三种虚拟列表原理与实现
前言
工作中一直有接触大量数据渲染的业务,使用react-window多之又多,所以对虚拟列表有了些浅显的理解。今天,我们就照着react-window的使用方式来实现三种虚拟列表。
- 元素固定高度的虚拟列表
- 元素不定高度的虚拟列表
- 元素动态高度的虚拟列表
虚拟列表核心原理
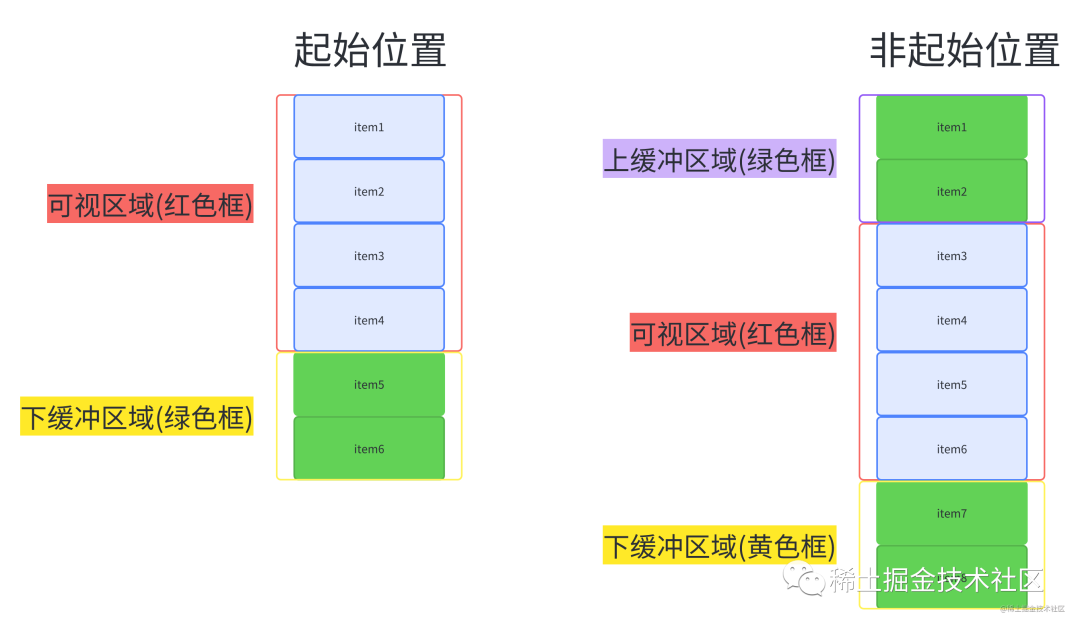
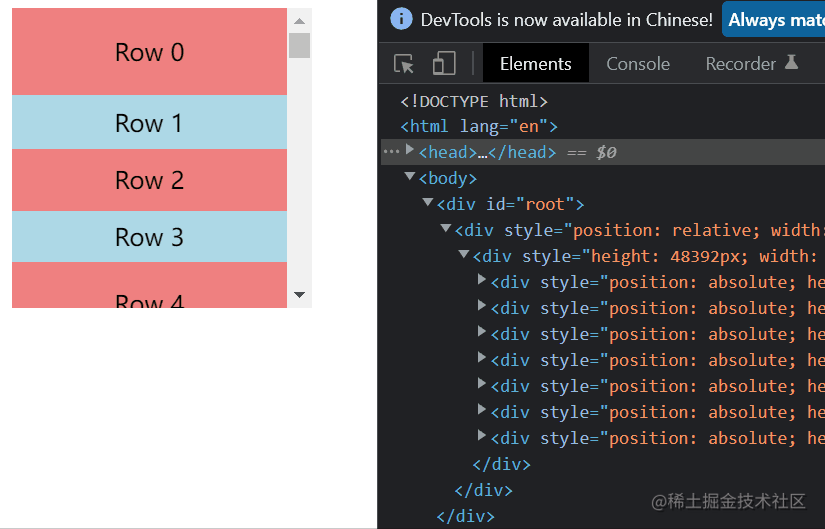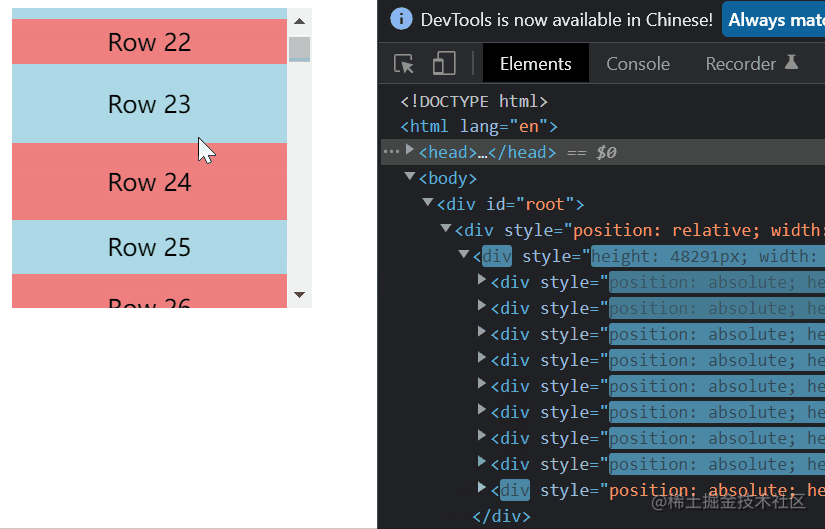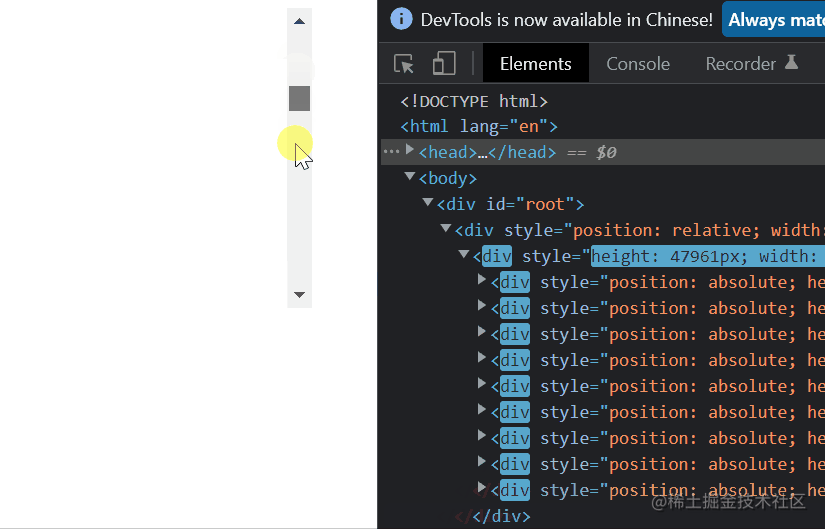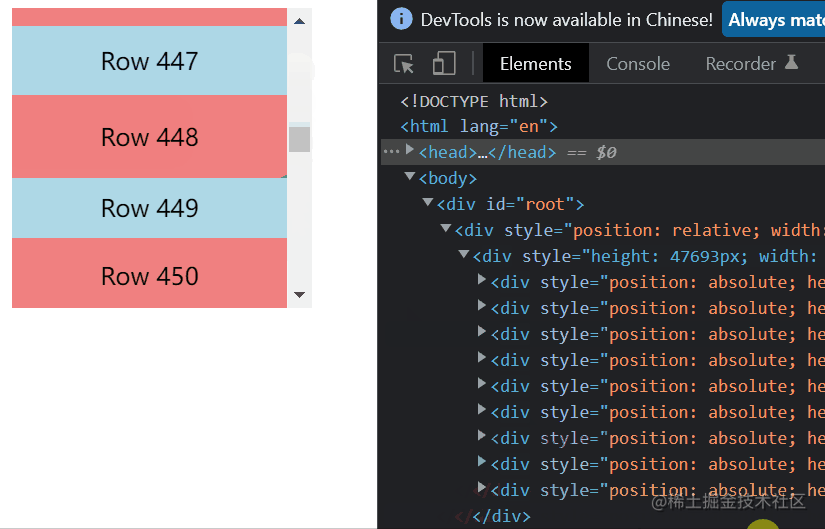
我们先来看一下整个虚拟列表元素的表现。
看右边的元素个数,会发现起初只有6个,之后无论怎么滚动,他都保持着8个元素,由此我们可以得出他的静态原理图是这样的。
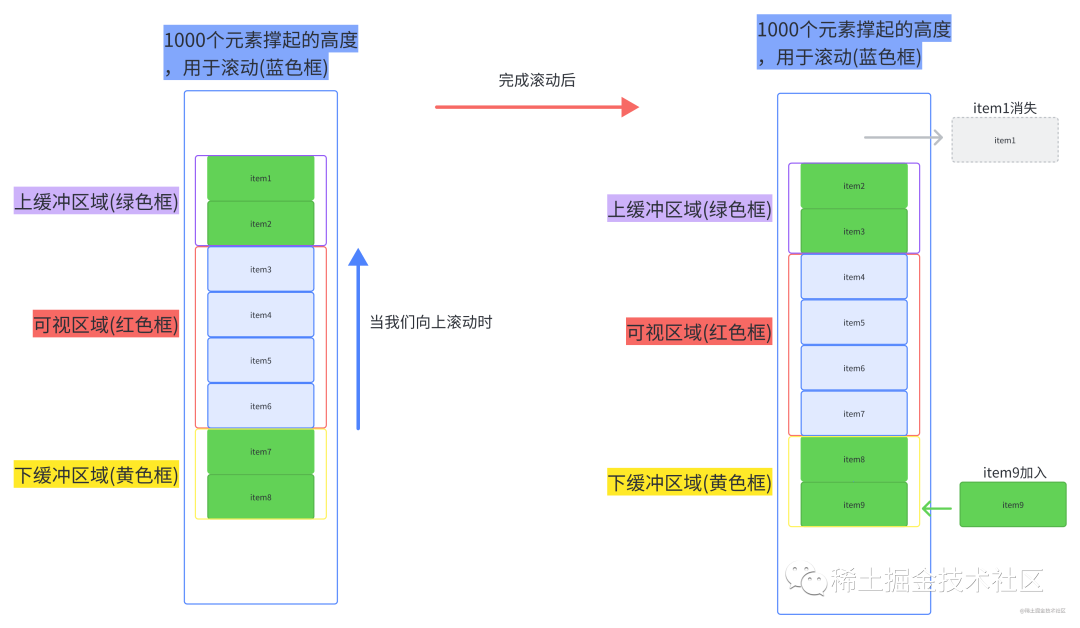
当我们进行了滚动后。
static-height-scroll.png从上面两图我们可以总结出,整个虚拟列表划分为三个区域,分别是上缓冲区(0/2个元素),可视区(n个元素),下缓冲区(2个元素)。当我们滚动到一个元素离开可视区范围内时,就去掉上缓冲区顶上的一个元素,然后再下缓冲区增加一个元素。这就是虚拟列表的核心原理了。
虚拟列表的实现
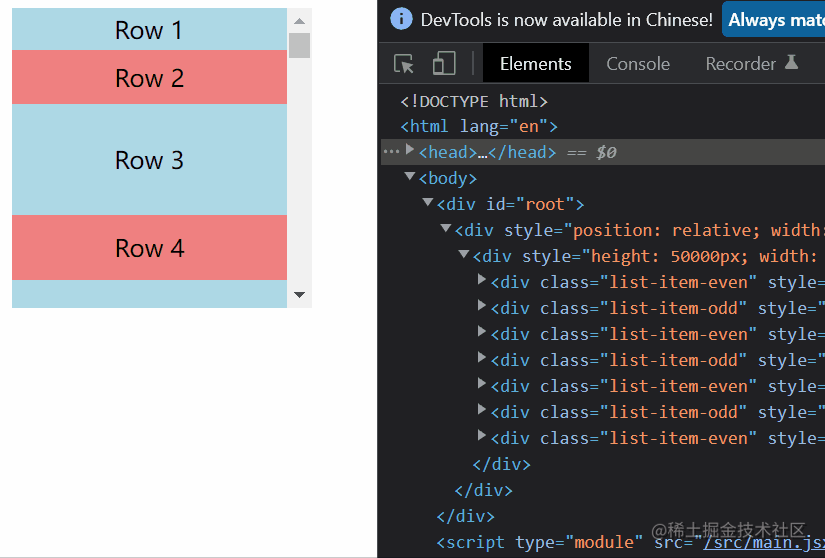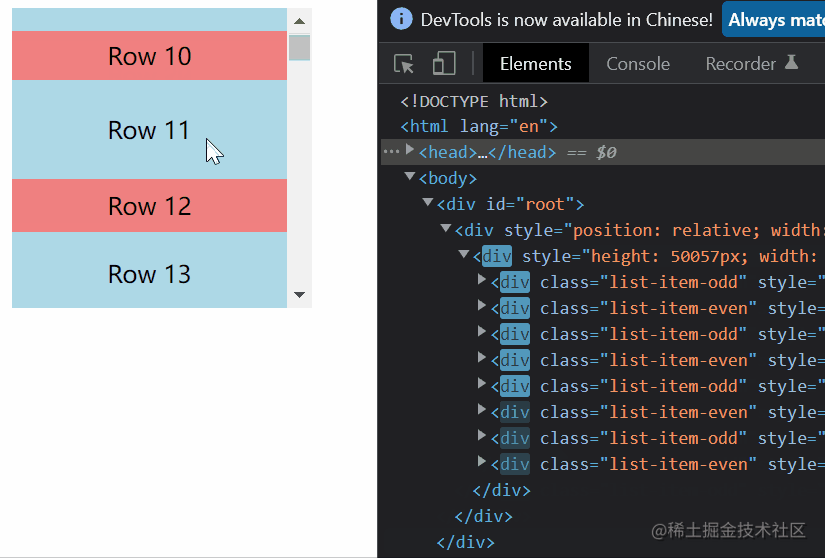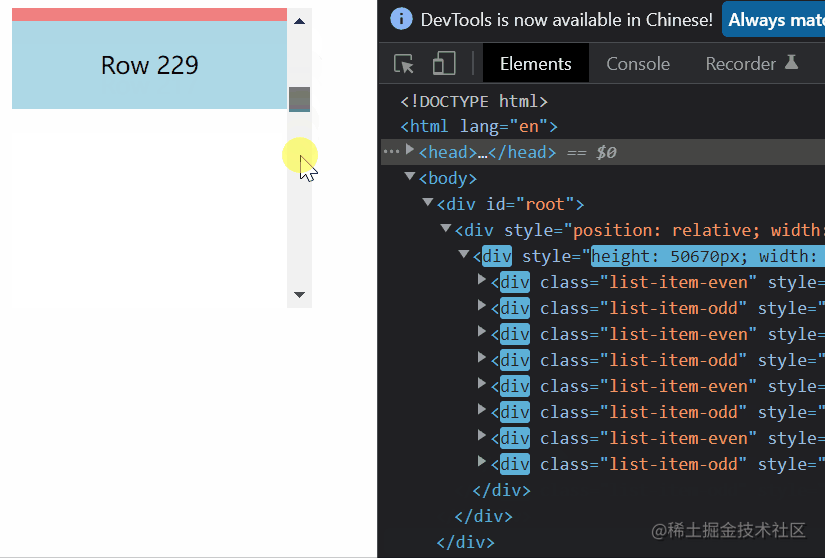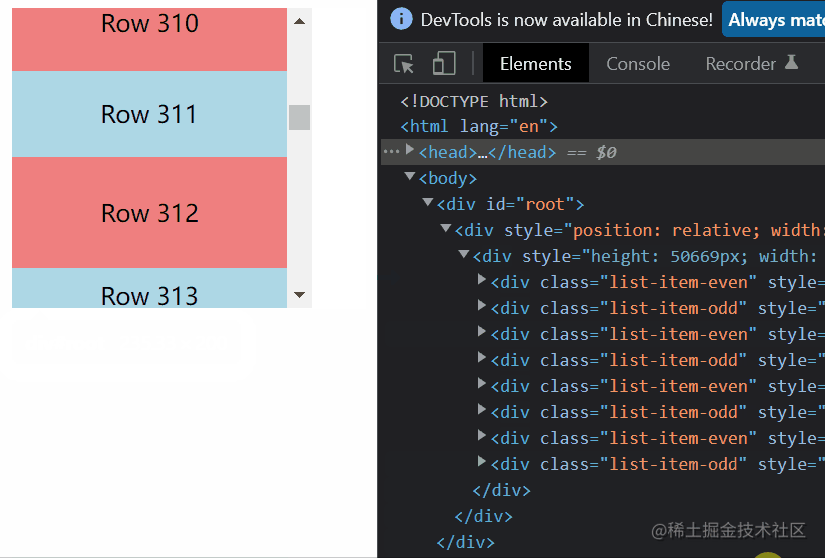
一、元素固定高度的虚拟列表
使用
const Row = ({ index, style, forwardRef }) => {
return (
<div className={index % 2 ? 'list-item-odd' : 'list-item-even'} style={style} ref={forwardRef}>
{`Row ${index}`}
</div>
)
}
const App = () => {
return (
<FixedSizeList
className="list"
height={200}
width={200}
itemSize={50}
itemCount={1000}
>
{Row}
</FixedSizeList>
);
}实现
(1)首先先计算出由1000个元素撑起的盒子(称之为container)的高度,撑开盒子,让用户能进行滚动操作。
(2)计算出可视区的起始索引、上缓冲区的起始索引以及下缓冲区的结束索引(就像上图滚动后,上缓冲区的起始索引为2,可视区起始索引为4,下缓冲区结束索引为9)。
(3)采用绝对定位,计算上缓冲区到下缓冲区之间的每一个元素在contianer中的top值,只有知道top值才能让元素出现在可视区内。
import { useState } from 'react';
const FixedSizeList = (props) => {
const { height, width, itemSize, itemCount, children: Child } = props;
// 记录滚动掉的高度
const [scrollOffset, setScrollOffset] = useState(0);
// 外部容器高度
const containerStyle = {
position: 'relative',
width,
height,
overflow: 'auto',
};
// 1000个元素撑起盒子的实际高度
const contentStyle = {
height: itemSize * itemCount,
width: '100%',
};
const getCurrentChildren = () => {
// 可视区起始索引
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollOffset / itemSize);
// 上缓冲区起始索引
const finialStartIndex = Math.max(0, startIndex - 2);
// 可视区能展示的元素的最大个数
