手把手教你实现一个常用的 antd form 组件
Antd Form相信大家并不陌生,在中后台业务中,表单页面经常用到,但是大家知道它是如何设计和实现的吗?本文并不涉及具体源码分析,而是手把手带你实现一个简易版的Antd Form。
1、Form组件解决的问题
我们从官网摘下来一段Form代码,可以很清晰的看出一个简单的表单,主要是为了统一收集和校验组件的值。
<Form
onFinish={(values) => {
console.log('values', values)
}}
>
<Form.Item
label="Username"
name="username"
rules={[{ required: true, message: 'Please input your username!' }]}
>
<Input />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item
label="Password"
name="password"
rules={[{ required: true, message: 'Please input your password!' }]}
>
<Input.Password />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item>
<Button type="primary" htmlType="submit">
Submit
</Button>
</Form.Item>
</Form>那么它是如何做到统一收集和校验呢?原理很简单,只需要通过监听表单组件的onChange事件,获取表单项的 value,根据定义的校验规则对 value 进行检验,生成检验状态和检验信息,再通过setState驱动视图更新,展示组件的值以及校验信息即可。
2、Antd Form 是怎么实现的
要实现上面的方案需要解决这几个问题:
- 如何实时收集组件的数据?
- 如何对组件的数据进行校验?
- 如何更新组件的数据?
- 如何跨层级传递传递
- 表单提交
接下来我们就带着这几个问题,一起来一步步实现
3、目录结构
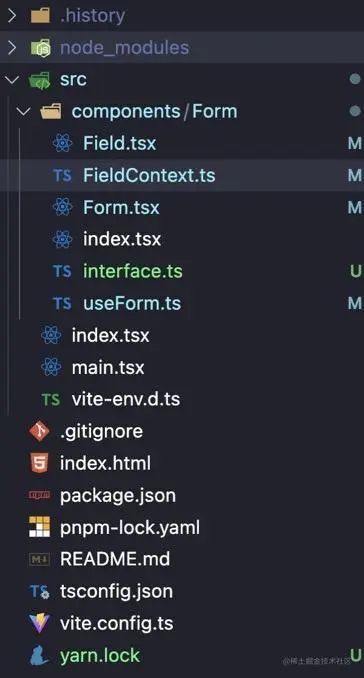
- src/index.tsx用于放测试代码
- src/components/Form文件夹用于存放Form组件信息
- interface.ts用于存放数据类型
- useForm存放数据仓库内容
- index.tsx导出Form组件相关
- FiledContext存放Form全局context
- Form外层组件
- Filed内层组件
4、数据类型定义
本项目采用ts来搭建,所以我们先定义数据类型;
// src/components/Form/interface.ts
export type StoreValue = any;
export type Store = Record<string, StoreValue>;
export type NamePath = string | number;
export interface Callbacks<Values = any> {
onFinish?: (values: Values) => void;
}
export interface FormInstance<Values = any> {
getFieldValue: (name: NamePath) => StoreValue;
submit: () => void;
getFieldsValue: () => Values;
setFieldsValue: (newStore: Store) => void;
setCallbacks: (callbacks: Callbacks) => void;
}5、数据仓库
因为我们的表单一定是各种各样不同的数据项,比如input、checkbox、radio等等,如果这些组件每一个都要自己管理自己的值,那组件的数据管理太杂乱了,我们做这个也就没什么必要性了。那要如何统一管理呢?其实就是我们自己定义一个数据仓库,在最顶层将定义的仓库操作和数据提供给下层。这样我们就可以在每层都可以操作数据仓库了。数据仓库的定义,说白了就是一些读和取的操作,将所有的操作都定义在一个文件,代码如下:
// src/components/Form/useForm.ts
import { useRef } from "react";
import type { Store, NamePath, Callbacks, FormInstance } from "./interface";
