浅谈TS运行时类型检查
What-什么是运行时类型检查?
编译时类型检查(静态类型检查):
在编译阶段对变量类型进行静态检查,编译后的代码不保留任何类型标注信息,对实际代码运行没有影响
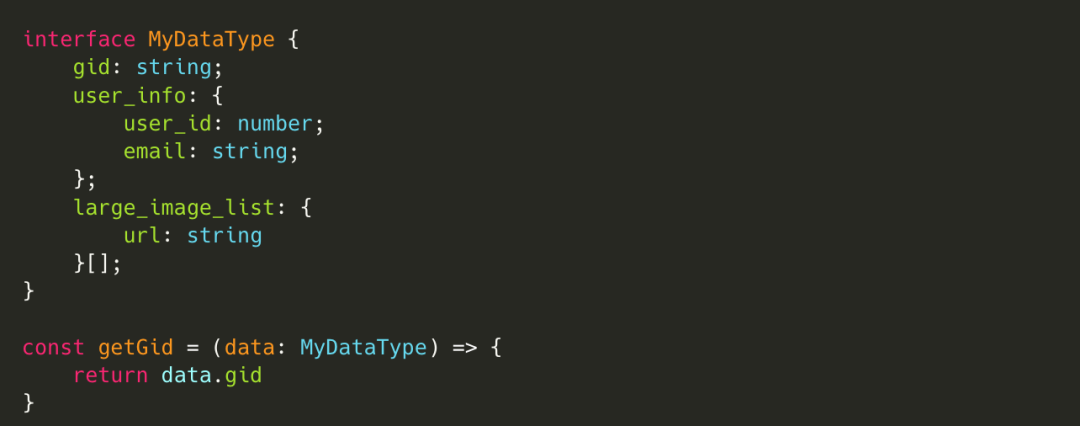
在代码实际运行过程中对数据类型进行检查,一般会用在约束函数参数、返回值这类内外部之间传递数据
Why-为什么需要运行时类型检查?
TypeScript 对于前端项目可维护性提升很大,也能帮我们保障内部编码时的类型安全,但在和外部进行数据传递时,仅仅有编译期类型检查还是免不了出一些问题,以我遇过的两次事故为例:
- 对内输入数据:线上接口返回的视频id字段类型由 string 变为 number 后前端获取后丢失精度,导致页面异常
- 向外输出数据:项目迭代需求时逻辑改动导致某个埋点字段丢失,过了很久要分析数据才发现,白白浪费了时间
如果我们在运行时做了相应的类型检查,发现异常上报监控,问题就能更早解决了,还有其他能想到的一些需要运行时类型检查的场景:
- 表单场景类型校验
- 为API/JSB接口编写测试
- 上报参数过滤敏感信息字段
可以看出,在涉及IO数据场景时额外的运行时检查是有必要的,以使数据类型不符合预期时,我们能及时发现问题。
How-怎么做运行时类型检查?
interface MyDataType {
video_id: string;
user_info: {
user_id: number;
email: string;
};
image_list: {
url: string
}[];
}
const data: MyDataType = await fetchMyData()
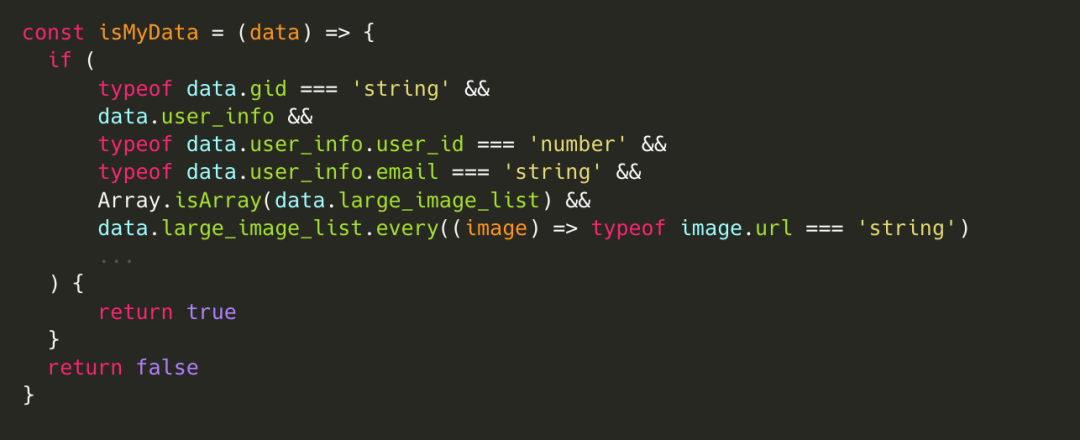
if (
typeof data.video_id === 'string' &&
data.user_info &&
typeof data.user_info.user_id === 'number' &&
typeof data.user_info.email === 'string' &&
Array.isArray(data.image_list) &&
data.image_list.every((image) => typeof image.url === 'string')
...