const numVisible = Math.ceil(height / itemSize);
// 下缓冲区结束索引
const endIndex = Math.min(itemCount, startIndex + numVisible + 2);
const items = [];
// 根据上面计算的索引值,不断添加元素给container
for (let i = finialStartIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
const itemStyle = {
position: 'absolute',
height: itemSize,
width: '100%',
// 计算每个元素在container中的top值
top: itemSize * i,
};
items.push(
<Child key={i} index={i} style={itemStyle} />
);
}
return items;
}
// 当触发滚动就重新计算
const scrollHandle = (event) => {
const { scrollTop } = event.currentTarget;
setScrollOffset(scrollTop);
}
return (
<div style={containerStyle} onScroll={scrollHandle}>
<div style={contentStyle}>
{getCurrentChildren()}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default FixedSizeList;结果
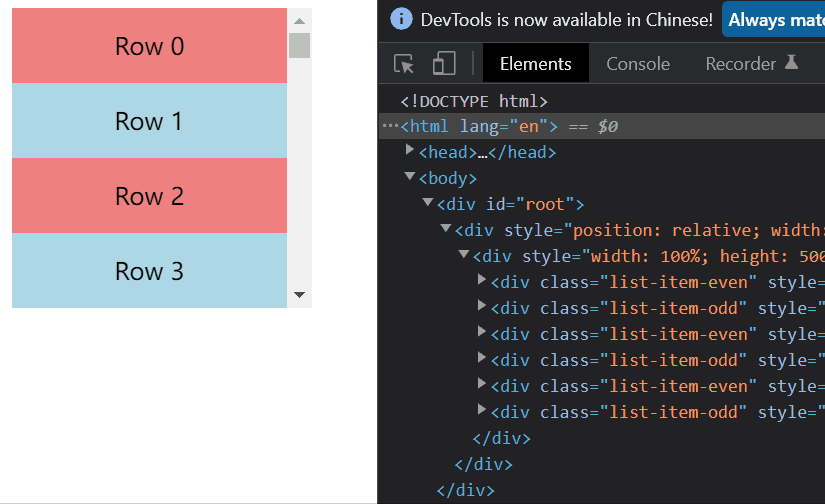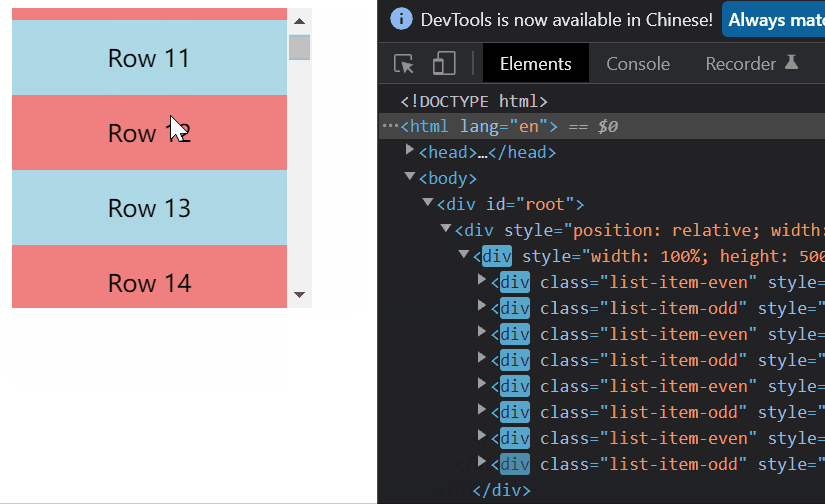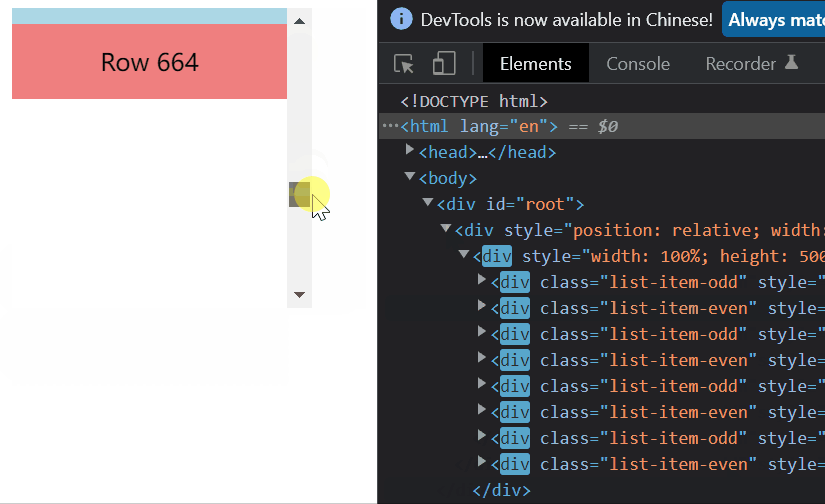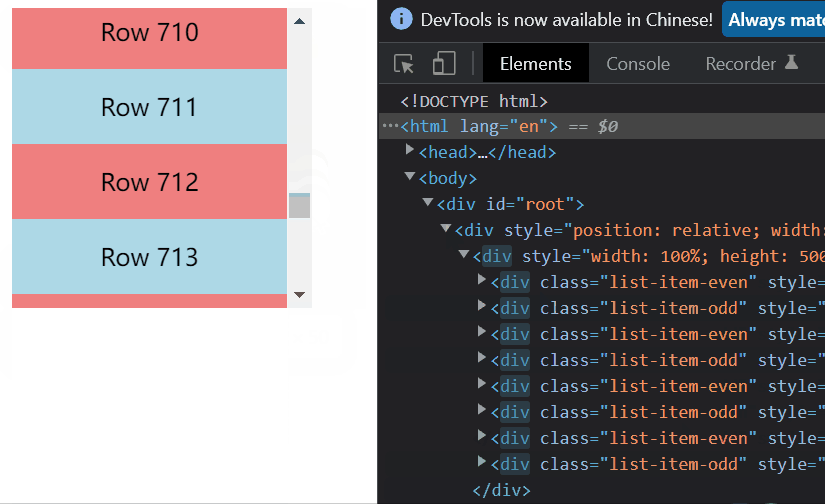
二、元素不定高度的虚拟列表
使用
const rowSizes = new Array(1000).fill(true).map(() => 25 + Math.round(Math.random() * 55))
const getItemSize = (index) => rowSizes[index];
const Row = ({ index, style }) => {
return (
<div className={index % 2 ? 'list-item-odd' : 'list-item-even'} style={style} >
Row {index}
</div>
)
}
const App = () => {
return (
<VariableSizeList
className="list"
height={200}
width={200}
itemSize={getItemSize}
itemCount={1000}
>
{Row}
</VariableSizeList>
);
}从代码可以看出,Row每一个高度都是随机的,就不能像第一种虚拟列表那样简单得通过itemSize * index计算出top值了。
思路
难点一:
由于每个元素高度不一,我们起先无法直接计算出container的总高度。
难点二:
每个元素高度不一,每个元素的top值不能通过itemSize * index直接计算出top值。
难点三:
每个元素高度不一,不能直接通过scrollOffset / itemSize计算出已被滚动掉的元素的个数,很难获取到可视区的起始索引。
难点一的解决方案
可以通过遍历所有的Row计算出总高度,但我认为计算出精确总高度的必要性不大,同时也为了兼容第三种虚拟列表,我们不去计算精确的总高度。现在我们回到出发点,思考container的高度的作用是什么?其实就是为了足够大,让用户能进行滚动操作,那我们可以自己假设每一个元素的高度,在乘上个数,弄出一个假的但足够高的container让用户去触发滚动事件。当然这种方案会带来一些小bug(这个bug的影响不大,我认为是可以忽略的)。
难点二和难点三的解决方案
其实难点二和难点三本质都一样,元素高度不一,导致不知道被滚动掉了多少元素,只要知道被滚动掉的元素的个数,top值和索引都迎刃而解。
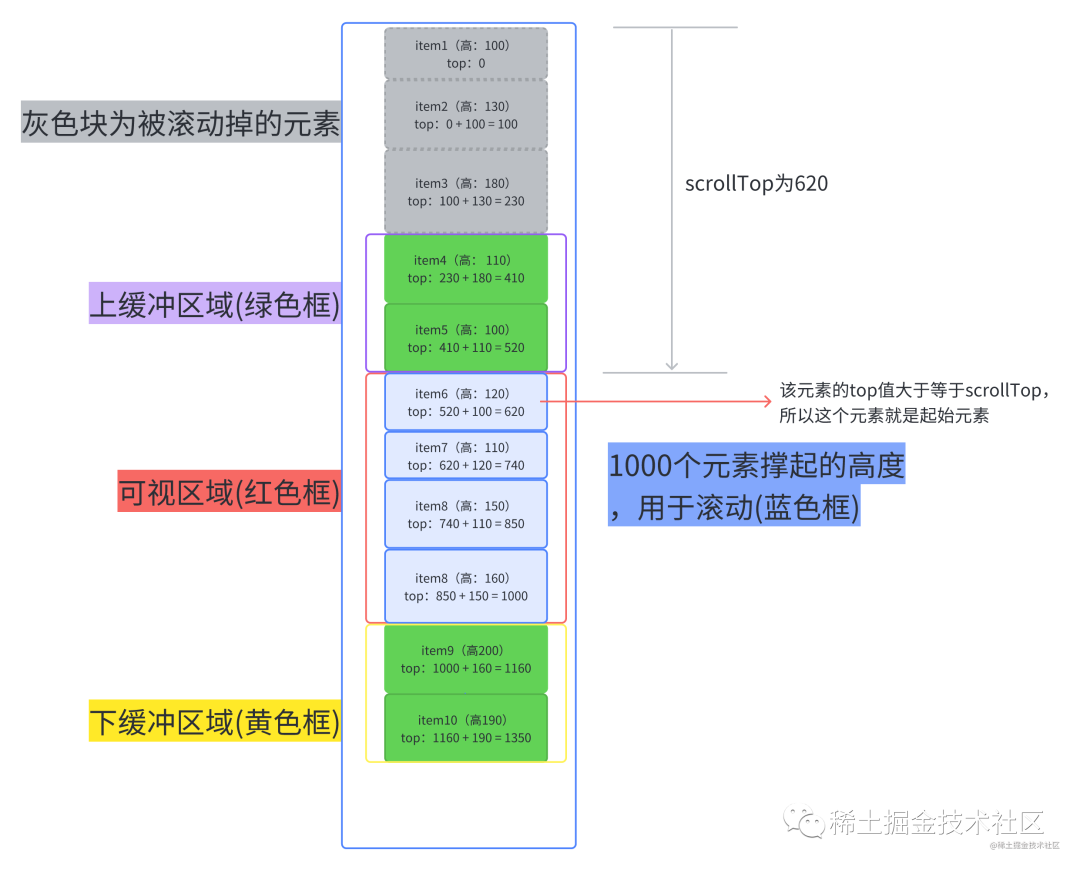
