在Python中处理日期和时间的基本知识点整理汇总
Python程序可以处理多种方式的日期和时间。日期格式之间的转换是一种常见计算机的杂活。 Python的时间和日历模块,能帮助处理日期和时间。
Tick是什么?
时间间隔为浮点数以秒为单位的数字。在特定的时间瞬间自上午12时00分,1970年1月1日(纪元)表示,单位为秒。
Python中可用的流行时间模块,它提供功能转换。该功能time.time()返回当前系统时间,因为上午12点,1970年1月1日(时代)。
例子:
#!/usr/bin/python
import time; # This is required to include time module.
ticks = time.time()
print "Number of ticks since 12:00am, January 1, 1970:", ticks
这将产生一个结果如下:
Number of ticks since 12:00am, January 1, 1970: 7186862.73399
日期计算是很容易。不过当日的时代之前,不能以这种形式来表示。在遥远的将来的日期也不能代表这种方式- 分界点是一段2038年在UNIX和Windows。
什么是TimeTuple?
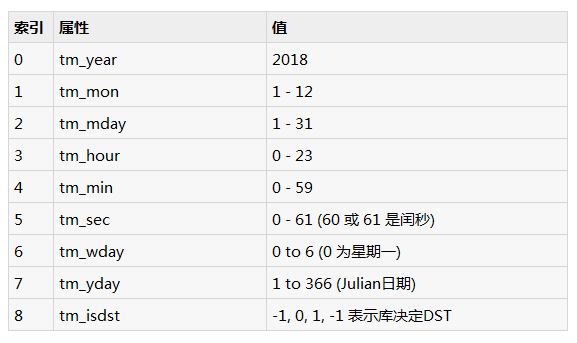
Python的时间函数处理时间为9个数字的元组,如下图所示:

上面的元组相当于struct_time结构。这种结构具有以下属性:
获取当前时间 :
转换一个时刻从秒epoch浮点值转换成时元组,浮点值传递给函数(例如,本地时间)返回时间元组的全部九项有效。
#!/usr/bin/python
import time;
localtime = time.localtime(time.time())
print "Local current time :", localtime
这将产生下面的结果,这可以在任何其他像样形式被格式化:
Local current time : time.struct_time(tm_year=2013, tm_mon=7,
tm_mday=17, tm_hour=21, tm_min=26, tm_sec=3, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=198, tm_isdst=0)
获取格式化的时间 :
可以随时根据要求格式化,但简单的方法来获取时间,可读的格式是asctime():
#!/usr/bin/python
import time;
localtime = time.asctime( time.localtime(time.time()) )
print "Local current time :", localtime
这将产生以下结果:
Local current time : Tue Jan 13 10:17:09 2009
获取日历月份:
日历模块提供了广泛的方法,如有年和月的日历。在这里,我们打印日历给定月份(2015年1月):
#!/usr/bin/python
import calendar
cal = calendar.month(2015, 1)
print "Here is the calendar:"
print cal;
这将产生以下结果:
Here is the calendar:
January 2008
Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su
1 2 3 4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12 13
14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27
28 29 30 31