告别BeanUtils,Mapstruct从入门到精通
如果你现在还在使用BeanUtils,看了本文,也会像我一样,从此改用Mapstruct。
对象之间的属性拷贝,之前用的是Spring的BeanUtils,有一次,在学习领域驱动设计的时候,看了一位大佬的文章,他在文章中提到使用Mapstruct做DO和Entity的相互转换,出于好奇,后来就去了解了一下Mapstruct,发现这个工具确实优秀,所以果断弃用BeanUtils。
如果你现在还在使用BeanUtils,看了本文,也会像我一样,从此改用Mapstruct。
先上结论,Mapstruct的性能远远高于BeanUtils,这应该是大佬使用Mapstruct的主要原因,下面是我的测试结果,可以看出随着属性个数的增加,BeanUtils的耗时也在增加,并且BeanUtils的耗时跟属性个数成正比,而Mapstruct的耗时却一直是1秒,所以从对比数据可以看出Mapstruct是非常优秀的,其性能远远超过BeanUtils。
下文会讲到Mapstruct性能好的根本原因。
| 对象转换次数 | 属性个数 | BeanUtils耗时 | Mapstruct耗时 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5千万次 | 6 | 14秒 | 1秒 |
| 5千万次 | 15 | 36秒 | 1秒 |
| 5千万次 | 25 | 55秒 | 1秒 |
Mapstruct 依赖
使用Mapstruct需要依赖的包如下,mapstruct、mapstruct-processor、lombok,可以去仓库中查看最新版本。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
</dependency>简单的属性拷贝下面我们先来看下Mapstruct最简单的使用方式。
当两个对象的属性类型和名称完全相同时,Mapstruct会自动拷贝;假设我们现在需要把UserPo的属性值拷贝到UserEntity中,我们需要做下面几件事情:
- 定义UserPo和UserEntity
- 定义转换接口
- 编写测试main方法
▐ 首先定义UserPo和UserEntity
UserPo和UserEntity的属性类型和名称完全相同。
package mapstruct;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserPo {
private Long id;
private Date gmtCreate;
private Date createTime;
private Long buyerId;
private Long age;
private String userNick;
private String userVerified;
}
package mapstruct;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class UserEntity {
private Long id;
private Date gmtCreate;
private Date createTime;
private Long buyerId;
private Long age;
private String userNick;
private String userVerified;
}▐ 定义转换接口
定义mapstruct接口,在接口上打上@Mapper注解。
接口中有一个常量和一个方法,常量的值是接口的实现类,这个实现类是Mapstruct默认帮我们实现的,下文会讲到。定义了一个po2entity的转换方法,表示把入参UserPo对象,转换成UserEntity。
注意@Mapper是Mapstruct的注解,不要引错了。
package mapstruct;
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
@Mapper
public interface IPersonMapper {