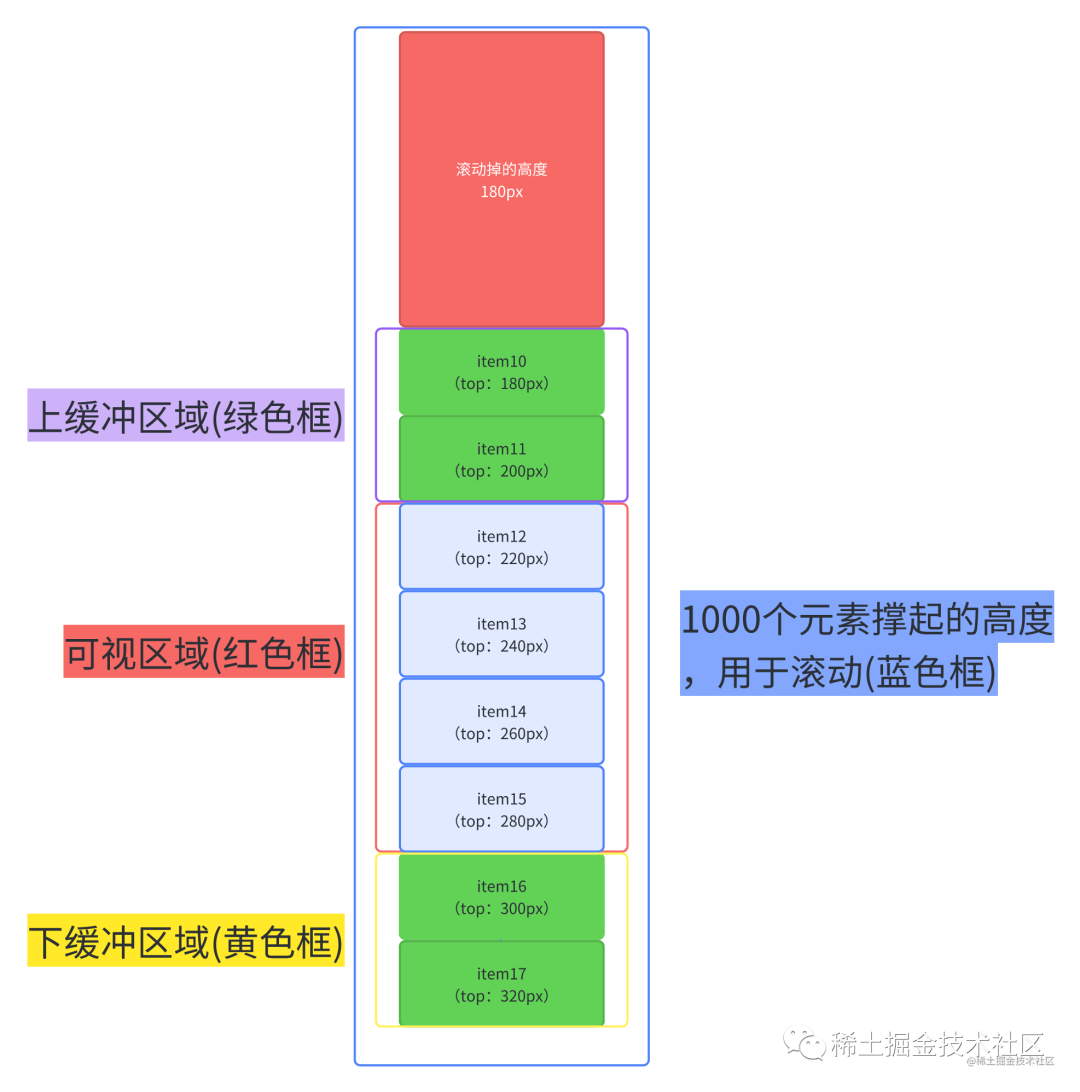
我们可以采用这种解决方案,那就是每次只需要计算上缓冲区到下缓冲区之间的元素,并记录他们,并且记录下最底下的那个元素的索引,当用户进行滚动时,如果我们是向上滚动,就可以直接从已经计算好的记录里取,如果向下滚动,我们根据上一次记录的最大的索引的那个元素不断累加新元素的高度,直到它大于已经滚动掉的高度,此时的索引值就是可视区的起始索引了,这个起始索引所对应的top就是累加的高度。
文字看起来生硬拗口,我们可以看下面这张图。
每一个元素的top值都能通过上一个元素的top值 + 上一个元素的height计算出来。
举个例子,假设我们需要知道item14的top值
(1)我们先在记录里找有没有item13的数据,如果有,我们就拿item13.top + item13.heighht得到item14的top。
(2)如果记录中(由上图得知我们只记录了item1-item10的数据)没有,我们就拿到记录中最后一个元素的数据(item10)进行累加,先计算并记录item11的,再计算并记录item12的,再计算并记录item13的,最后就是item14的了。
实现
import { useState } from 'react';
// 元数据
const measuredData = {
measuredDataMap: {},
LastMeasuredItemIndex: -1,
};
const estimatedHeight = (defaultEstimatedItemSize = 50, itemCount) => {
let measuredHeight = 0;
const { measuredDataMap, LastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
// 计算已经获取过真实高度的项的高度之和
if (LastMeasuredItemIndex >= 0) {
const lastMeasuredItem = measuredDataMap[LastMeasuredItemIndex];
measuredHeight = lastMeasuredItem.offset + lastMeasuredItem.size;
}
// 未计算过真实高度的项数
const unMeasuredItemsCount = itemCount - measuredData.LastMeasuredItemIndex - 1;
// 预测总高度
const totalEstimatedHeight = measuredHeight + unMeasuredItemsCount * defaultEstimatedItemSize;
return totalEstimatedHeight;
}
const getItemMetaData = (props, index) => {
const { itemSize } = props;
const { measuredDataMap, LastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
// 如果当前索引比已记录的索引要大,说明要计算当前索引的项的size和offset
if (index > LastMeasuredItemIndex) {
let offset = 0;
// 计算当前能计算出来的最大offset值
if (LastMeasuredItemIndex >= 0) {
const lastMeasuredItem = measuredDataMap[LastMeasuredItemIndex];
offset += lastMeasuredItem.offset + lastMeasuredItem.size;
}
// 计算直到index为止,所有未计算过的项
for (let i = LastMeasuredItemIndex + 1; i <= index; i++) {
const currentItemSize = itemSize(i);
measuredDataMap[i] = { size: currentItemSize, offset };
offset += currentItemSize;
}
// 更新已计算的项的索引值
measuredData.LastMeasuredItemIndex = index;
}
return measuredDataMap[index];
};