class FormStore {
private store: Store = {};
private callbacks: Callbacks = {};
getFieldsValue = () => {
return { ...this.store };
};
getFieldValue = (name: NamePath) => {
return this.store[name];
};
setFieldsValue = (newStore: Store) => {
this.store = {
...this.store,
...newStore,
};
};
setCallbacks = (callbacks: Callbacks) => {
this.callbacks = { ...this.callbacks, ...callbacks };
};
submit = () => {
const { onFinish } = this.callbacks;
if (onFinish) {
onFinish(this.getFieldsValue());
}
};
getForm = (): FormInstance => {
return {
getFieldsValue: this.getFieldsValue,
getFieldValue: this.getFieldValue,
setFieldsValue: this.setFieldsValue,
submit: this.submit,
setCallbacks: this.setCallbacks,
};
};
}当然,数据仓库不能就这么放着,我们需要把里面的内容暴露出去。这里用ref来保存,来确保组件初次渲染和更新阶段用的都是同一个数据仓库实例;
// src/components/Form/useForm.ts
export default function useForm<Values = any>(
form?: FormInstance<Values>
): [FormInstance<Values>] {
const formRef = useRef<FormInstance>();
if (!formRef.current) {
if (form) {
formRef.current = form;
} else {
const formStore = new FormStore();
formRef!.current = formStore.getForm();
}
}
return [formRef.current];
}6、实时收集组件的数据
我们先来定义一下表单的结构,如下代码所示:
// src/index.tsx
import React from "react";
import Form, { Field } from "./components/Form";
const index: React.FC = () => {
return (
<Form
onFinish={(values) => {
console.log("values", values);
}}
>
<Field name={"userName"}>
<input placeholder="用户名" />
</Field>
<Field name={"password"}>
<input placeholder="密码" />
</Field>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</Form>
);
};
export default index;定义了数据仓库,就要想办法在每一层都要拥有消费它的能力,所以这里在最顶层用context来跨层级数据传递。通过顶层的form将数据仓库向下传递,代码如下:
// src/components/Form/Form.tsx
import React from "react";
import FieldContext from "./FieldContext";
import useForm from "./useForm";
import type { Callbacks, FormInstance } from "./interface";
interface FormProps<Values = any> {
form?: FormInstance<Values>;
onFinish?: Callbacks<Values>["onFinish"];
}
const Form: React.FC<FormProps> = (props) => {
const { children, onFinish, form } = props;