IPersonMapper INSTANCT = Mappers.getMapper(IPersonMapper.class);
UserEntity po2entity(UserPo userPo);
}▐ 测试类
创建一个UserPo对象,并使用Mapstruct做转化。
package mapstruct;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import java.util.Date;
public class MapStructTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testNormal();
}
public static void testNormal() {
System.out.println("-----------testNormal-----start------");
UserPo userPo = UserPo.builder()
.id(1L)
.gmtCreate(new Date())
.buyerId(666L)
.userNick("测试mapstruct")
.userVerified("ok")
.age(18L)
.build();
System.out.println("1234" + userPo);
UserEntity userEntity = IPersonMapper.INSTANCT.po2entity(userPo);
System.out.println(userEntity);
System.out.println("-----------testNormal-----ent------");
}
}▐ 测试结果
可以看到,所有赋值的属性都做了处理,且两边的值都一样,结果符合预期。
Mapstruct 性能优于 BeanUtils 的原因
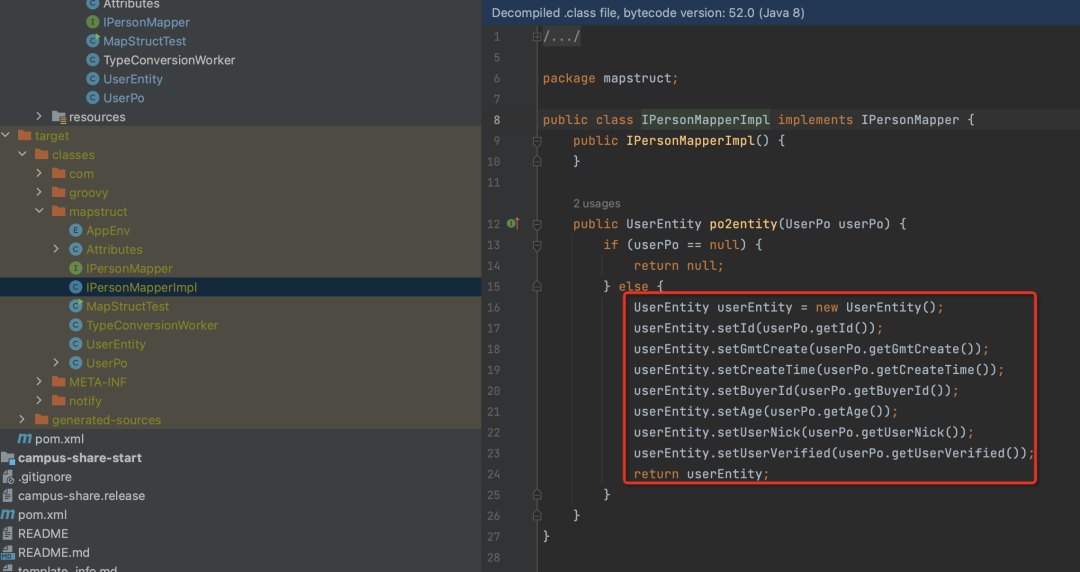
Java程序执行的过程,是由编译器先把java文件编译成class字节码文件,然后由JVM去解释执行class文件。Mapstruct正是在java文件到class这一步帮我们实现了转换方法,即做了预处理,提前编译好文件,如果用过lombok的同学一定能理解其好处,通过查看class文件,可以看出IPersonMapper被打上org.mapstruct.Mapper注解后,编译器自动会帮我们生成一个实现类IPersonMapperImpl,并实现了po2entity这个方法,看下面的截图。
▐ IPersonMapperImpl代码
从生成的代码可以看出,转化过程非常简单,只使用了UserPo的get方法和UserEntity的set方法,没有复杂的逻辑处理,清晰明了,所以性能很高。
下面再去看BeanUtils的默认实现。
▐ Spring的BeanUtils源**码**
BeanUtils部分源码如下,转换的原理是使用的反射,反射的效率相对来说是低的,因为jvm优化在这种场景下有可能无效,所以在对性能要求很高或者经常被调用的程序中,尽量不要使用。我们平时在研发过程中,也会遵守这个原则,非必要,不反射。
从下面的BeanUtils代码中可以看出,转化逻辑非常复杂,有很多的遍历,去获取属性,获取方法,设置方法可访问,然后执行,所以执行效率相对Mapstruct来说,是非常低的。回头看Mapstruct自动生成的实现类,简洁、高效。
private static void copyProperties(Object source, Object target, Class<?> editable, String... ignoreProperties)
throws BeansException {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
Assert.notNull(target, "Target must not be null");