const getStartIndex = (props, scrollOffset) => {
const { itemCount } = props;
let index = 0;
while (true) {
const currentOffset = getItemMetaData(props, index).offset;
if (currentOffset >= scrollOffset) return index;
if (index >= itemCount) return itemCount;
index++
}
}
const getEndIndex = (props, startIndex) => {
const { height, itemCount } = props;
// 获取可视区内开始的项
const startItem = getItemMetaData(props, startIndex);
// 可视区内最大的offset值
const maxOffset = startItem.offset + height;
// 开始项的下一项的offset,之后不断累加此offset,直到等于或超过最大offset,就是找到结束索引了
let offset = startItem.offset + startItem.size;
// 结束索引
let endIndex = startIndex;
// 累加offset
while (offset <= maxOffset && endIndex < (itemCount - 1)) {
endIndex++;
const currentItem = getItemMetaData(props, endIndex);
offset += currentItem.size;
}
return endIndex;
};
const getRangeToRender = (props, scrollOffset) => {
const { itemCount } = props;
const startIndex = getStartIndex(props, scrollOffset);
const endIndex = getEndIndex(props, startIndex);
return [
Math.max(0, startIndex - 2),
Math.min(itemCount - 1, endIndex + 2),
startIndex,
endIndex,
];
};
const VariableSizeList = (props) => {
const { height, width, itemCount, itemEstimatedSize, children: Child } = props;
const [scrollOffset, setScrollOffset] = useState(0);
const containerStyle = {
position: 'relative',
width,
height,
overflow: 'auto',
willChange: 'transform'
};
const contentStyle = {
height: estimatedHeight(itemEstimatedSize, itemCount),
width: '100%',
};
const getCurrentChildren = () => {
const [startIndex, endIndex, originStartIndex, originEndIndex] = getRangeToRender(props, scrollOffset)
const items = [];
for (let i = startIndex; i <= endIndex; i++) {
const item = getItemMetaData(props, i);
const itemStyle = {
position: 'absolute',
height: item.size,
width: '100%',
top: item.offset,
};
items.push(
<Child key={i} index={i} style={itemStyle} />
);
}
return items;
}
const scrollHandle = (event) => {
const { scrollTop } = event.currentTarget;