const [formInstance] = useForm(form);
formInstance.setCallbacks({ onFinish });
return (
<form
onSubmit={(e) => {
e.preventDefault();
formInstance.submit();
}}
>
<FieldContext.Provider value={formInstance}>
{children}
</FieldContext.Provider>
</form>
);
};
export default Form;子组件来做存与取的操作。这里有个疑问,为什么不直接在input、radio这些组件上直接加入存取操作,非得在外面包一层Field(在正式的antd中是Form.Item)呢?这是因为需要在它基础的能力上扩展一些能力。
// src/components/Form/Field.tsx
import React, { ChangeEvent } from "react";
import FieldContext from "./FieldContext";
import type { NamePath } from "./interface";
const Field: React.FC<{ name: NamePath }> = (props) => {
const { getFieldValue, setFieldsValue } = React.useContext(FieldContext);
const { children, name } = props;
const getControlled = () => {
return {
value: getFieldValue && getFieldValue(name),
onChange: (e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
const newValue = e?.target?.value;
setFieldsValue?.({ [name]: newValue });
},
};
};
return React.cloneElement(children as React.ReactElement, getControlled());
};
export default Field;这样我们就完成了数据收集以及保存的功能了。
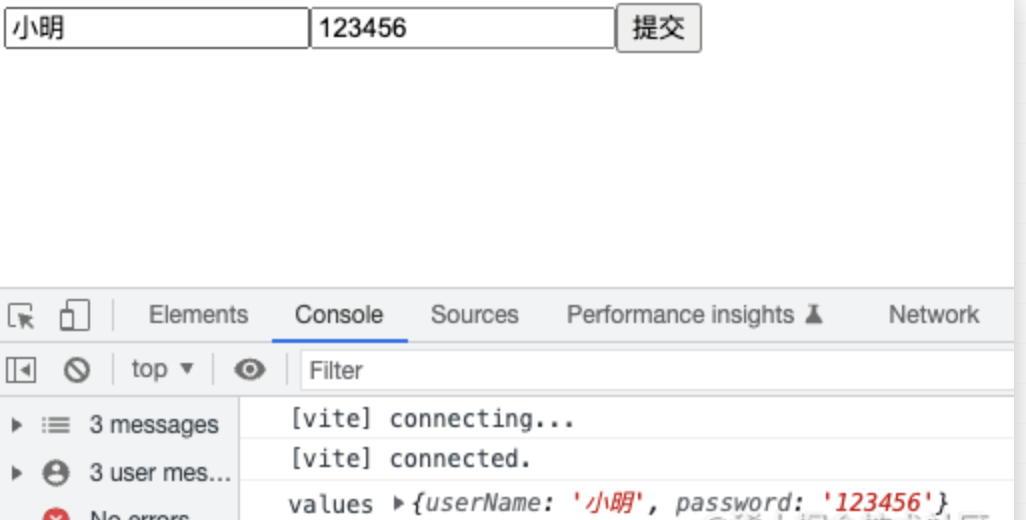
很简单吧,我们来试一下onFinish操作!
接下来我们继续完善其他的功能。
7、完善组件渲染
我们来修改一下Form的代码,加入一条设置默认值:
// src/index.tsx
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import Form, { Field, useForm } from "./components/Form";
const index: React.FC = () => {
const [form] = useForm();
// 新加入代码
useEffect(() => {
form.setFieldsValue({ username: "default" });
}, []);
return (
// ...省略...
);
};
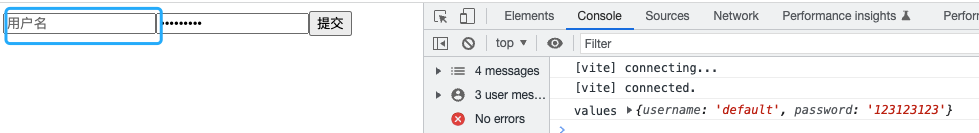
export default index;来看一眼页面,发现我们设置的默认值并没有展示在表单中,但是我们提交的时候还是可以打印出数据的,证明我们的数据是已经存入到store中了,只是没有渲染到组件中,接下来我们需要做的工作就是根据store变化完成组件表单的响应功能。
我们在useForm中加入订阅和取消订阅功能代码;
// 订阅与取消订阅
registerFieldEntities = (entity: FieldEntity) => {
this.fieldEntities.push(entity);
return () => {
this.fieldEntities = this.fieldEntities.filter((item) => item !== entity);
const { name } = entity.props;
name && delete this.store[name];
};
};forceUpdate的作用是进行子组件更新;
// src/components/Form/Field.tsx
// ...省略...