Class<?> actualEditable = target.getClass();
if (editable != null) {
if (!editable.isInstance(target)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Target class [" + target.getClass().getName() +
"] not assignable to Editable class [" + editable.getName() + "]");
}
actualEditable = editable;
}
PropertyDescriptor[] targetPds = getPropertyDescriptors(actualEditable);
List<String> ignoreList = (ignoreProperties != null ? Arrays.asList(ignoreProperties) : null);
for (PropertyDescriptor targetPd : targetPds) {
Method writeMethod = targetPd.getWriteMethod();
if (writeMethod != null && (ignoreList == null || !ignoreList.contains(targetPd.getName()))) {
PropertyDescriptor sourcePd = getPropertyDescriptor(source.getClass(), targetPd.getName());
if (sourcePd != null) {
Method readMethod = sourcePd.getReadMethod();
if (readMethod != null &&
ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType())) {
try {
if (!Modifier.isPublic(readMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {
readMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
Object value = readMethod.invoke(source);
if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
writeMethod.invoke(target, value);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new FatalBeanException(
"Could not copy property '" + targetPd.getName() + "' from source to target", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
属性类型相同名称不同 对于属性名称不同的属性进行处理时,需要使用@Mapping,比如修改UserEntity中的userNick为userNick1,然后进行转换。
▐ 修改UserEntity属性userNick1
package mapstruct;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class UserEntity {
private Long id;
private Date gmtCreate;
private Date createTime;
private Long buyerId;
private Long age;
private String userNick1;
private String userVerified;
}▐ @Mapping注解指定source和target字段名称对应关系