setScrollOffset(scrollTop);
}
return (
<div style={containerStyle} onScroll={scrollHandle}>
<div style={contentStyle}>
{getCurrentChildren()}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VariableSizeList;难点的地方都给了注释,如果一遍看不懂的话,可以去调试调试。
以上代码主要写了个思路和功能,其实优化点是很多的,这里给出两个显而易见的优化点。
- 缓存每一个已经计算完成的item的样式,这样回滚的时候不用重新计算样式。
- getStartIndex可以通过二分法去优化。
结果
结果还是挺满意的了,这里提一下上文提到的小bug,那就是在向下拉动滚动条时,鼠标和滚动条时脱节的。
元素动态高度的虚拟列表
最后这一种虚拟列表其实就是基于第二种来实现的,只不过增加监听元素高度变化事件,在某个元素发生变化的时候重新计算各种数据。
使用
const items = [];
const itemCount = 1000;
for (let i = 0; i < itemCount; i++) {
const height = (30 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 30));
const style = {
height,
width: '100%',
}
items.push(
<div className={i % 2 ? 'list-item-odd' : 'list-item-even'} style={style}>Row {i}</div>
)
}
const Row = ({ index }) => items[index];
const App = () => {
// 注意:这里我没有把itemSize传过去
return (
<VariableSizeList
className="list"
height={200}
width={200}
itemCount={itemCount}
isDynamic
>
{Row}
</VariableSizeList>
);
}从上面代码可以看出,我们没将itemSize传过去,虚拟列表是不知道每一个元素的高度的,只有在渲染的时候执行了Row才知道。
实现
在上面那种虚拟列表进行改动
// 修改getCurrentChildren函数
const getCurrentChildren = () => {
const [startIndex, endIndex] = getRangeToRender(props, scrollOffset)
const items = [];
for (let i = startIndex; i <= endIndex; i++) {
const item = getItemMetaData(props, i);
const itemStyle = {
position: 'absolute',
height: item.size,
width: '100%',
top: item.offset,
};
items.push(
<ListItem key={i} index={i} style={itemStyle} ComponentType={Child} onSizeChange={sizeChangeHandle} />
);
}
return items;
}
// 增加sizeChangeHandle
const sizeChangeHandle = (index, domNode) => {
const height = domNode.offsetHeight;
const { measuredDataMap, lastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
const itemMetaData = measuredDataMap[index];
itemMetaData.size = height;
let offset = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= lastMeasuredItemIndex; i++) {
const itemMetaData = measuredDataMap[i];
itemMetaData.offset = offset;