) {
// do something
}如上,我们可以手动编写一份运行时类型检查代码,但这样写起来效率低、维护性差,而且没有用上已有的TS类型,导致我们要同时维护两份类型,保证之间的同步。
下面向大家介绍业内几种类型检查方案,个人认为一个好方案至少要满足两点:
- 只需维护一份类型规则即可享有静态类型提示和运行时检查校验
- 在静态和运行时的类型检查能力等价(起码运行时不能比静态检查宽松,不然会出线上bug)
方案1-动态 to 静态
编写运行时校验规则,并从中提取出静态类型
JSON 形式
通过编写 JSON 来描述校验规则,典型的有 ajv、tv4,用法如下:
import Ajv, { JTDDataType } from "ajv/dist/jtd"
const ajv = new Ajv()
const schema = {
properties: {
video_id: { type: "string" },
user_info: {
properties: {
user_id: { type: "int32" },
email: { type: "string" }
}
},
image_list: {
elements: {
properties: {
url: { type: "string" },
}
}
}
}
} as const
type MyDataType = JTDDataType<typeof schema>
// type MyDataType = {
// video_id: string;
// user_info: {
// user_id: number;
// email: string;
// } & {};
// image_list: ({
// url: string;
// } & {})[];
// } & {}
const data: MyDataType = await fetchMyData()
const validate = ajv.compile(schema)
validate(data)
if (validate.errors) {
// do something
}优点:
- JTD 支持从已有的schema提取TS类型,避免维护两份类型定义
- 校验库都会提供一些常用的高级校验规则(如日期范围、邮箱格式等)
- JSON 格式易存储传输,甚至其他语言也能用,可以做到动态下发校验规则
缺点:
- Schema 格式有额外学习成本,JSON 写起来太过冗长枯燥提示也不友好
实现原理:
- 类型检查:根据 schema 规则遍历比较数据字段
- 提取类型:结合 extends、infer、in keyof、递归等语法
API 形式
通过调用API来描述组成校验规则,典型例子有 zod 、superstruct、io-ts,用法如下:
import { z } from "zod";
const schema = z.object({
video_id: z.string(),
user_info: z.object({
user_id: z.number().positive(),
email: z.string().email()
}),
image_list: z.array(z.object({
url: z.string()
}))
});
type MyDataType = z.infer<typeof schema>
// type MyDataType = {
// video_id: string;
// user_info: {
// user_id: number;
// email: string;
// };
// image_list: {
// url: string;
// }[];
// }
const data: MyDataType = await fetchMyData()
const parseRes = schema.safeParse(data)