@Mapping(target = "userNick1", source = "userNick"),此处的意思就是在转化的过程中,将UserPo的userNick属性值赋值给UserEntity的userNick1属性。
package mapstruct;
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.Mapping;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
@Mapper
public interface IPersonMapper {
IPersonMapper INSTANCT = Mappers.getMapper(IPersonMapper.class);
@Mapping(target = "userNick1", source = "userNick")
UserEntity po2entity(UserPo userPo);
}
▐ 执行结果
可以看到,正常映射,符合预期。
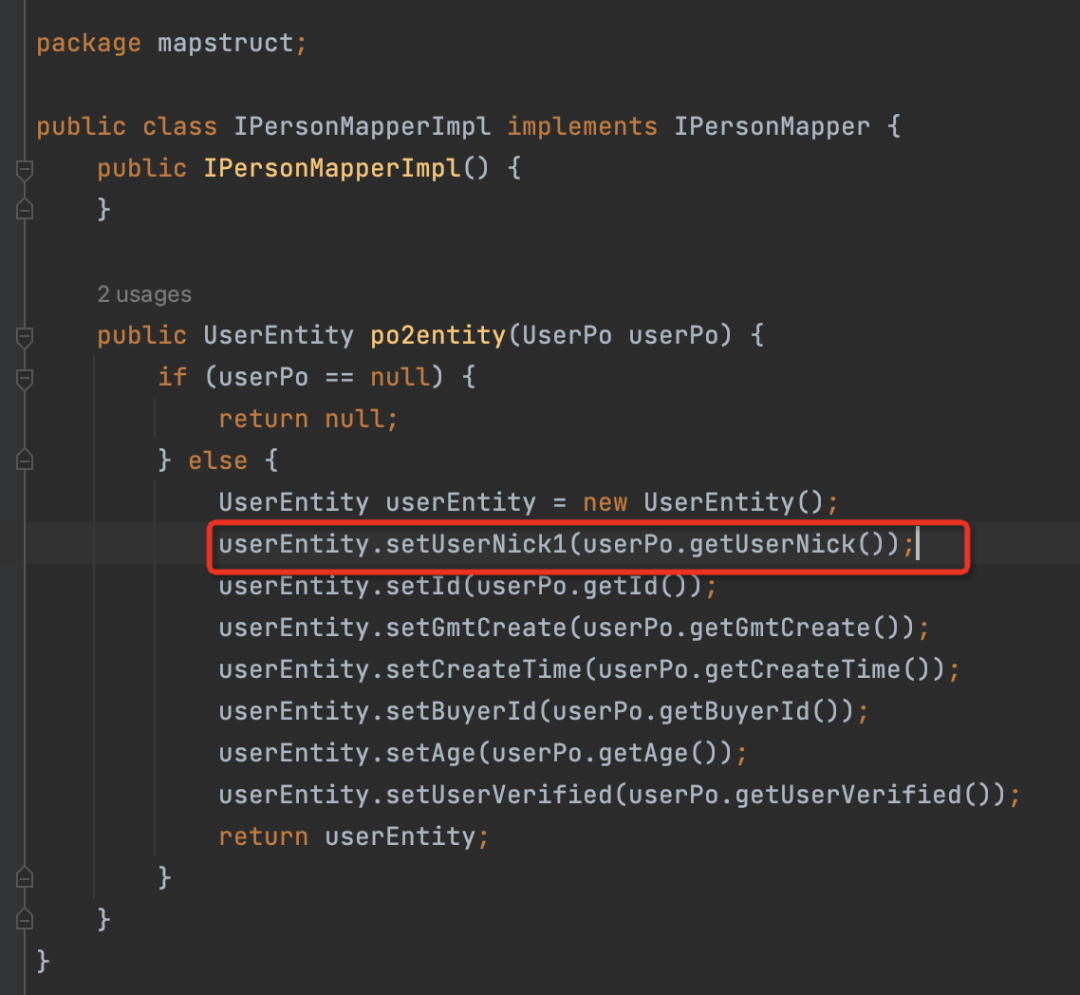
▐ 查看class文件
我们再来看实现类,可以看到,Mapstruct帮我们做了处理,把po的userNick属性赋值给了entity的userNick1。
String转日期&String转数字&忽略某个字端&给默认值等
@Mapping(target = "createTime", source = "createTime", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd")
@Mapping(target = "age", source = "age", numberFormat = "#0.00")
@Mapping(target = "id", ignore = true)
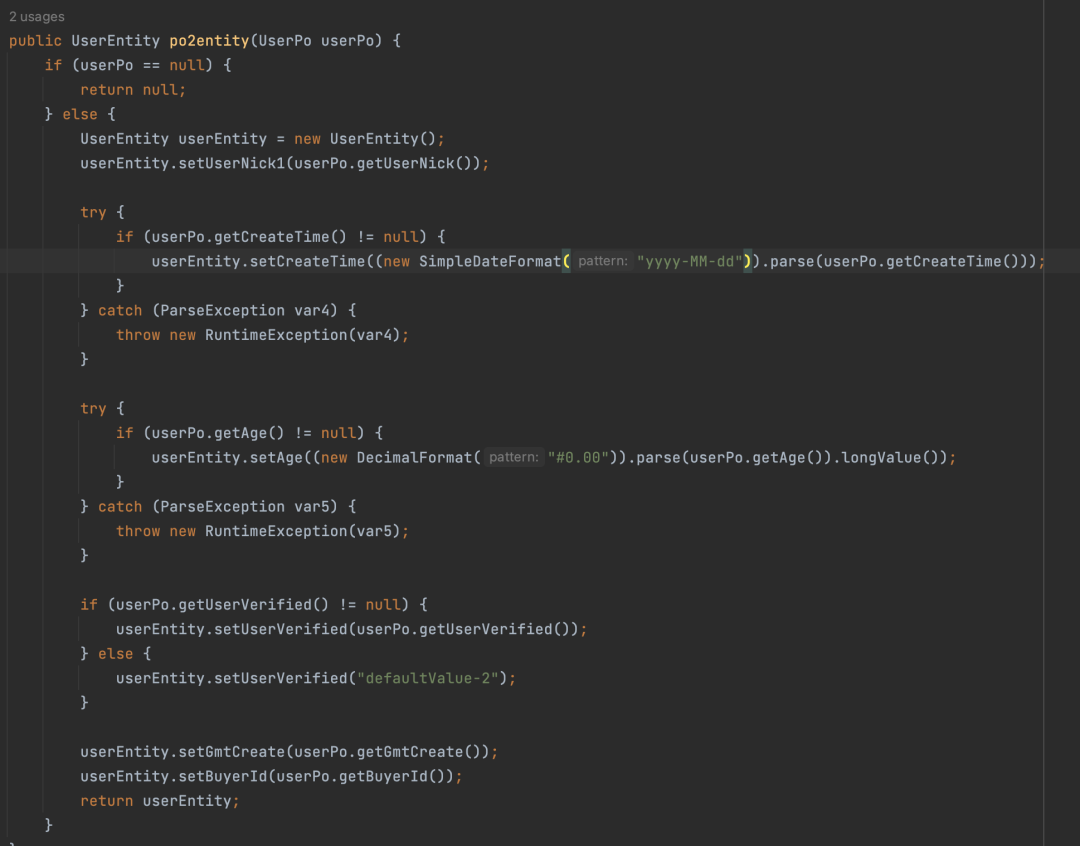
@Mapping(target = "userVerified", defaultValue = "defaultValue-2")▐ 查看class实现类
- createTime:可以看到对日期使用了SimpleDateFormat进行转换,这里建议不要使用这个,因为每次都创建了一个SimpleDateFormat,可以参考《阿里巴巴Java开发手册》关于日期转换的建议。
- age:字符串转数字,也是帮忙做了处理
- id:字段赋值没有了
- userVerified:如果为null赋值默认值
自定义转换
如果现有的能力都不能满足需要,可以自定义一个转换器,比如我们需要把一个字符串使用JSON工具转换成对象。
▐ 添加属性
我们在po中加入一个字符串的attributes属性,在entity中加入Attributes类型的属性
package mapstruct;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Attributes {
private Long id;
private String name;
}
package mapstruct;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserPo {
private Long id;
private Date gmtCreate;
private String createTime;
private Long buyerId;
private String age;
private String userNick;
private String userVerified;
private String attributes;
}package mapstruct;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class UserEntity {
private Long id;
private Date gmtCreate;