offset += itemMetaData.size;
}
setState({});
}// 增加一个ListItem组件
class ListItem extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.domRef = React.createRef();
this.resizeObserver = null;
}
componentDidMount() {
if (this.domRef.current) {
const domNode = this.domRef.current.firstChild;
const { index, onSizeChange } = this.props;
this.resizeObserver = new ResizeObserver(() => {
onSizeChange(index, domNode);
});
this.resizeObserver.observe(domNode);
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this.resizeObserver && this.domRef.current.firstChild) {
this.resizeObserver.unobserve(this.domRef.current.firstChild);
}
}
render() {
const { index, style, ComponentType } = this.props;
return (
<div style={style} ref={this.domRef}>
<ComponentType index={index} />
</div>
)
}
}完整代码
import React, { useState } from 'react';
// 元数据
const measuredData = {
measuredDataMap: {},
lastMeasuredItemIndex: -1,
};
const estimatedHeight = (defaultEstimatedItemSize = 50, itemCount) => {
let measuredHeight = 0;
const { measuredDataMap, lastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
// 计算已经获取过真实高度的项的高度之和
if (lastMeasuredItemIndex >= 0) {
const lastMeasuredItem = measuredDataMap[lastMeasuredItemIndex];
measuredHeight = lastMeasuredItem.offset + lastMeasuredItem.size;
}
// 未计算过真实高度的项数
const unMeasuredItemsCount = itemCount - measuredData.lastMeasuredItemIndex - 1;
// 预测总高度
const totalEstimatedHeight = measuredHeight + unMeasuredItemsCount * defaultEstimatedItemSize;
return totalEstimatedHeight;
}
const getItemMetaData = (props, index) => {
const { itemSize, itemEstimatedSize = 50 } = props;
const { measuredDataMap, lastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
// 如果当前索引比已记录的索引要大,说明要计算当前索引的项的size和offset
if (index > lastMeasuredItemIndex) {
let offset = 0;
// 计算当前能计算出来的最大offset值
if (lastMeasuredItemIndex >= 0) {
const lastMeasuredItem = measuredDataMap[lastMeasuredItemIndex];
offset += lastMeasuredItem.offset + lastMeasuredItem.size;