if (parseRes.error) {
// do something
}优点:
- 通过API组装类型的形式相比JSON更灵活和易编写
- 提供一些常用的高级校验规则(如日期范围、邮箱格式等)
- 支持从已有的schema提取TS类型,避免维护两份类型定义
缺点:
- 有一些额外学习成本,不能直接运用我们已掌握的TS语法描述类型
实现原理:
和JSON形式类似,但实现更轻量(ajv有35k,zod只有10k)
方案2-静态 + 动态
把静态类型和动态类型检查写在一起
主要是基于类属性装饰器来生成校验规则,典型例子有 class-validator、typeorm,用法如下:
import 'reflect-metadata'
import { plainToClass, Type } from "class-transformer";
import {
validate,
IsString,
IsInt,
IsEmail,
IsObject,
IsArray,
ValidateNested,
} from "class-validator";
class UserInfo {
@IsInt()
user_id: number;
@Length(10, 20,{message: 'name的长度不能小于10不能大于20'})
@IsEmail()
email: string;
}
class LargeImage {
@IsString()
url: string
}
class MyData {
@IsString()
@IsNotEmpty({message:'video_id 不能为空'})
video_id: string;
@IsObject()
@ValidateNested()
@Type(() => UserInfo)
user_info: UserInfo;
@IsArray({message:'数组 不能为空'})
@ValidateNested({each: true})
@Type(() => LargeImage)
image_list: LargeImage[];
}
const data: MyData = await fetchMyData()
const dataAsClassInstance = plainToClass(
MyData, data
);
validate(dataAsClassInstance).then(message => {
// do something
});优点:
- 强迫分原子类型,ORM风格,适合服务端场景使用
- 提供一些常用的高级校验规则(如日期范围、邮箱格式等)
- 校验属性值的报错信息可以自定义,如@IsArray({message:'数组 不能为空'})
缺点:
- 运行时检查类型和TS类型都要写,但写在一块起码方便同步
- 校验规则需要声明class,特别是有嵌套对象时,写起来麻烦
- 只能检查类的实例,普通对象要配合 class-transformer 转换
实现原理:
装饰器+反射(通过装饰器给字段加入类型规则元数据,运行时再通过反射获取这些元数据做校验)
方案3-静态 to 动态
通过处理 TS 类型,使之在运行时可用
TS类型自动转换JSON Schema
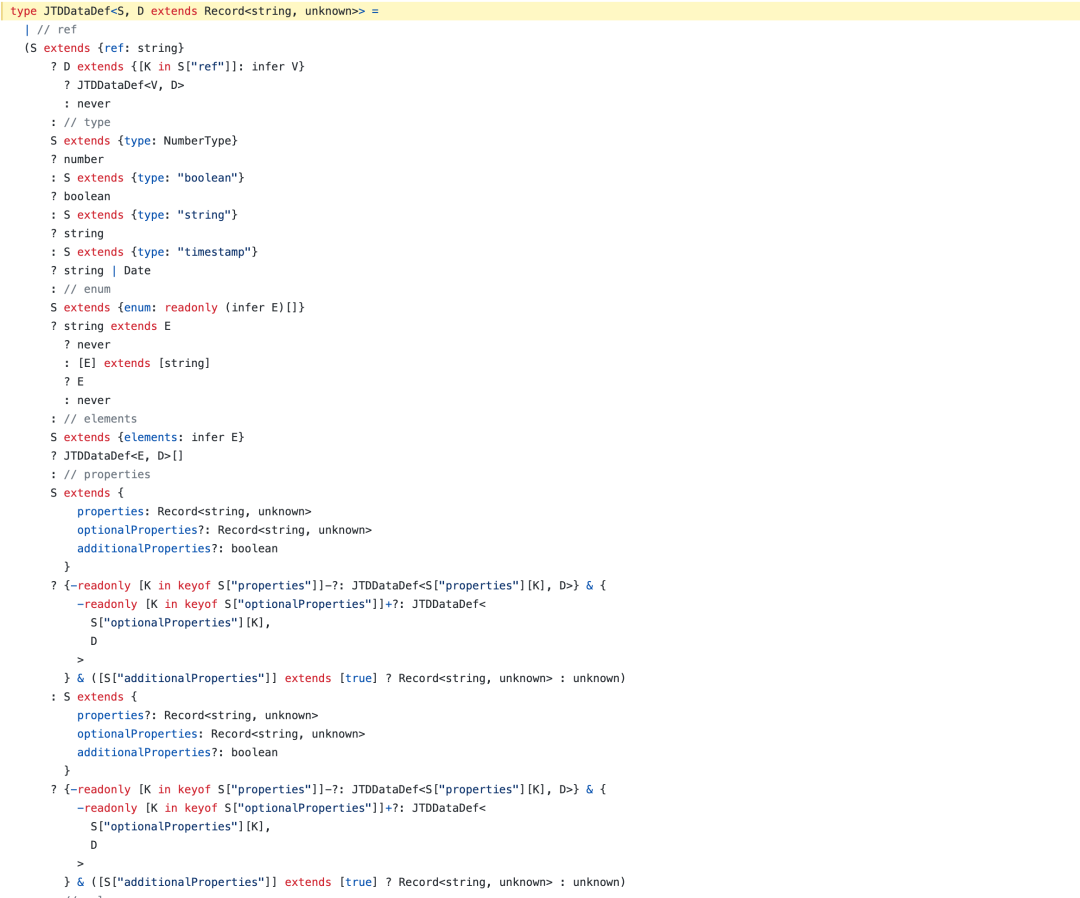
典型例子有 typescript-json-schema,用法如下:
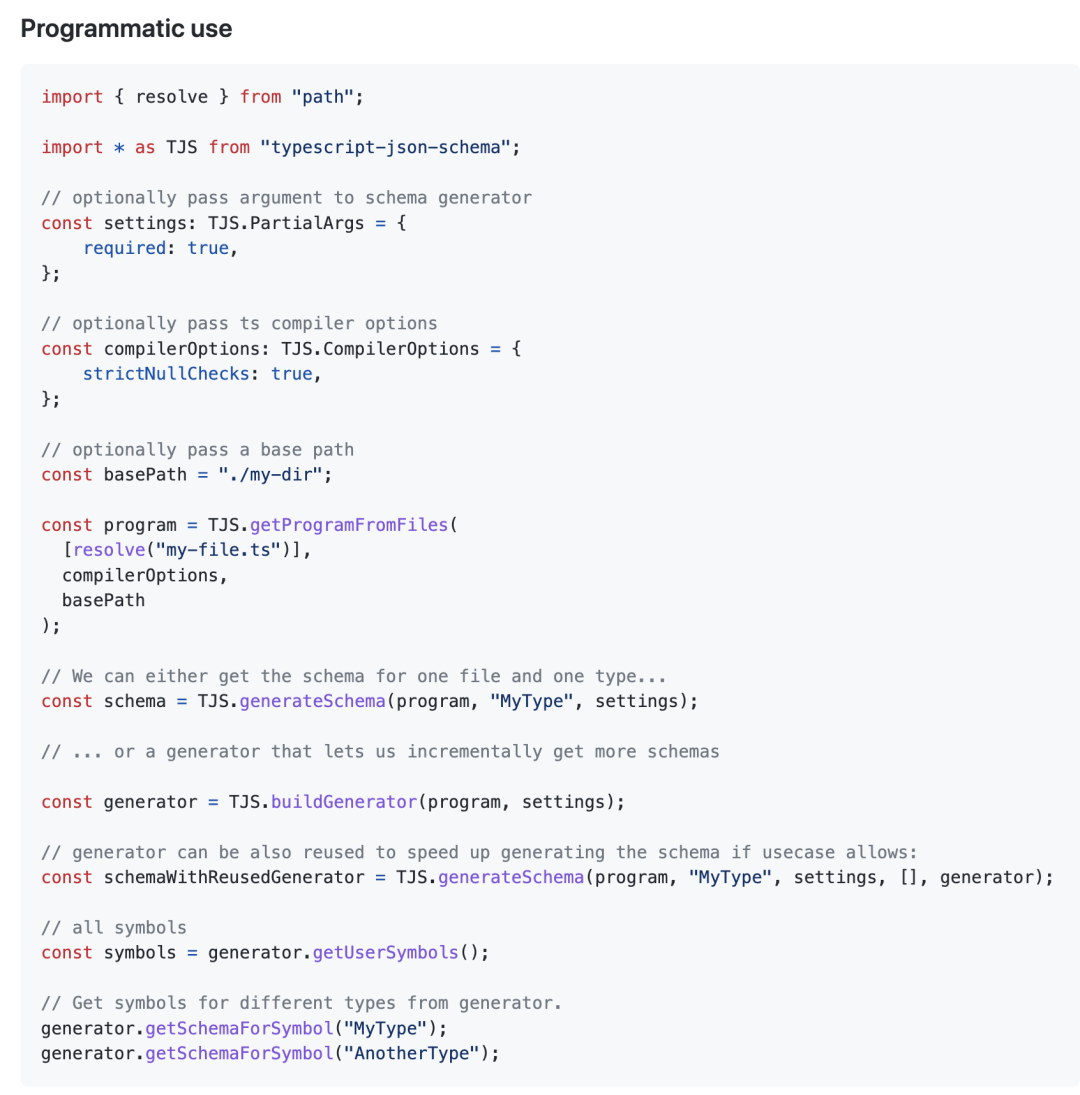
优点:
- 不需要手动维护两份类型定义
缺点:
- 本身不提供检查能力,需要配合额外校验库
- 部分TS类型语法不支持转换(如联合类型)
- 有些规则需要另外学习它的注释语法,写起来也不方便
实现原理:
解析处理 TypeScript AST https://github.com/YousefED/typescript-json-schema/blob/master/typescript-json-schema.ts
