialize the root as a leaf.
if (!node) return tree._root = leaf, tree;
// 类似二分,自上向下搜索
// Find the existing leaf for the new point, or add it.
while (node.length) {
if (right = x >= (xm = (x0 + x1) / 2)) x0 = xm; else x1 = xm;
if (bottom = y >= (ym = (y0 + y1) / 2)) y0 = ym; else y1 = ym;
// case2: 判断当前添加节点所在象限是否为空
if (parent = node, !(node = node[i = bottom << 1 | right])) return parent[i] = leaf, tree;
}
// case4: 添加节点是否与父节点重合
// Is the new point is exactly coincident with the existing point?
xp = +tree._x.call(null, node.data);
yp = +tree._y.call(null, node.data);
if (x === xp && y === yp) return leaf.next = node, parent ? parent[i] = leaf : tree._root = leaf, tree;
// case3: 不停分割,直到处于不同象限
// Otherwise, split the leaf node until the old and new point are separated.
do {
parent = parent ? parent[i] = new Array(4) : tree._root = new Array(4);
if (right = x >= (xm = (x0 + x1) / 2)) x0 = xm; else x1 = xm;
if (bottom = y >= (ym = (y0 + y1) / 2)) y0 = ym; else y1 = ym;
} while ((i = bottom << 1 | right) === (j = (yp >= ym) << 1 | (xp >= xm)));
return parent[j] = node, parent[i] = leaf, tree;
}斥力的优化求解
节点间的斥力优化关键为电荷斥力[4]求解优化,最基本的一个节点所受的力,需要与其他所有节点进行计算求和,复杂度为 。
整合受力
而四叉树结构与 Barnes-Hut[5] 近似,复杂度可降为 。当前节点所受周围点的斥力进行整合处理,大小由 Barnes-Hut 近似精度 (默认值为 ) 决定,最后根据 Velocity Verlet[6] 对速度进行求解。
象限面积 ,节点(node)与象限点(quad)形成的面积
// d3-force/manyBody.js
var distanceMin2 = 1,
distanceMax2 = Infinity,
theta2 = 0.81;
function apply(quad, x1, _, x2) {
if (!quad.value) return true;
var x = quad.x - node.x,
y = quad.y - node.y,
w = x2 - x1,
l = x * x + y * y;
// Barnes-Hut成立
// 如何点非常近,冲突的时候随机方向
if (w * w / theta2 < l) {
if (l < distanceMax2) {
if (x === 0) x = jiggle(random), l += x * x;
if (y === 0) y = jiggle(random), l += y * y;
if (l < distanceMin2) l = Math.sqrt(distanceMin2 * l);
node.vx += x * quad.value * alpha / l;
node.vy += y * quad.value * alpha / l;
}
return true;
}
// Barnes-Hut不成立且 quad 有节点
else if (quad.length || l >= distanceMax2) return;
// 排除自身对自身影响,还可以继续向下遍历
if (quad.data !== node || quad.next) {
if (x === 0) x = jiggle(random), l += x * x;
if (y === 0) y = jiggle(random), l += y * y;
if (l < distanceMin2) l = Math.sqrt(distanceMin2 * l);
}
do if (quad.data !== node) {
w = strengths[quad.data.index] * alpha / l;
node.vx += x * w;
node.vy += y * w;
} while (quad = quad.next);
}节点连线的处理
先初始化连线,计算节点的度和每一条边对起始节点度(source/target degree)的占比,使 ,alpha为阻尼系数,默认边长度(distance)为30,默认弹簧劲度(strength)为 ,减少度大节点的引力,提高稳定性。计算连线两边的引力,最终推导出速度的变化。
同理可得出
// d3-force/link.js
function force(alpha) {
for (var k = 0, n = links.length; k < iterations; ++k) {
for (var i = 0, link, source, target, x, y, l, b; i < n; ++i) {
link = links[i], source = link.source, target = link.target;
x = target.x + target.vx - source.x - source.vx || jiggle(random);
y = target.y + target.vy - source.y - source.vy || jiggle(random);
l = Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
l = (l - distances[i]) / l * alpha * strengths[i];
x *= l, y *= l;
target.vx -= x * (b = bias[i]);
target.vy -= y * b;
source.vx += x * (b = 1 - b);
source.vy += y * b;
}
}
}布局的形成
通过不断的迭代运算,每次运算都可以看做一步,通过模拟退火的衰减方案最后达到稳定状态。
// d3-force/simulation.js
var simulation,
alpha = 1,
alphaMin = 0.001,
// alpha衰减率
alphaDecay = 1 - Math.pow(alphaMin, 1 / 300),
alphaTarget = 0,
// 速度衰减
velocityDecay = 0.6,
stepper = timer(step),
// tick事件与end事件
event = dispatch("tick", "end");
function step() {
tick();
event.call("tick", simulation);
if (alpha < alphaMin) {
stepper.stop();
event.call("end", simulation);
}
}
function tick() {
// alpha不断衰减
alpha += (alphaTarget - alpha) * alphaDecay;
// 不停迭代
forces.each(function(force) {
force(alpha);
});
// 速度转化为距离改变
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
node = nodes[i];
if (node.fx == null) node.x += node.vx *= velocityDecay;
// 具有fx,说明当前节点被控制,不需要受到力的影响,速度置为0
else node.x = node.fx, node.vx = 0;
if (node.fy == null) node.y += node.vy *= velocityDecay;
else node.y = node.fy, node.vy = 0;
}
}实战示例
Demo:
React-d3js[7]
代码:
https://github.com/SmaIIstars/react-demo/blob/master/src/pages/d3-force/index.tsx
遇见的问题
1 . Svg 中绘制复杂内容
可以使用 foreignObject 节点进行绘制,在 foreignObject 中可以编写 XML 命名空间的元素。
2 . 节点迭代次数过多,导致页面卡顿
通常初次生成图布局的时候,需要一个过渡动画,在模拟退火的过程中,节点、线会不断的移动。监听数据的变化,使用 React.memo 和 useCallback 减少不必要的运算。
3 . 节点间重叠,相互遮盖
增大排斥力,增常线段长度,增加碰撞体积。但是在有限的空间内,仍然无法完全避免重叠的问题。
4 . 节点过多,超出画布
使用设备的宽高作为画布,对内容进行缩放和拖拽,让用户可以查看到所有内容。
参考
- GitHub - d3/d3-force: Force-directed graph layout using velocity Verlet integration.[8]
- D3.js(Data-Driver Documents)力导向图理论知识[9]
参考资料
[1]D3.js: https://github.com/d3/d3
[2]图布局: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000039054038
[3]力导向图: https://observablehq.com/@sandravizmad/force-directed-layout
[4]电荷斥力: https://bytedance.feishu.cn/docs/doccnyBnKUxyMSdw74Tws6lavfd#8M5j10
[5]Barnes-Hut: https://bytedance.feishu.cn/docs/doccnyBnKUxyMSdw74Tws6lavfd#yeVWli
[6]Velocity Verlet: https://bytedance.feishu.cn/docs/doccnyBnKUxyMSdw74Tws6lavfd#lfo9UK
[7]React-d3js: http://demo.smallstars.top/demo/d3-force
[8]GitHub - d3/d3-force: Force-directed graph layout using velocity Verlet integration.: https://github.com/d3/d3-force
[9]D3.js(Data-Driver Documents)力导向图理论知识: https://bytedance.feishu.cn/docs/doccnyBnKUxyMSdw74Tws6lavfd#WmTLGZ