private Date createTime;
private Long buyerId;
private Long age;
private String userNick1;
private String userVerified;
private Attributes attributes;
}▐ 编写自定义转换处理类
转换器很简单,就是一个普通的Java类,只要在方法上打上Mapstruct的注解@Named。
package mapstruct;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.mapstruct.Named;
public class AttributeConvertUtil {
/**
* json字符串转对象
*
* @param jsonStr
* @return
*/
@Named("jsonToObject")
public Attributes jsonToObject(String jsonStr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(jsonStr)) {
return null;
}
return JSONObject.parseObject(jsonStr, Attributes.class);
}
}▐ 修改转换接口
- 在@Mapper上引用我们的自定义转换代码类AttributeConvertUtil
- 使用qualifiedByName指定我们使用的自定义转换方法
package mapstruct;
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.Mapping;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
/**
* @author jiangzhengyin
*/
@Mapper(uses = AttributeConvertUtil.class)
public interface IPersonMapper {
IPersonMapper INSTANCT = Mappers.getMapper(IPersonMapper.class);
@Mapping(target = "attributes", source = "attributes", qualifiedByName = "jsonToObject")
@Mapping(target = "userNick1", source = "userNick")
@Mapping(target = "createTime", source = "createTime", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd")
@Mapping(target = "age", source = "age", numberFormat = "#0.00")
@Mapping(target = "id", ignore = true)
@Mapping(target = "userVerified", defaultValue = "defaultValue-2")
UserEntity po2entity(UserPo userPo);
}▐ 测试类及结果
可以看出我们将把String转成了JSON对象
public class MapStructTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testNormal();
}
public static void testNormal() {
System.out.println("-----------testNormal-----start------");
String attributes = "{\"id\":2,\"name\":\"测试123\"}";
UserPo userPo = UserPo.builder()