编译期从TS类型生成检查代码
在编译期将TS代码转成类型检查能力等价的JS代码,典型例子有 typescript-is、ts-auto-guard,用法如下:
配置 ts-loader 插件:
import typescriptIsTransformer from 'typescript-is/lib/transform-inline/transformer'
...
{
test: /.ts$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
loader: 'ts-loader',
options: {
getCustomTransformers: program => ({
before: [typescriptIsTransformer(program)]
})
}
}
...编译前源代码:
import { is } from "typescript-is"
interface MyDataType {
gid: number;
user_info: {
user_id: number;
email: string;
};
large_image_list: {
url: string;
}[];
}
const data: MyDataType = fetchMyData()
const isRightType = is<MyDataType>(data)编译产物代码:
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true });
const typescript_is_1 = require("typescript-is");
const data = (0, fetchMyData)();
const isRightType = (0, typescript_is_1.is)(data, object => { function _number(object) { ; if (typeof object !== "number")
return {};
else
return null; } function _string(object) { ; if (typeof object !== "string")
return {};
else
return null; } function _1(object) { ; if (typeof object !== "object" || object === null || Array.isArray(object))
return {}; {
if ("user_id" in object) {
var error = _number(object["user_id"]);
if (error)
return error;
}
else
return {};
} {
if ("email" in object) {
var error = _string(object["email"]);
if (error)
return error;
}
else
return {};
} return null; } function _4(object) { ; if (typeof object !== "object" || object === null || Array.isArray(object))
return {}; {
if ("url" in object) {
var error = _string(object["url"]);
if (error)
return error;
}
else
return {};
} return null; } function sa__4_ea_4(object) { ; if (!Array.isArray(object))