}
// 计算直到index为止,所有未计算过的项
for (let i = lastMeasuredItemIndex + 1; i <= index; i++) {
const currentItemSize = itemSize ? itemSize(i) : itemEstimatedSize;
measuredDataMap[i] = { size: currentItemSize, offset };
offset += currentItemSize;
}
// 更新已计算的项的索引值
measuredData.lastMeasuredItemIndex = index;
}
return measuredDataMap[index];
};
const getStartIndex = (props, scrollOffset) => {
const { itemCount } = props;
let index = 0;
while (true) {
const currentOffset = getItemMetaData(props, index).offset;
if (currentOffset >= scrollOffset) return index;
if (index >= itemCount) return itemCount;
index++
}
}
const getEndIndex = (props, startIndex) => {
const { height, itemCount } = props;
// 获取可视区内开始的项
const startItem = getItemMetaData(props, startIndex);
// 可视区内最大的offset值
const maxOffset = startItem.offset + height;
// 开始项的下一项的offset,之后不断累加此offset,知道等于或超过最大offset,就是找到结束索引了
let offset = startItem.offset + startItem.size;
// 结束索引
let endIndex = startIndex;
// 累加offset
while (offset <= maxOffset && endIndex < (itemCount - 1)) {
endIndex++;
const currentItem = getItemMetaData(props, endIndex);
offset += currentItem.size;
}
return endIndex;
};
const getRangeToRender = (props, scrollOffset) => {
const { itemCount } = props;
const startIndex = getStartIndex(props, scrollOffset);
const endIndex = getEndIndex(props, startIndex);
return [
Math.max(0, startIndex - 2),
Math.min(itemCount - 1, endIndex + 2),
startIndex,
endIndex,
];
};
class ListItem extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.domRef = React.createRef();
this.resizeObserver = null;
}
componentDidMount() {
if (this.domRef.current) {
const domNode = this.domRef.current.firstChild;
const { index, onSizeChange } = this.props;
this.resizeObserver = new ResizeObserver(() => {
onSizeChange(index, domNode);
});
this.resizeObserver.observe(domNode);
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this.resizeObserver && this.domRef.current.firstChild) {