.id(1L)
.gmtCreate(new Date())
.buyerId(666L)
.userNick("测试mapstruct")
.userVerified("ok")
.age("18")
.attributes(attributes)
.build();
System.out.println("1234" + userPo);
UserEntity userEntity = IPersonMapper.INSTANCT.po2entity(userPo);
System.out.println(userEntity);
System.out.println("-----------testNormal-----ent------");
}
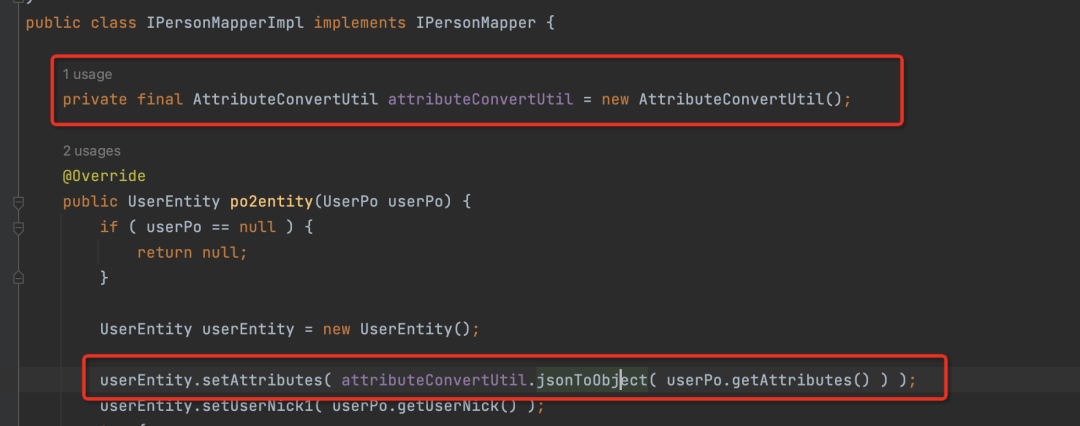
}▐ 查看实现类
可以看到,在实现类中Mapstruct帮我们new了一个AttributeConvertUtil的对象,并调用了该对象的jsonToObject方法,将字符串转成JSON,最终赋值给了UserEntity的attributes属性,实现很简单,也是我们可以猜到的。
性能对比
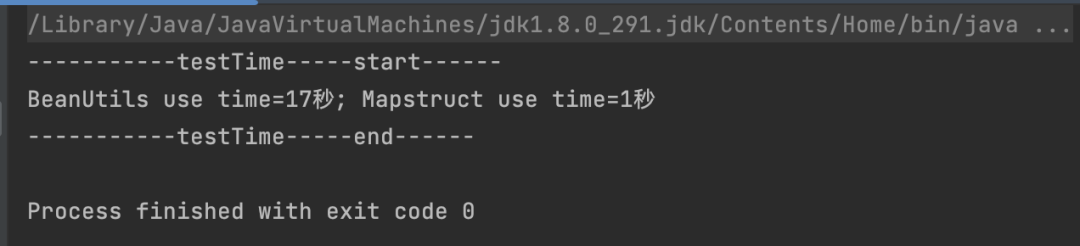
代码很简单,循环的创建UserPo对象,使用两种方式,转换成UserEntity对象,最终输出两种方式的执行耗时。可以加减属性或者修改转换次数,对比不同场景下的执行耗时。
public static void testTime() {
System.out.println("-----------testTime-----start------");
int times = 50000000;
final long springStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
UserPo userPo = UserPo.builder()
.id(1L)
.gmtCreate(new Date())
.buyerId(666L)
.userNick("测试123")
.userVerified("ok")
.build();
UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(userPo, userEntity);
}
final long springEndTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
UserPo userPo = UserPo.builder()
.id(1L)
.gmtCreate(new Date())
.buyerId(666L)
.userNick("测试123")
.userVerified("ok")
.build();
UserEntity userEntity = IPersonMapper.INSTANCT.po2entity(userPo);
}
final long mapstructEndTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("BeanUtils use time=" + (springEndTime - springStartTime) / 1000 + "秒" +
"; Mapstruct use time=" + (mapstructEndTime - springEndTime) / 1000 + "秒");
System.out.println("-----------testTime-----end------");
}总结
通过本次调研,Mapstruct的高性能是毋庸置疑的,这也是我选择使用他的根本原因。在使用方式上和BeanUtils对比,Mapstruct需要创建mapper接口和自定义转换工具类,其实上手成本并不高,但是我们换取了高性能,这是非常值得的,所以强烈推荐大家使用Mapstruct,是时候和BeanUtils说再见了。
保持好奇,不断探索,让程序更友好!