return {}; for (let i = 0; i < object.length; i++) {
var error = _4(object[i]);
if (error)
return error;
} return null; } function _0(object) { ; if (typeof object !== "object" || object === null || Array.isArray(object))
return {}; {
if ("video_id" in object) {
var error = _number(object["video_id"]);
if (error)
return error;
}
else
return {};
} {
if ("user_info" in object) {
var error = _1(object["user_info"]);
if (error)
return error;
}
else
return {};
} {
if ("image_list" in object) {
var error = sa__4_ea_4(object["image_list"]);
if (error)
return error;
}
else
return {};
} return null; } return _0(object); });优点:
- 使用方便,无需维护两份类型和学习额外校验规则,只写TS代码就行
缺点:
- 每次会生成大片检查代码(即使类型存在复用),导致代码产物体积膨胀
- 校验能力完全依赖TS类型检查,不像校验库有一些高级规则(如日期范围、邮箱格式等)
实现原理:
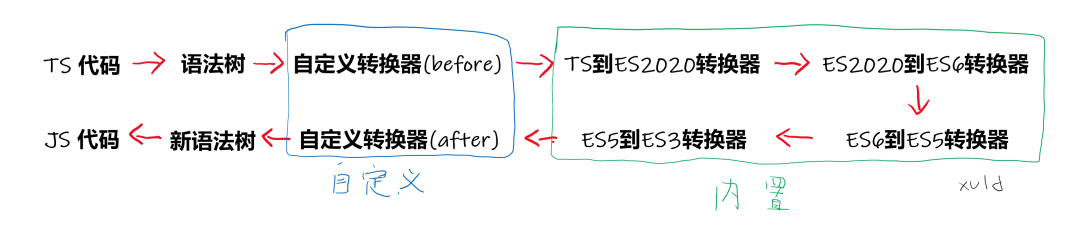
编写 TypeScript Transformer Plugin,运行机制类似 babel 插件(源码->解析语法树->修改语法树->转换)
提取TS类型信息在运行时动态检查
典型的方案有 DeepKit,基本上是把TS类型系统带到了JS运行时:
编译前源代码:
import { is } from '@deepkit/type'
interface MyDataType {
video_id: string;
user_info: {
user_id: number;
email: string;
};
image_list: {
url: string;
}[];
}
const data: MyDataType = await fetchMyData()
const isRightType = is<MyDataType>(data)编译产物代码:
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", ({ value: true }));
const type_1 = __webpack_require__(/*! @deepkit/type */ "@deepkit/type");
const __ΩMyDataType = ['video_id', 'user_id', 'email', 'user_info', 'url', 'image_list', 'P&4!P&4"'4#&4$M4%P&4&MF4'M'];
const data = (0, fetchMyData)();
const isRes = (0, type_1.is)(data, undefined, undefined, [() => __ΩMyDataType, 'n!']);
console.log('deepkit', isRes);优点:
- 使用方便,无需维护两份类型,且提供邮箱格式等高级校验能力
- 类型校验规则编译后生成的运行时代码很少,体积不容易膨胀
缺点:
- 项目较新,还没有被大范围使用,稳定性未知
- 运行时的类型解释器可能比较重,性能开销未知
实现原理:
在编译期将 TypeScript 类型信息转换成字节码(Bytecode),TS 类型信息都被完整保留到了运行时,之后在运行时用一个解释器计算出类型信息,我们在运行时也能使用它提供的丰富 API 反射类型信息,用在如生成 Mock 数据的场景。
import { typeOf, ReflectionKind } from '@deepkit/type';
typeOf<string>(); // {kind: ReflectionKind.string}
typeOf<number>(); // {kind: ReflectionKind.number}
typeOf<boolean>(); // {kind: ReflectionKind.boolean}
typeOf<string | number>();
// {kind: ReflectionKind.union, types: [{kind: ReflectionKind.string}, {kind: ReflectionKind.number}]}
class MyClass {
id: number = 0;
}
typeOf<MyClass>();
//{kind: ReflectionKind.class, classType: MyClass, types: [
// {kind: ReflectionKind.property, name: 'id', type: {kind: ReflectionKind.number}, default: () => 0}
//]}
import { ReflectionClass } from '@deepkit/type';
class MyClass {
id: number = 0;
doIt(arg: string): void {}
}
const reflection = ReflectionClass.from(MyClass);
reflection.getProperty('id').type; // {kind: ReflectionKind.number}
reflection.getProperty('id').isOptional(); //false
reflection.getPropertyNames(): ['id'];
reflection.getMethod('doIt').getReturnType(); //{kind: ReflectionKind.void}
reflection.getMethod('doIt').getParameter('arg').type; //{kind: ReflectionKind.string}
//works with interfaces as well
interface User {
id: number;
}
const reflection = ReflectionClass.from<User>();总结
没有十全十美的方案,综合来看当下使用如 zod 这类 API 形式的校验库会比较好,既成熟强大,也兼具灵活和易。,着眼未来 deepkit 似乎很有潜力,它其实是一整套 Web 开发方案,校验只是其中一部分,还有很多充分利用了运行时类型的功能特性。
那以后 TypeScript 会支持运行时类型检查吗?github 上也一直有人提相关的 issue,甚至有人专门建了一个请愿页面,但基本不太可能,因为 design goal 中已明确表示过不会增加任何运行时代码:
Add or rely on run-time type information in programs, or emit different code based on the results of the type system. Instead, encourage programming patterns that do not require run-time metadata.