const [, forceUpdate] = React.useReducer((x) => x + 1, 0);
useLayoutEffect(() => {
const unregister =
registerFieldEntities &&
registerFieldEntities({
props,
onStoreChange: forceUpdate,
});
return unregister;
}, []);
// ...省略...当然光是注册是不够的,我们需要在设置值的时候完成响应;
// src/components/Form/useForm.tsx
setFieldsValue = (newStore: Store) => {
this.store = {
...this.store,
...newStore,
};
// 新加入代码
// update Filed
this.fieldEntities.forEach((entity) => {
Object.keys(newStore).forEach((k) => {
if (k === entity.props.name) {
entity.onStoreChange();
}
});
});
};我们来看一下效果,发现组件已经将值更新啦;
8、加入校验功能
到现在为止,我们发现提交表单还没有校验功能。表单校验通过,则执行onFinish。表单校验的依据就是Field的rules,表单校验通过,则执行onFinish,失败则执行onFinishFailed。接下来我们来实现一个简单的校验。
修改代码结构
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import Form, { Field, useForm } from "./components/Form";
const nameRules = { required: true, message: "请输入姓名!" };
const passworRules = { required: true, message: "请输入密码!" };
const index: React.FC = () => {
const [form] = useForm();
useEffect(() => {
form.setFieldsValue({ username: "default" });
}, []);
return (
<Form
onFinish={(values) => {
console.log("values", values);
}}
onFinishFailed={(err) => {
console.log("err", err);
}}
form={form}
>
<Field name={"username"} rules={[nameRules]}>
<input placeholder="用户名" />
</Field>
<Field name={"password"} rules={[passworRules]}>
<input placeholder="密码" type="password" />
</Field>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</Form>
);
};
export default index;添加validateField方法进行表单校验。注意:此版本校验只添加了required校验,后续小伙伴们可以根据自己的需求继续完善哦!
// src/components/Form/useForm.tsx
// ...省略...
validateField = () => {
const err: any[] = [];
this.fieldEntities.forEach((entity) => {
const { name, rules } = entity.props;
const value: NamePath = name && this.getFieldValue(name);
let rule = rules?.length && rules[0];
if (rule && rule.required && (value === undefined || value === "")) {
name && err.push({ [name]: rule && rule.message, value });
}
});
return err;
};我们只需要在form提交的时候判断一下就可以啦;
submit = () => {
const { onFinish, onFinishFailed } = this.callbacks;
// 调用校验方法
const err = this.validateField();
if (err.length === 0) {
onFinish && onFinish(this.getFieldsValue());
} else {
onFinishFailed && onFinishFailed(err);
}
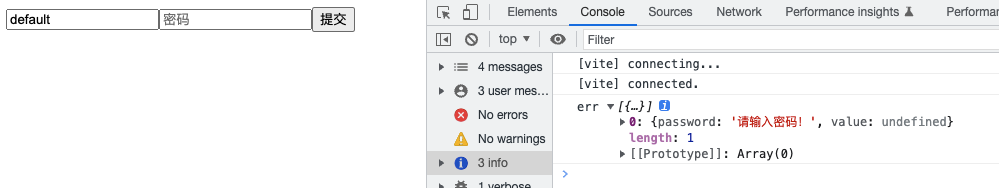
};密码为空时的实现效果;
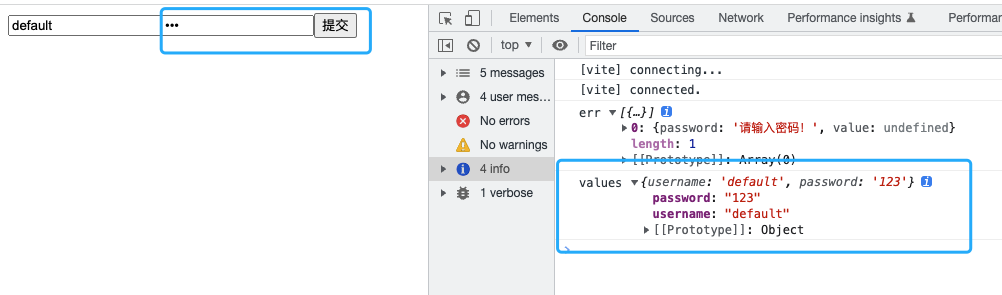
账号密码都不为空时的实现效果;
做到这里,我们已经基本实现了一个Antd Form表单了,但是细节功能还需要慢慢去完善,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以接着继续向下做!
9、总结
其实我们在看Antd Form源码的时候会发现它是基于rc-field-form来写的。所以想继续向下写的小伙伴可以下载rc-field-form源码,边学习边写,这样就可以事半功倍了,攻克源码!