this.resizeObserver.unobserve(this.domRef.current.firstChild);
}
}
render() {
const { index, style, ComponentType } = this.props;
return (
<div style={style} ref={this.domRef}>
<ComponentType index={index} />
</div>
)
}
}
const VariableSizeList = (props) => {
const { height, width, itemCount, itemEstimatedSize = 50, children: Child } = props;
const [scrollOffset, setScrollOffset] = useState(0);
const [, setState] = useState({});
const containerStyle = {
position: 'relative',
width,
height,
overflow: 'auto',
willChange: 'transform'
};
const contentStyle = {
height: estimatedHeight(itemEstimatedSize, itemCount),
width: '100%',
};
const sizeChangeHandle = (index, domNode) => {
const height = domNode.offsetHeight;
const { measuredDataMap, lastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
const itemMetaData = measuredDataMap[index];
itemMetaData.size = height;
let offset = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= lastMeasuredItemIndex; i++) {
const itemMetaData = measuredDataMap[i];
itemMetaData.offset = offset;
offset += itemMetaData.size;
}
setState({});
}
const getCurrentChildren = () => {
const [startIndex, endIndex] = getRangeToRender(props, scrollOffset)
const items = [];
for (let i = startIndex; i <= endIndex; i++) {
const item = getItemMetaData(props, i);
const itemStyle = {
position: 'absolute',
height: item.size,
width: '100%',
top: item.offset,
};
items.push(
<ListItem key={i} index={i} style={itemStyle} ComponentType={Child} onSizeChange={sizeChangeHandle} />
);
}
return items;
}
const scrollHandle = (event) => {
const { scrollTop } = event.currentTarget;
setScrollOffset(scrollTop);
}
return (
<div style={containerStyle} onScroll={scrollHandle}>
<div style={contentStyle}>
{getCurrentChildren()}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VariableSizeList;结果
结尾
react-window只有前两种虚拟列表,最后一种虚拟列表是在别的虚拟列表库中有,借鉴了一下各路大佬的思路实现的,总得来说三种虚拟列表虽然表现和实现都不同,但只要掌握了核心原理,手撸出来虚拟列表还是手到擒来的。
最后,希望这篇文章能帮助到各位读者。同时也非常欢迎各位大佬对上面的各种实现提出建议,也希望各位大佬对于第二种虚拟列表提出更多的优化点。